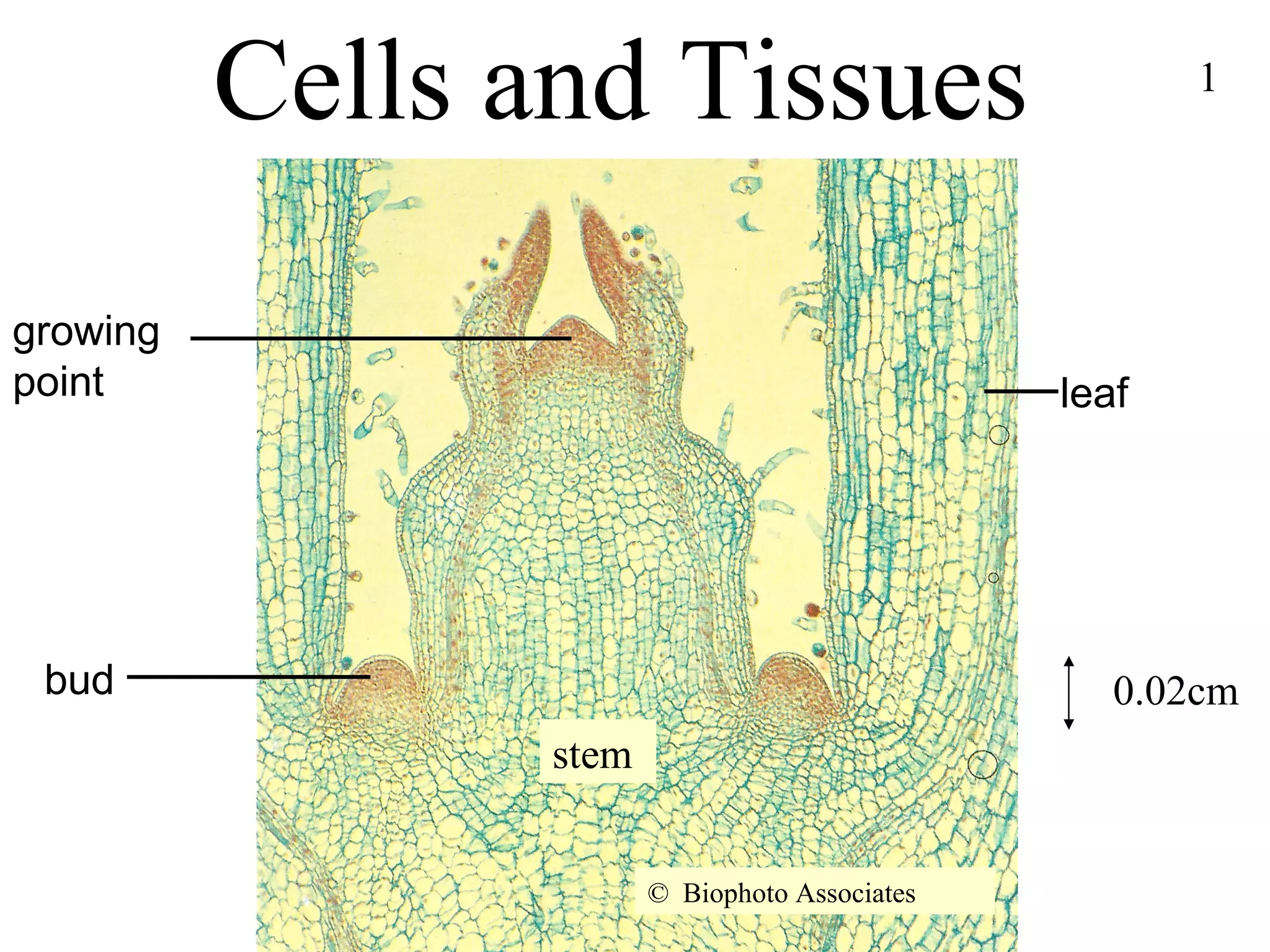
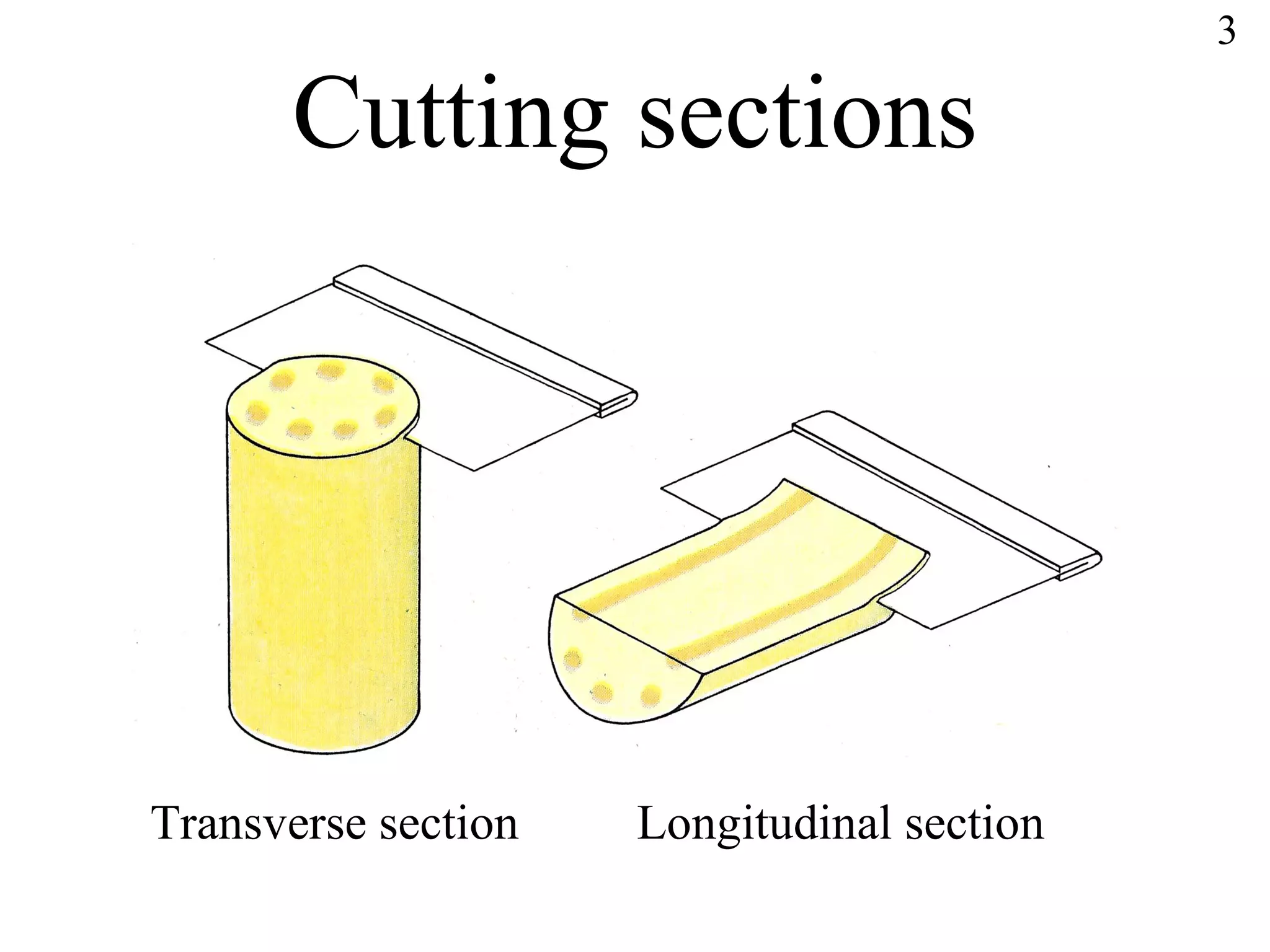
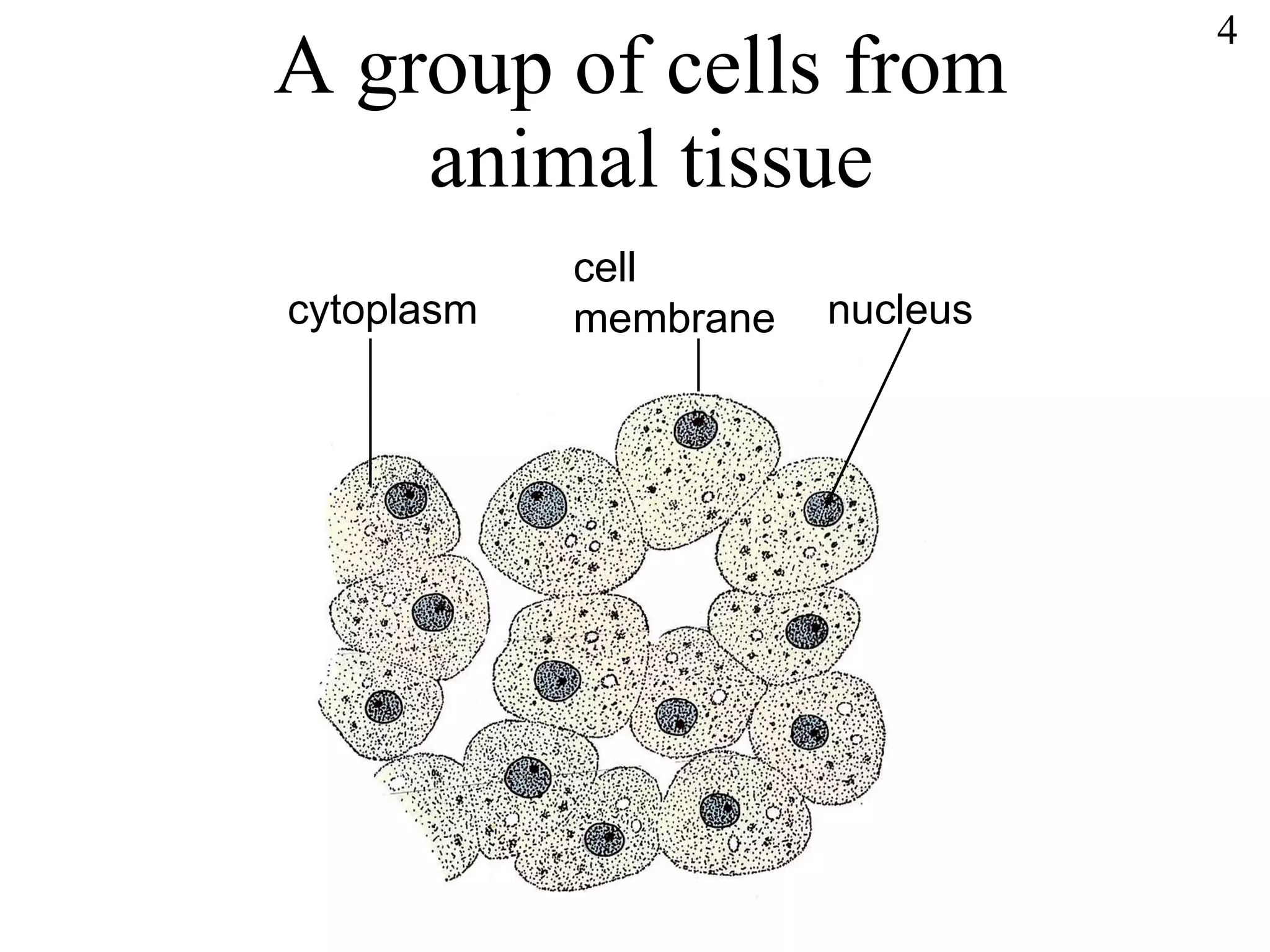
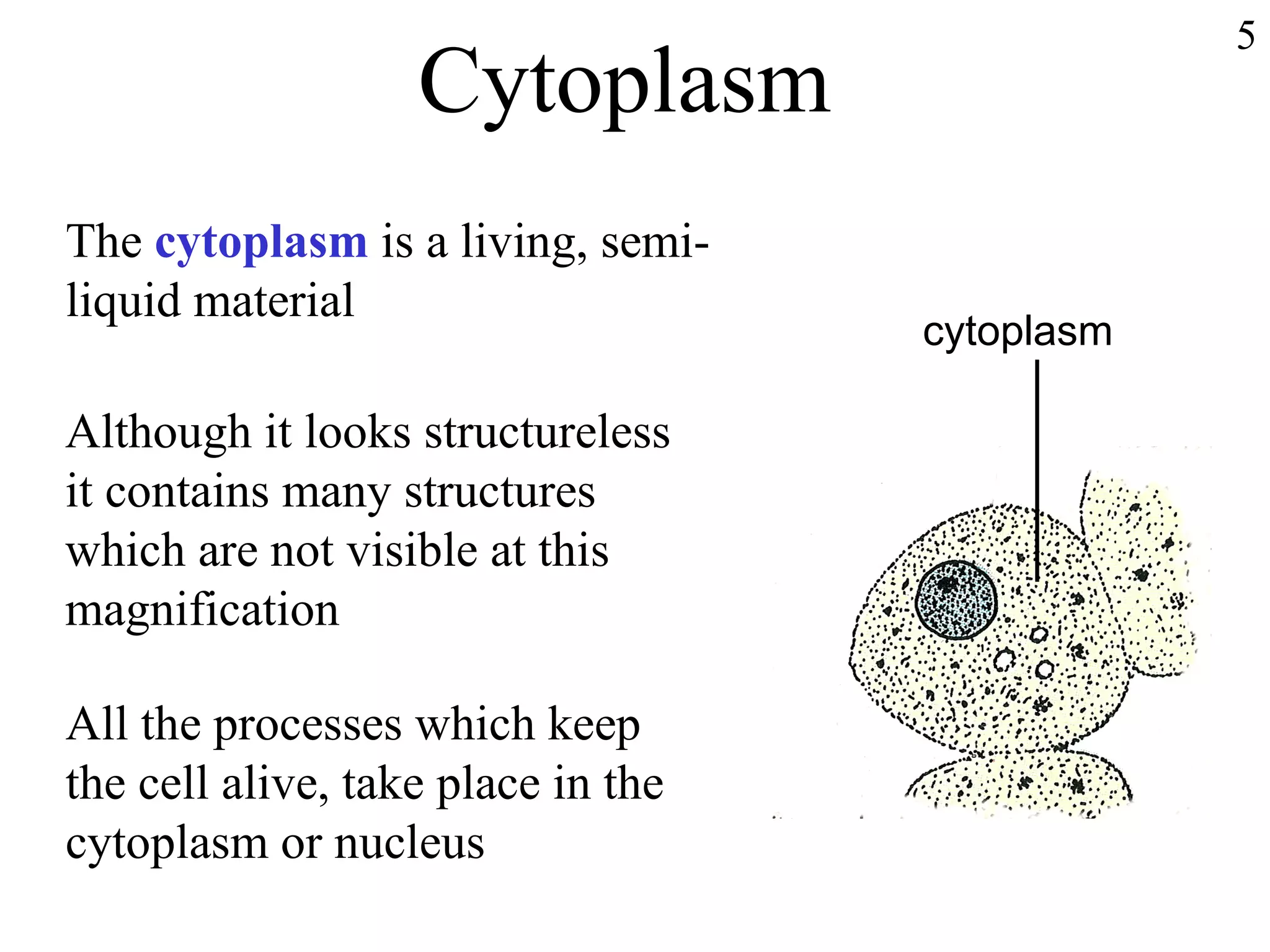
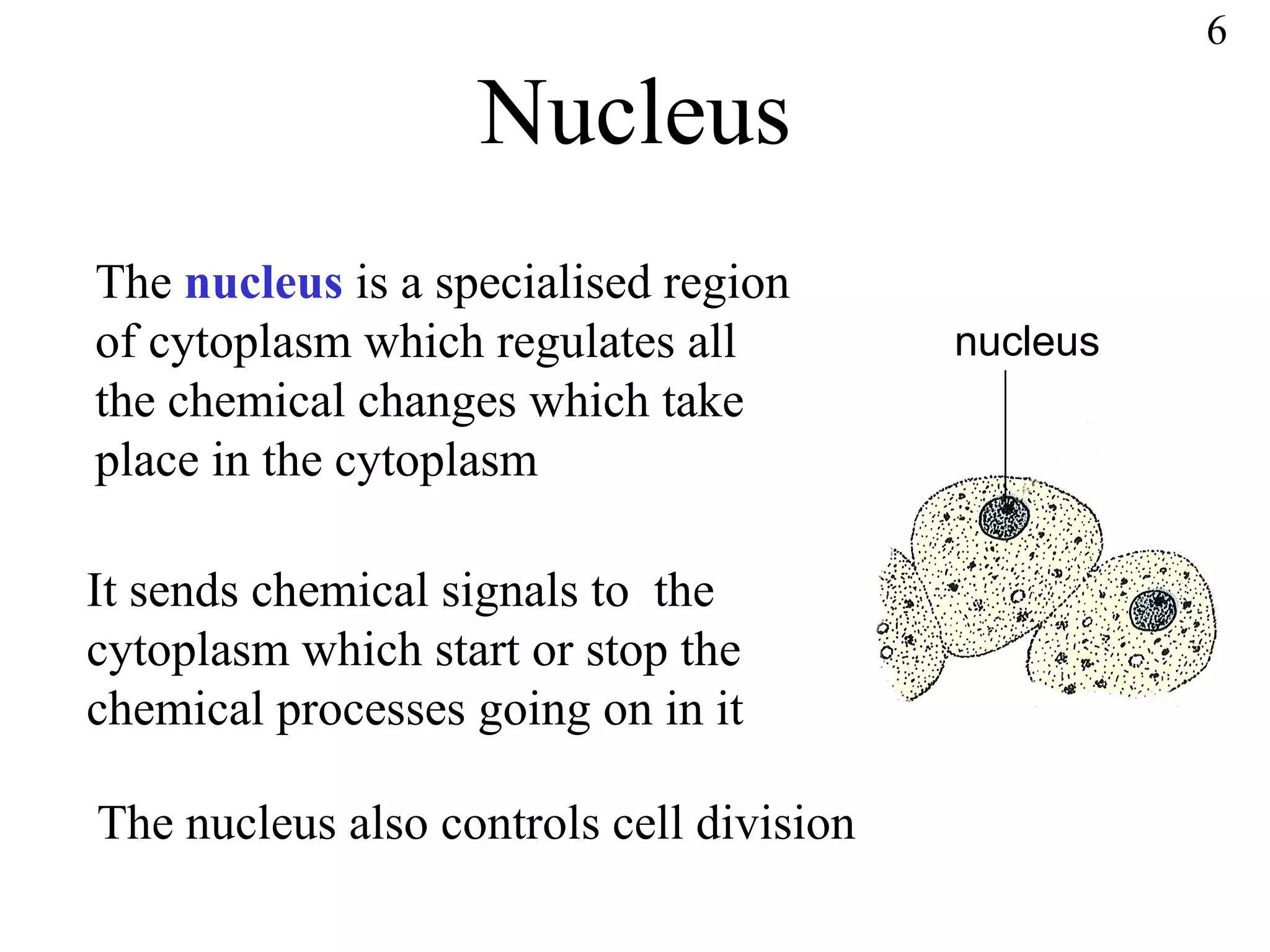
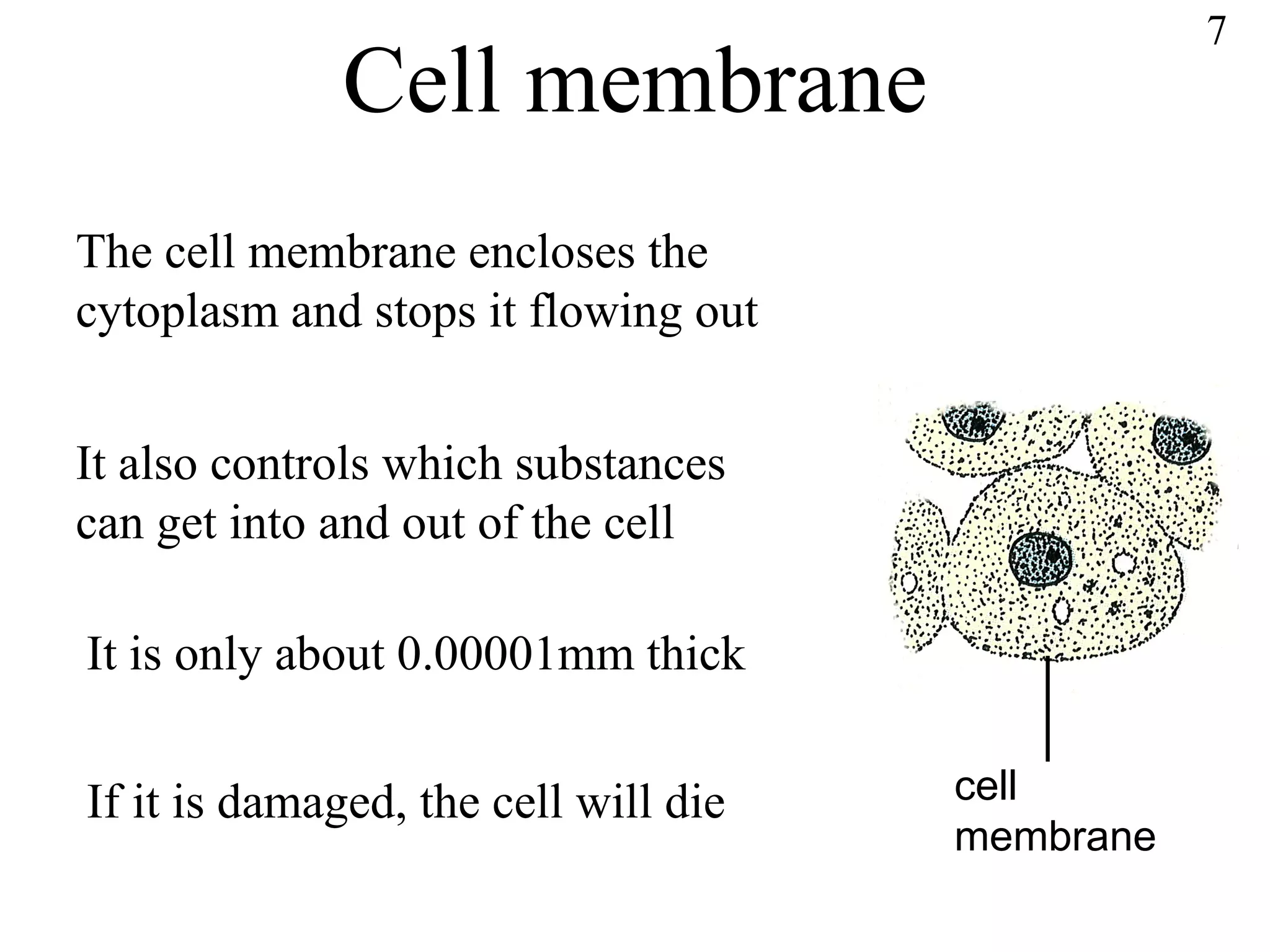
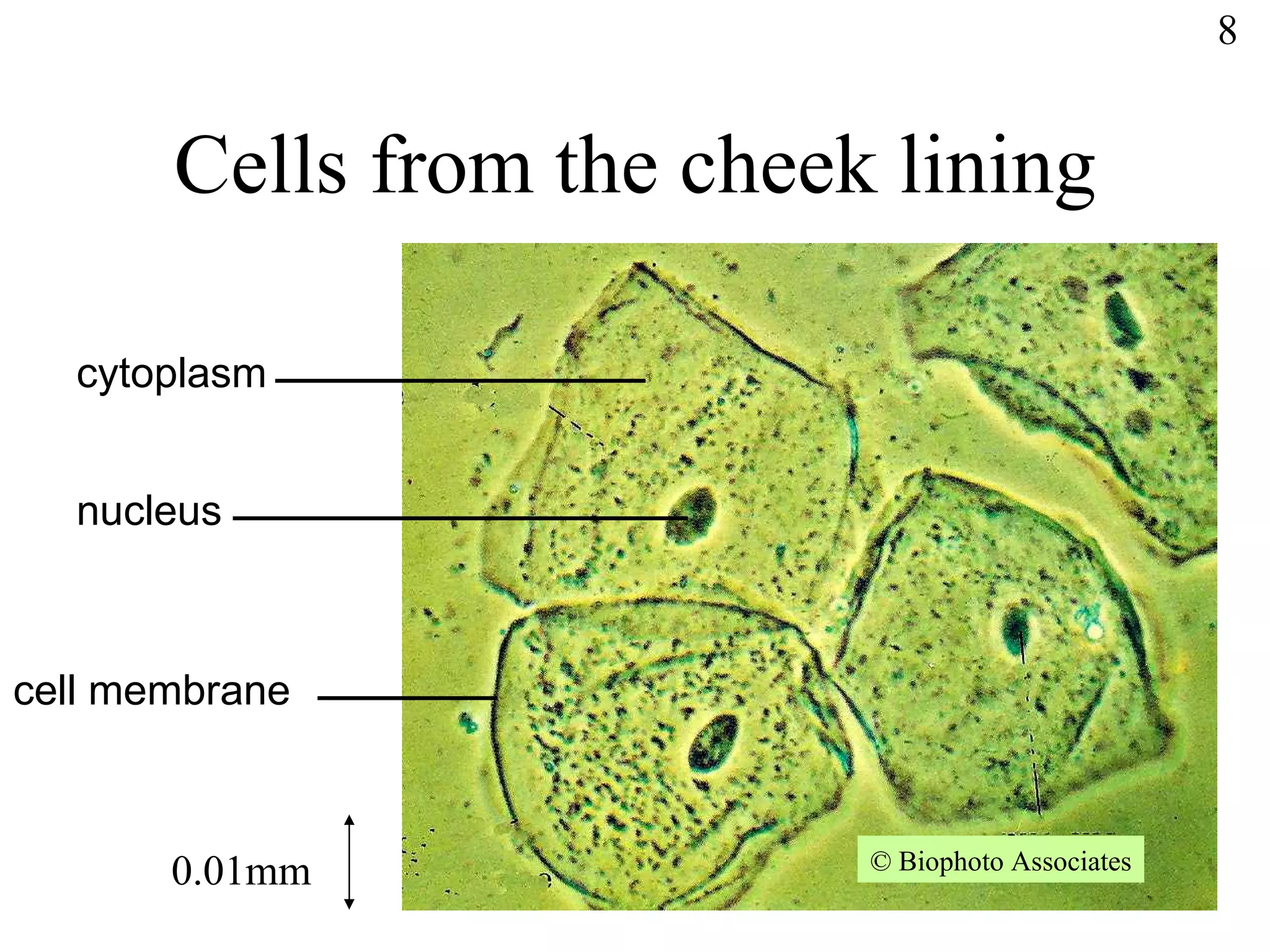
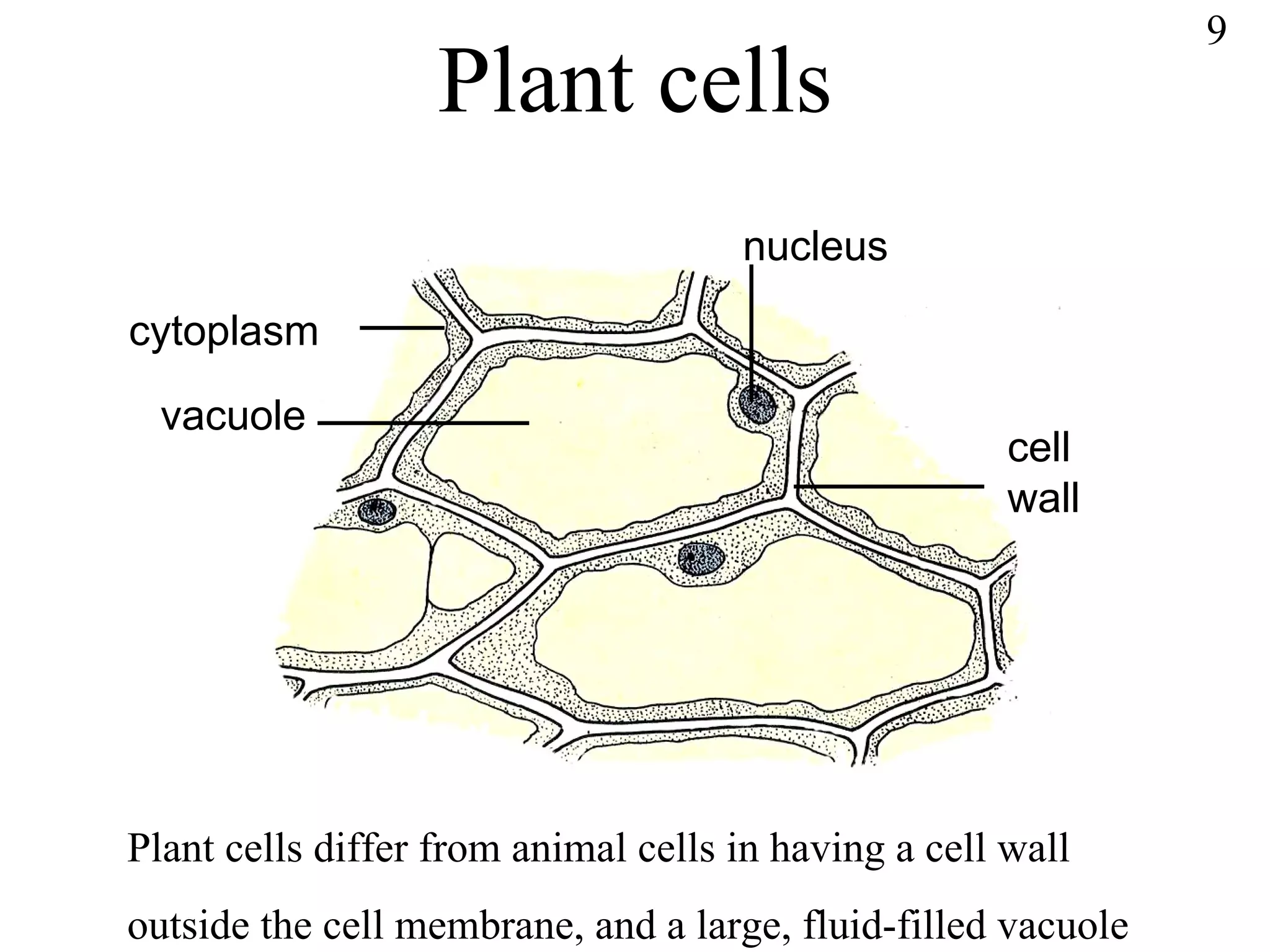
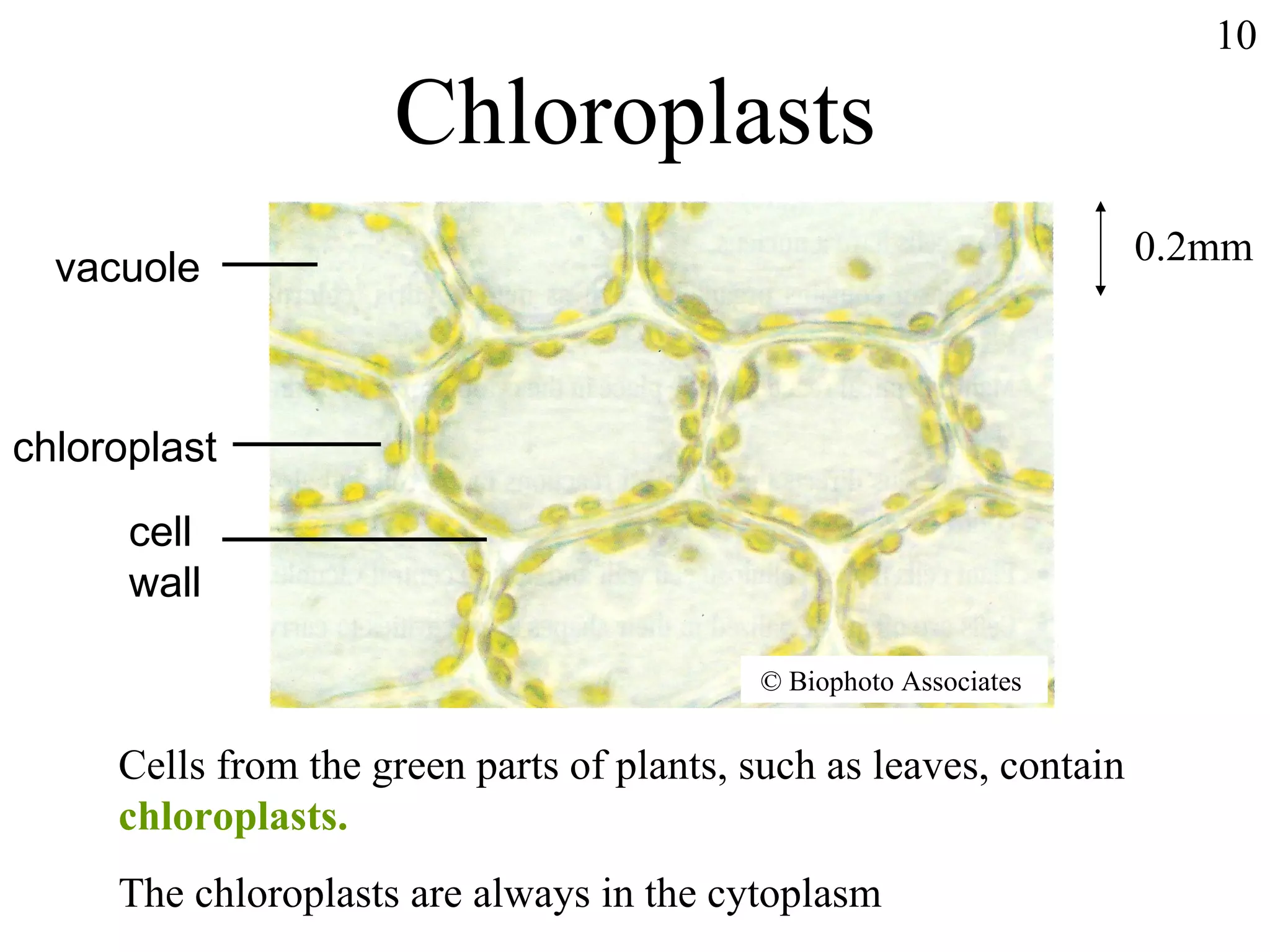
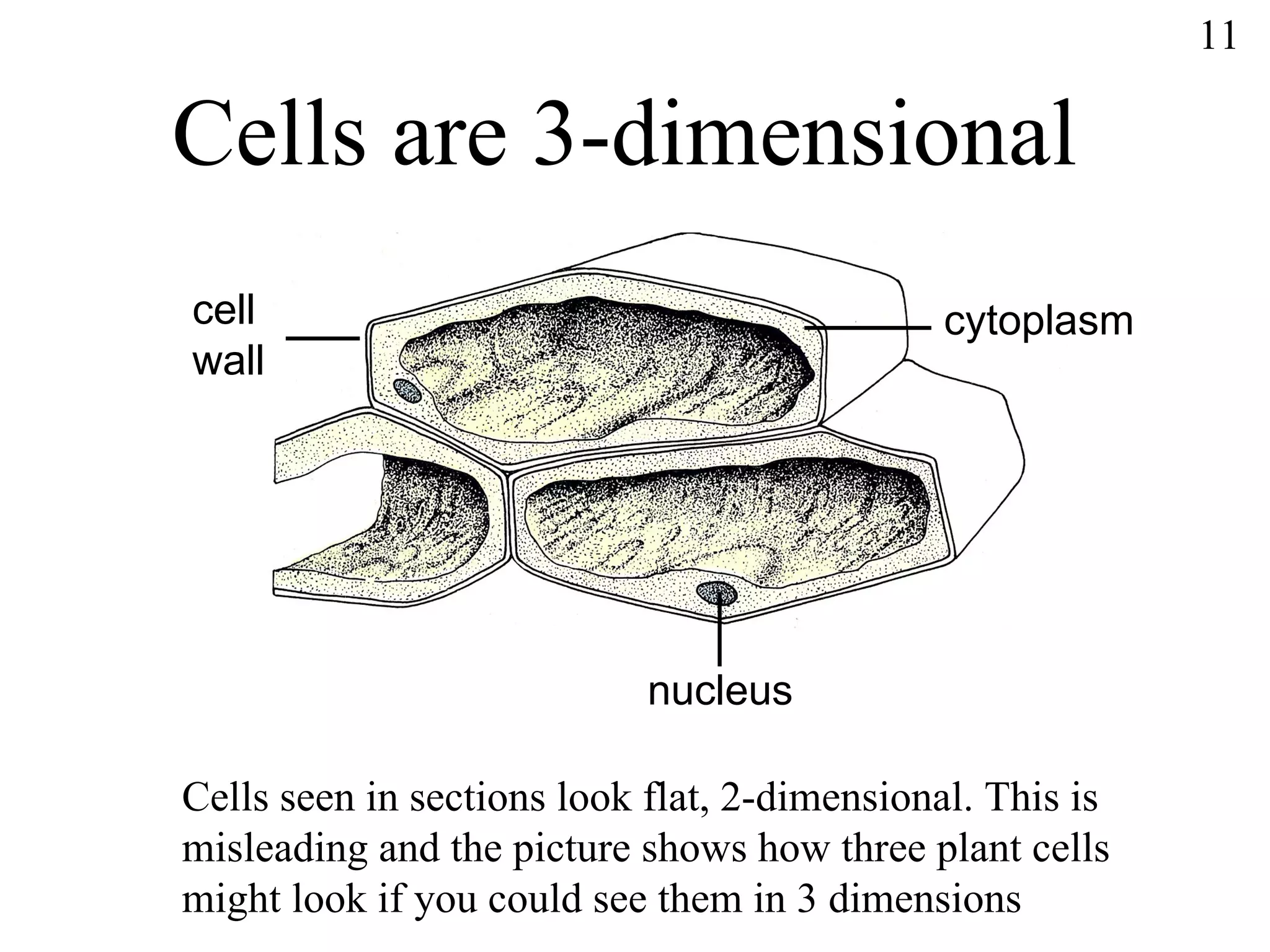
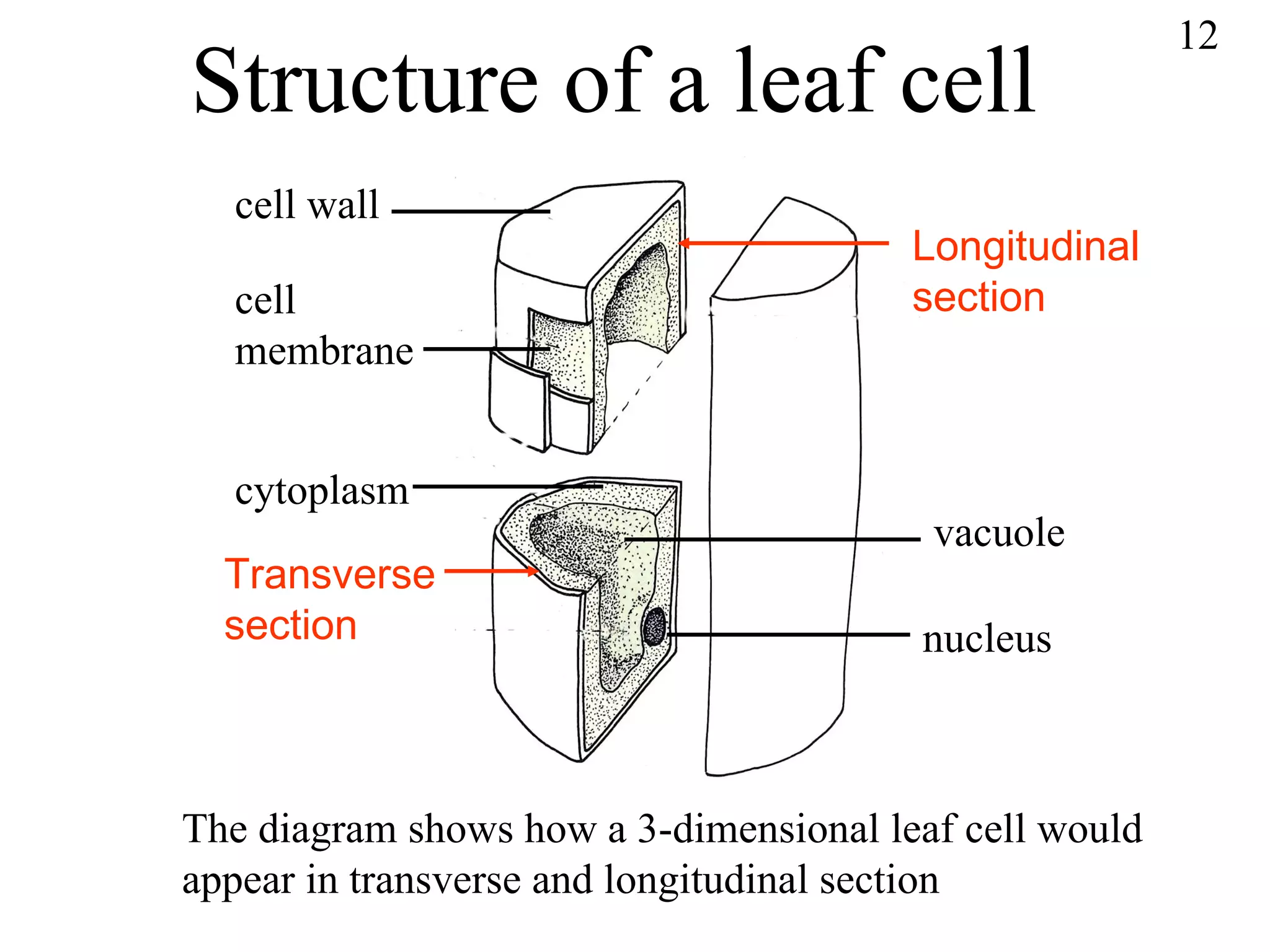
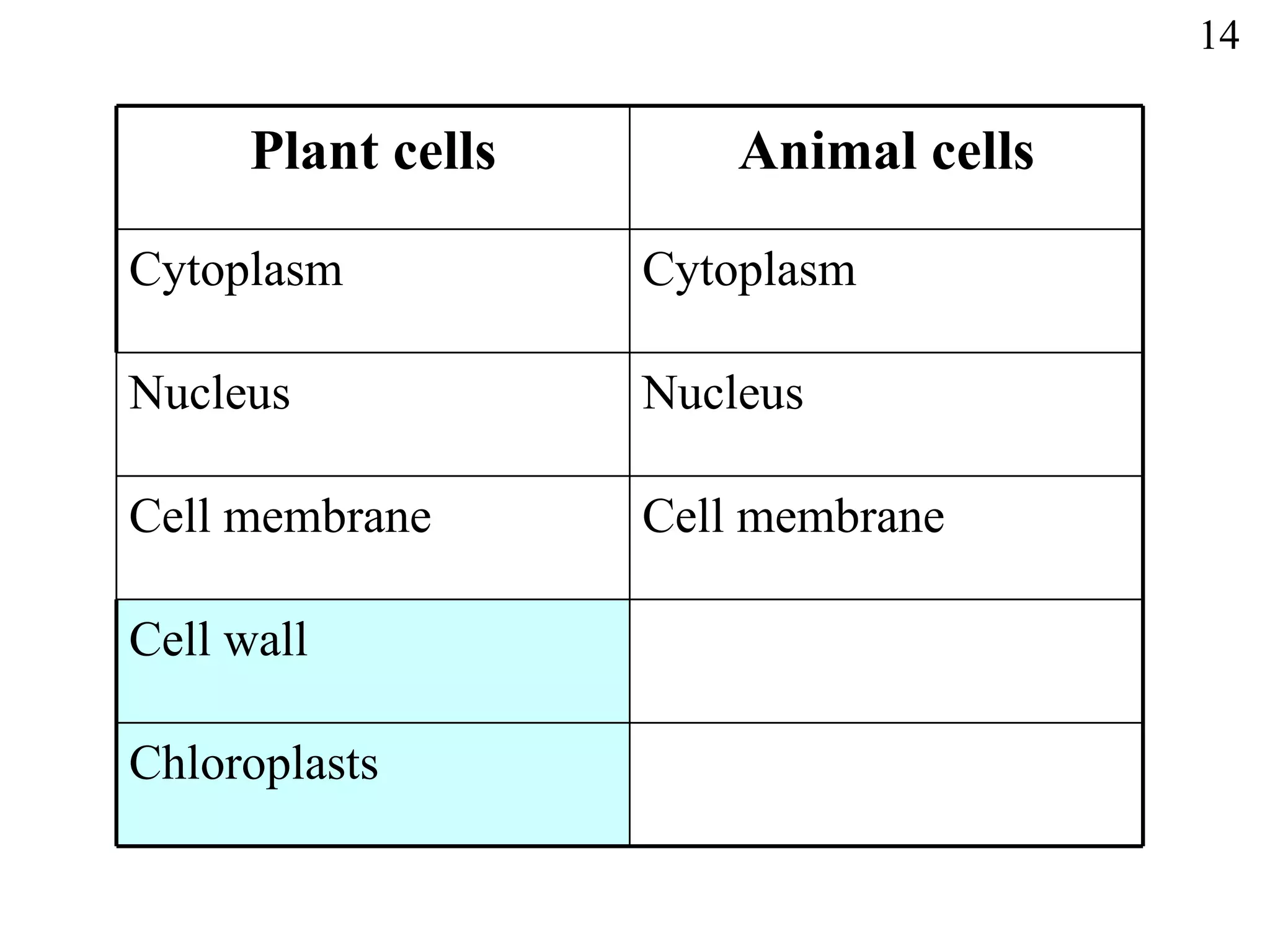
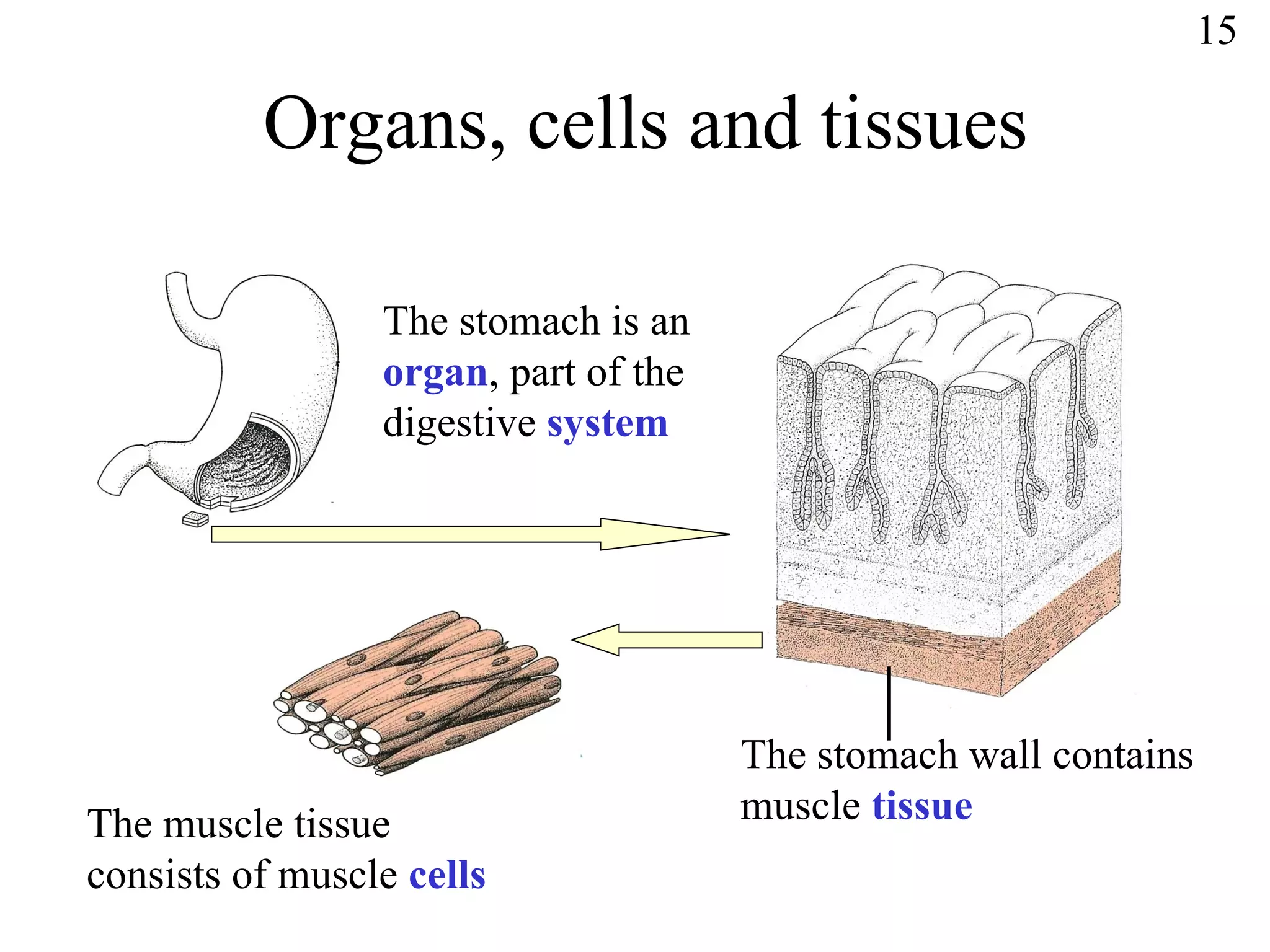
The document discusses cells and tissues. It provides information on plant and animal cells, including their main components like the cytoplasm, nucleus, cell membrane, cell wall, vacuole, and chloroplasts. Plant cells differ from animal cells in having a cell wall and vacuole. The document also discusses how cells are organized into tissues and organs.