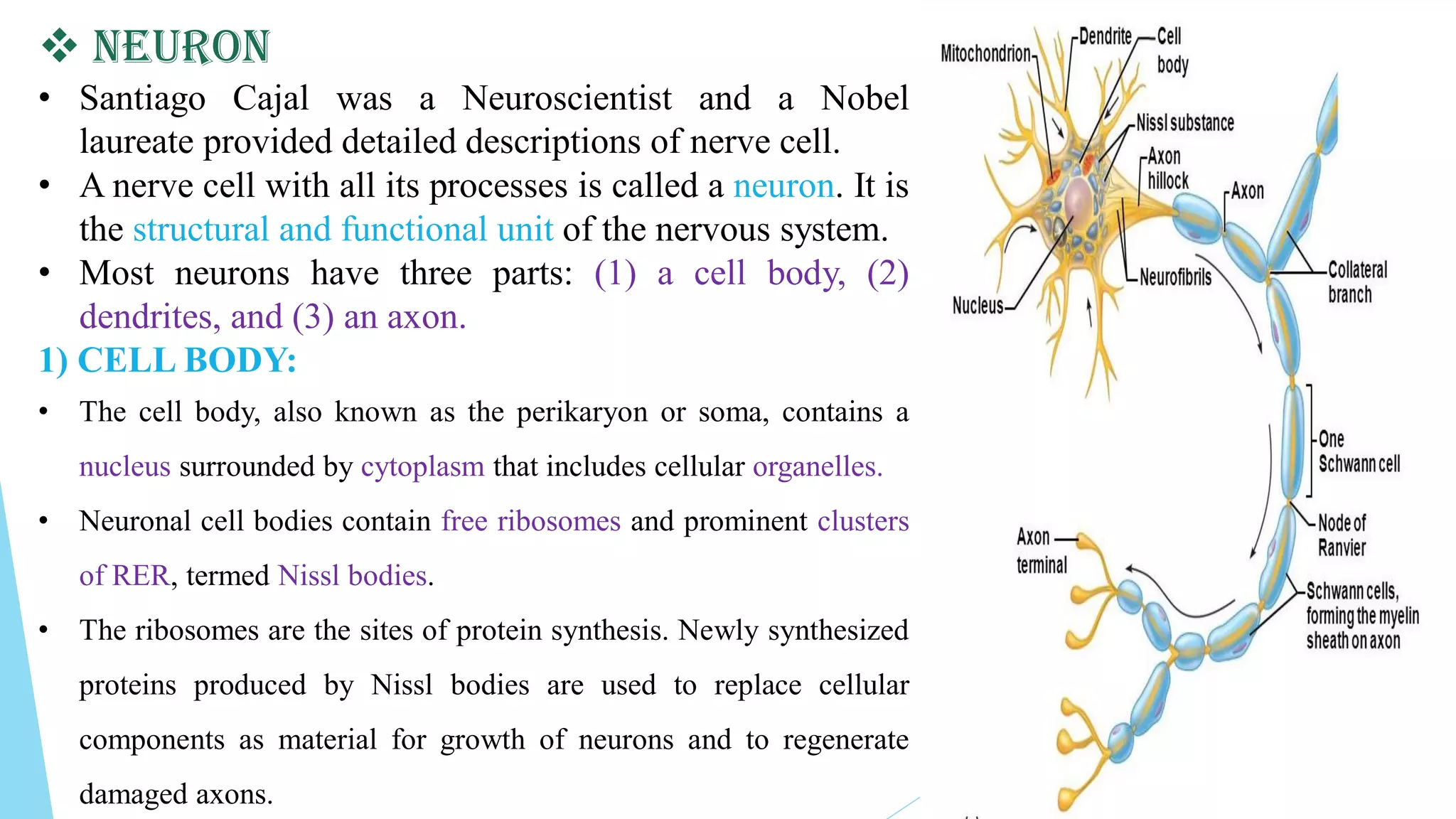
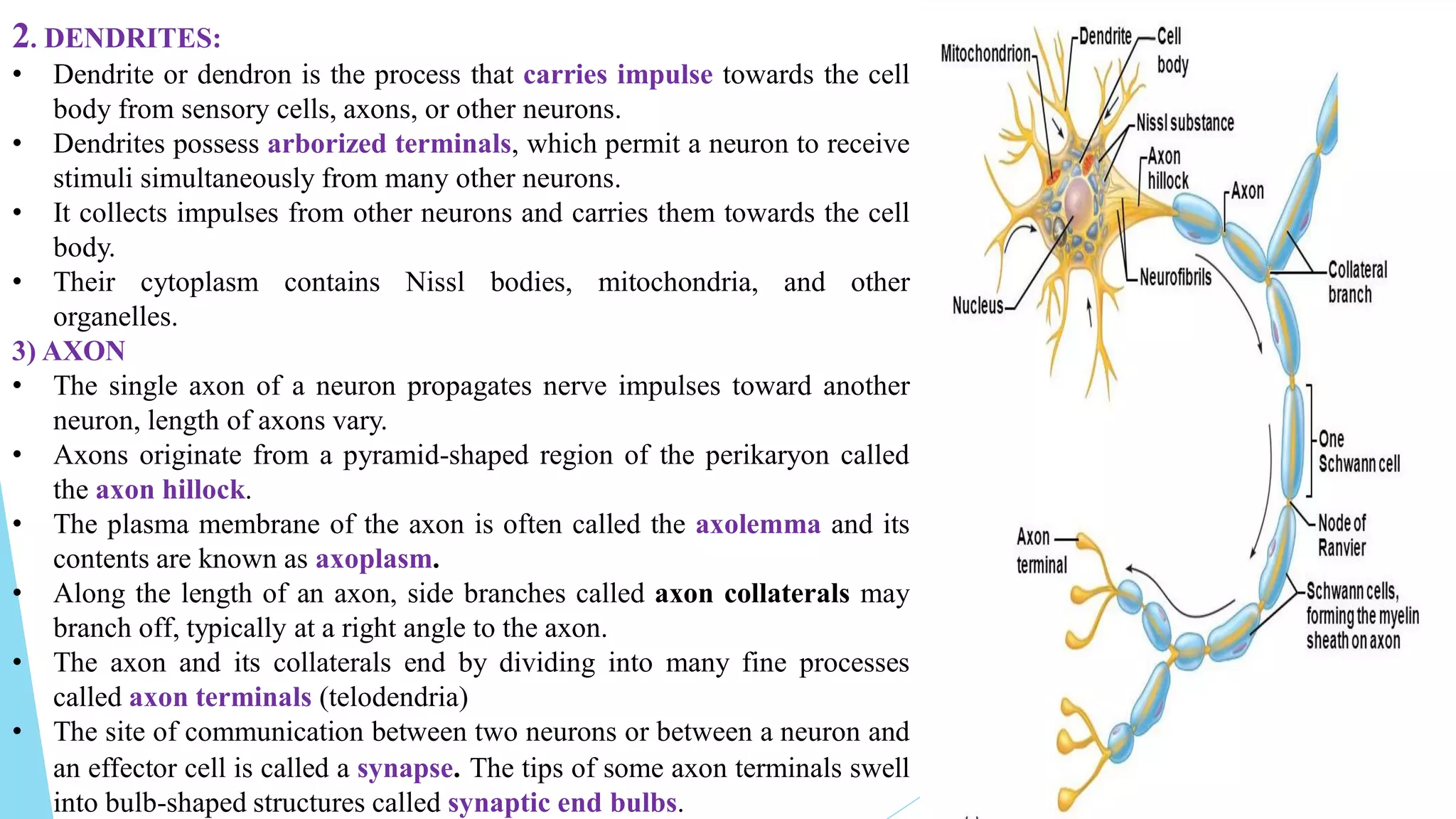
This document summarizes nervous tissue, including its cells and classification. It describes the two main cell types: neurons, which transmit electrical signals, and neuroglia cells, which support and protect neurons. Neurons are composed of a cell body, dendrites that receive signals, and an axon that transmits signals. There are different types of neurons classified by their structure. Neuroglia include oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, ependymal cells, microglia, Schwann cells, and satellite cells that each have distinct functions in supporting the nervous system. Together, neurons and glia allow the nervous system to coordinate voluntary and involuntary body functions through electrical signaling.