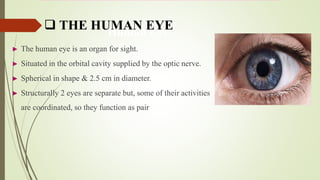
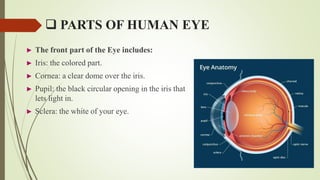
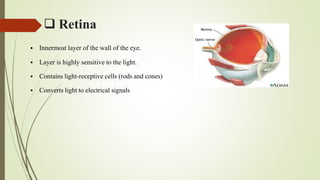
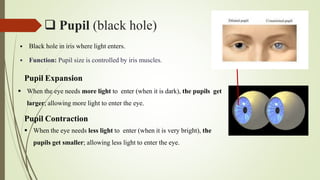
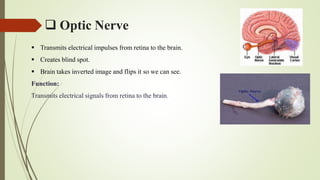
The human eye has three layers: an outer fibrous layer, middle vascular layer, and inner nervous tissue layer. It contains several parts that work together to allow vision, including the iris, pupil, cornea, retina, and optic nerve. The cornea and pupil allow light to enter while the retina converts light to electrical signals transmitted by the optic nerve to the brain. Contraction and relaxation of the iris and ciliary muscles control the amount of light entering through the pupil and focus of the lens.