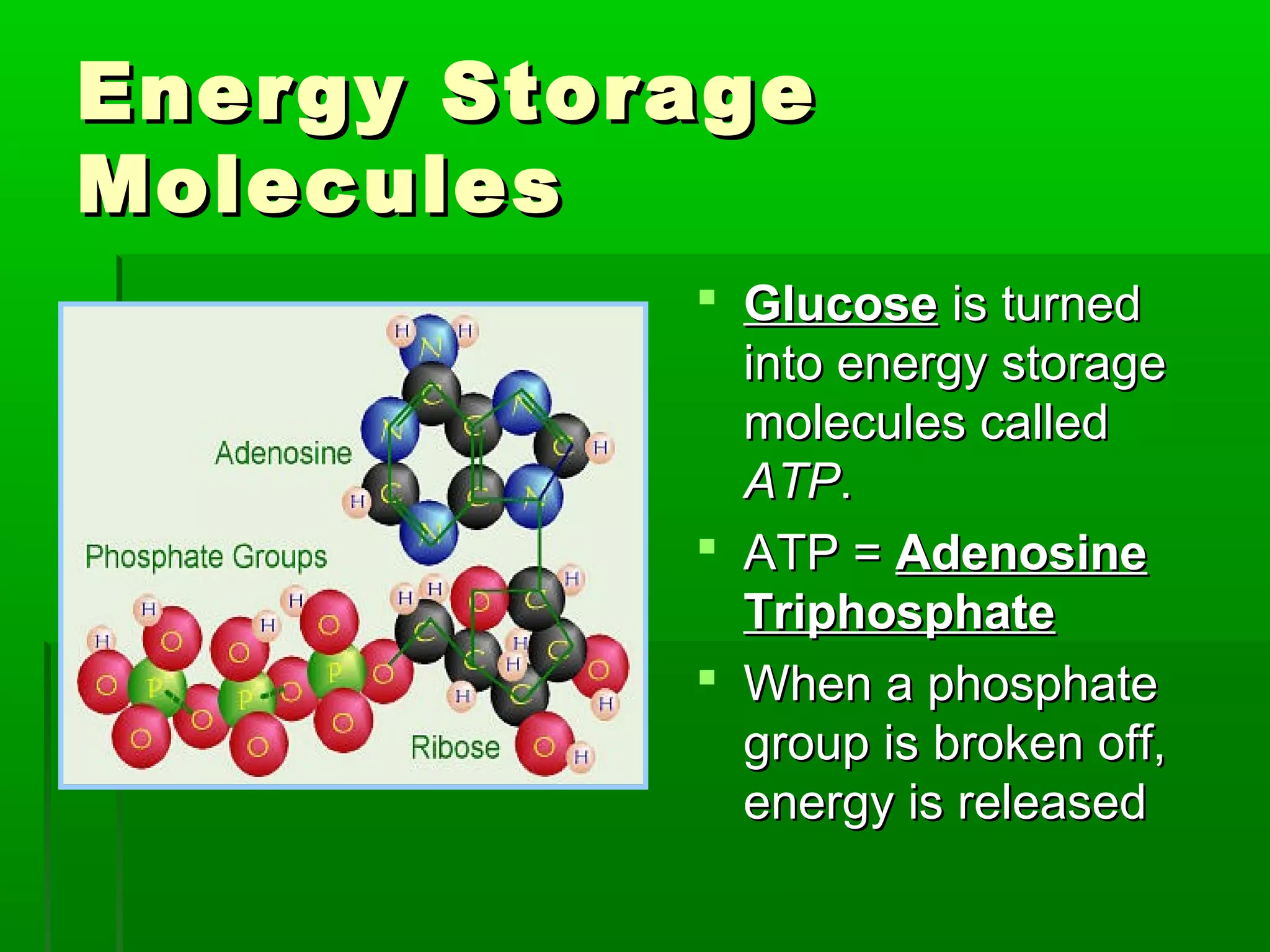
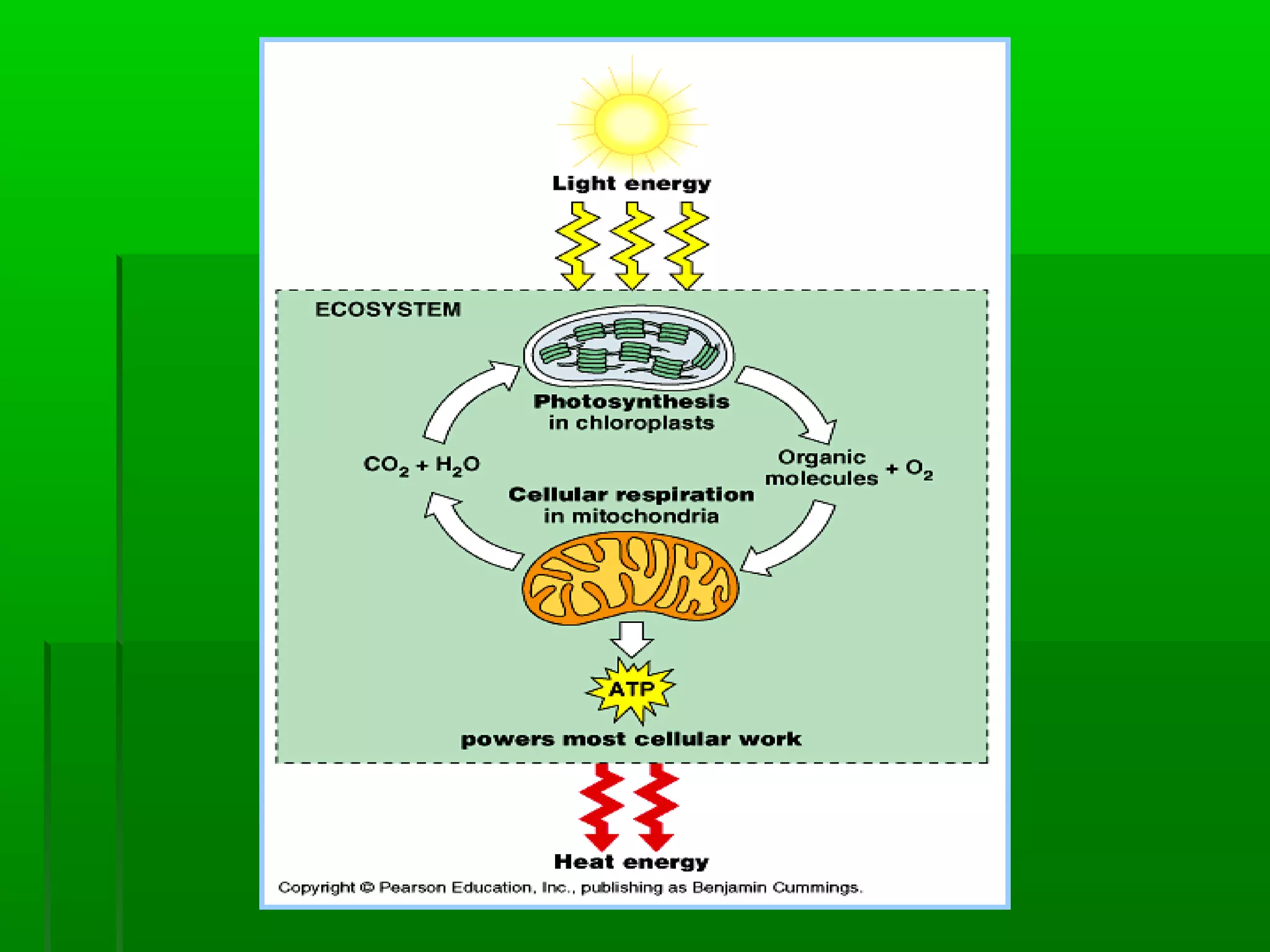
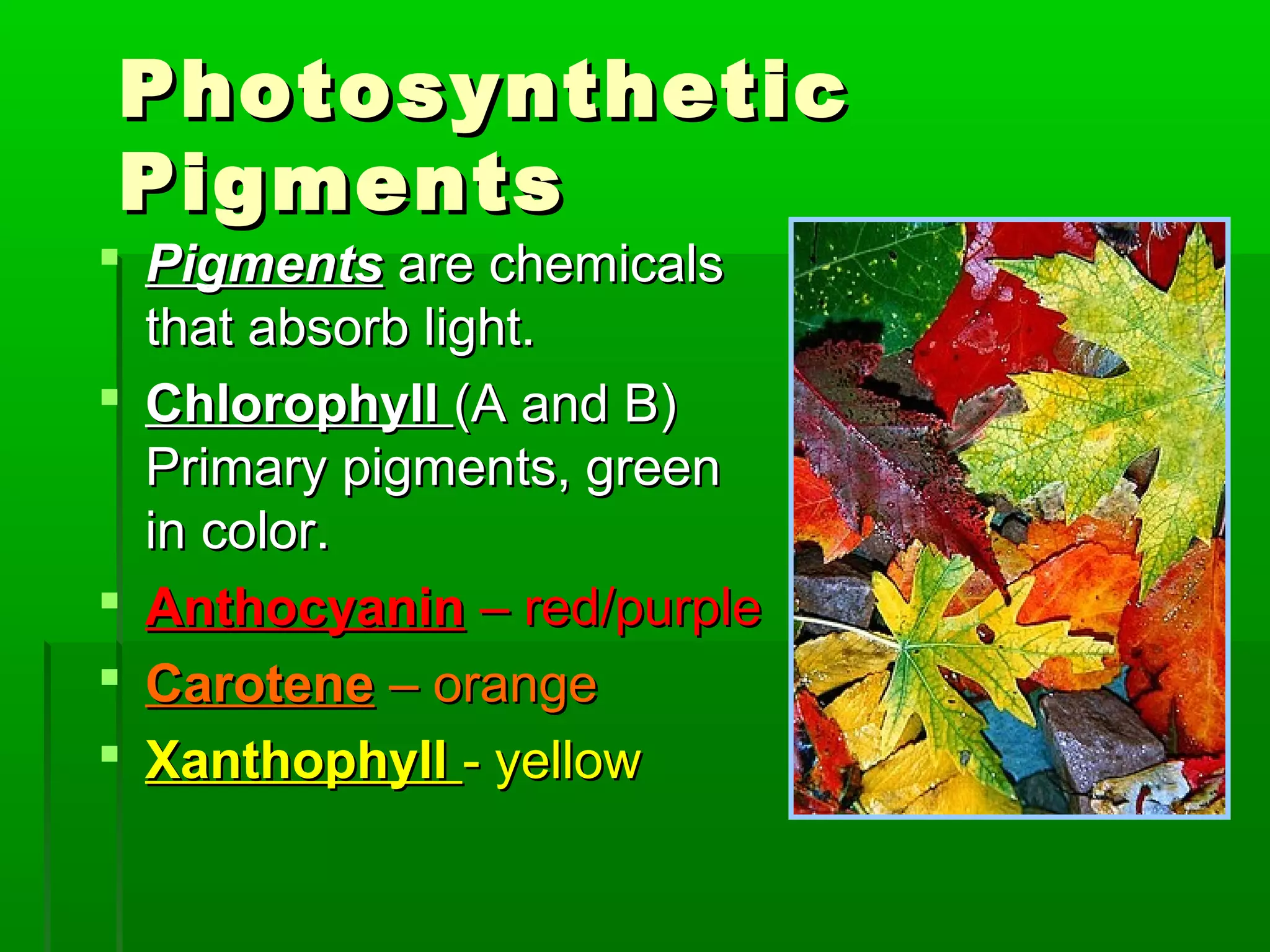
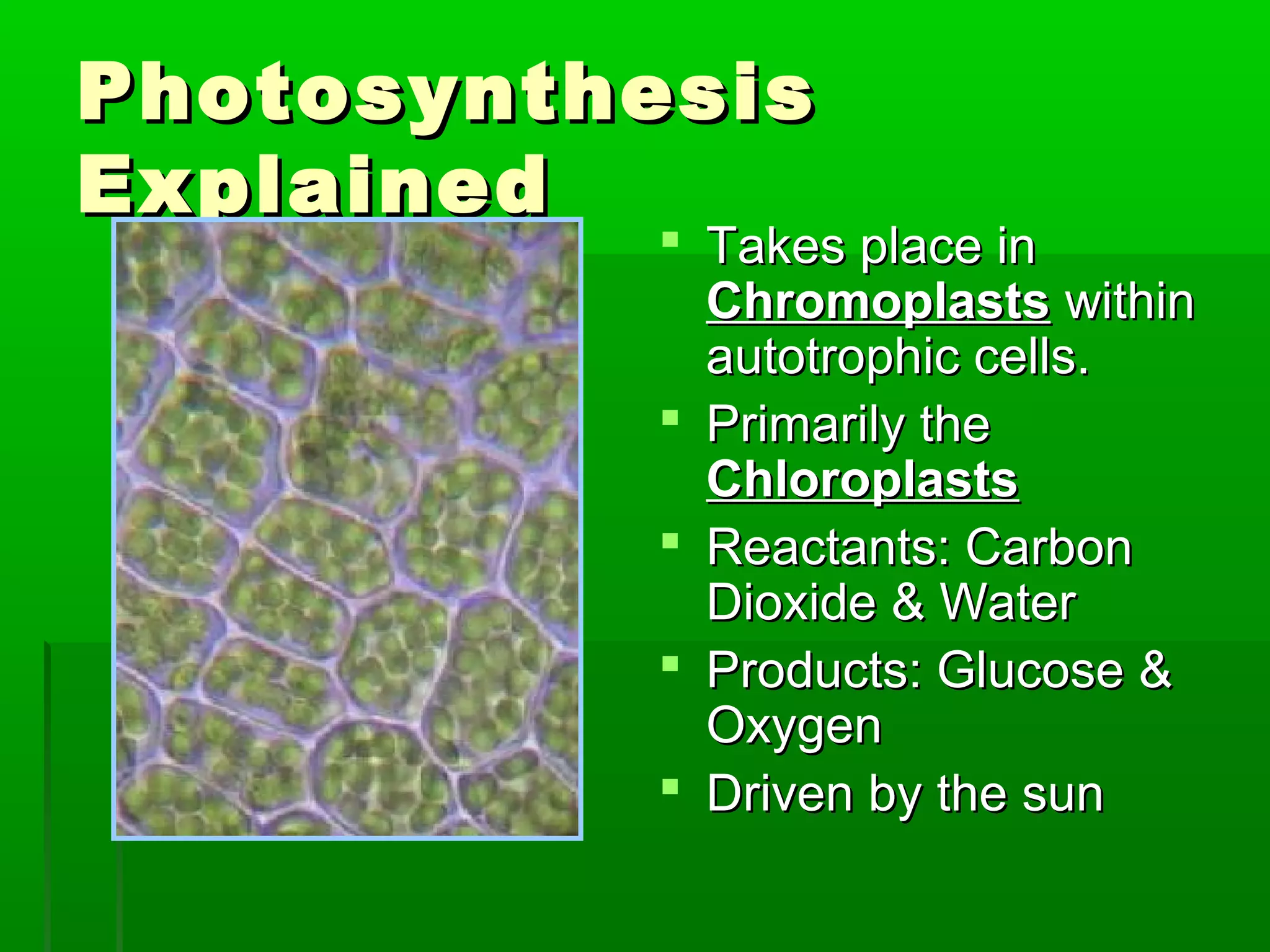
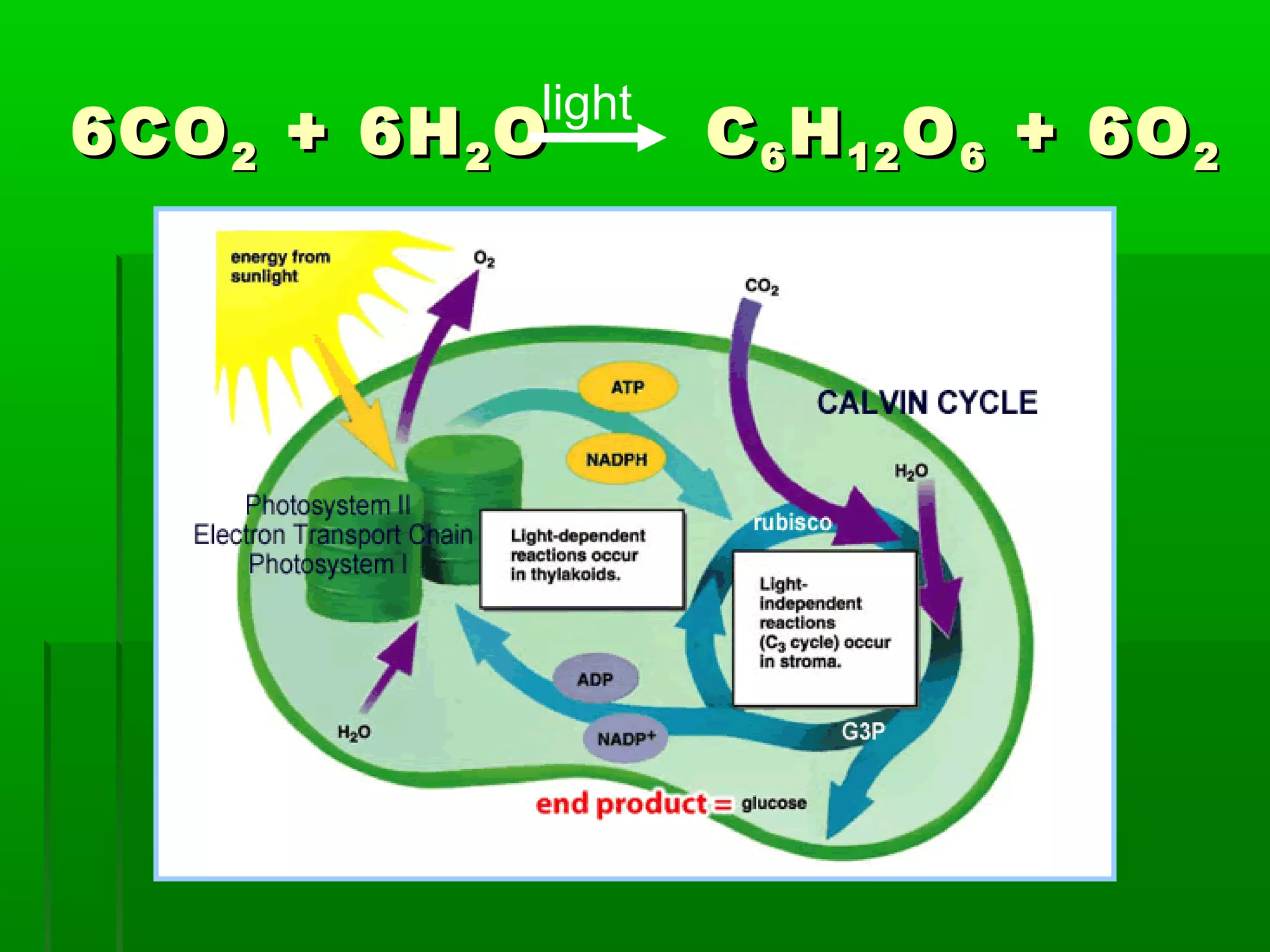
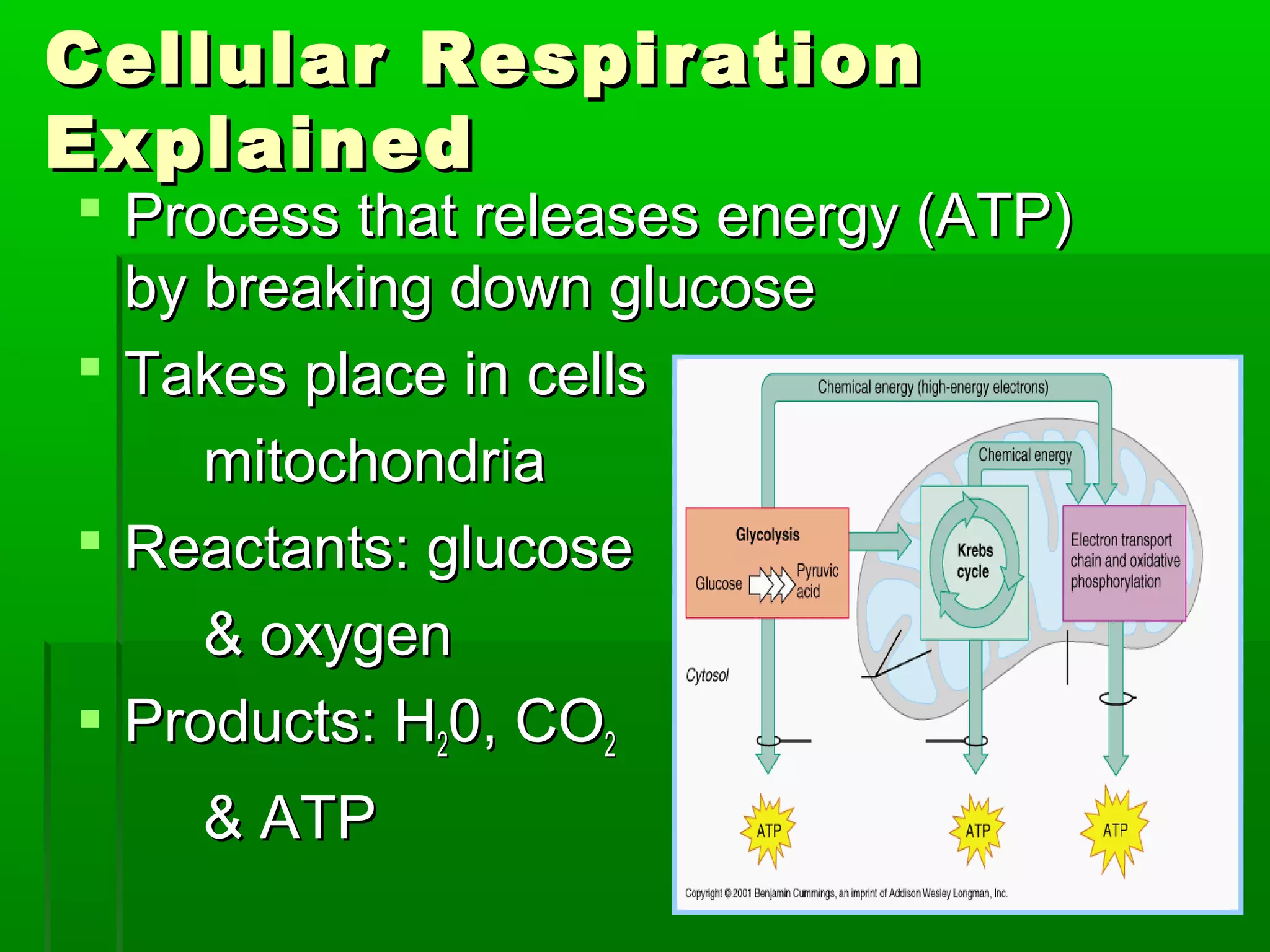
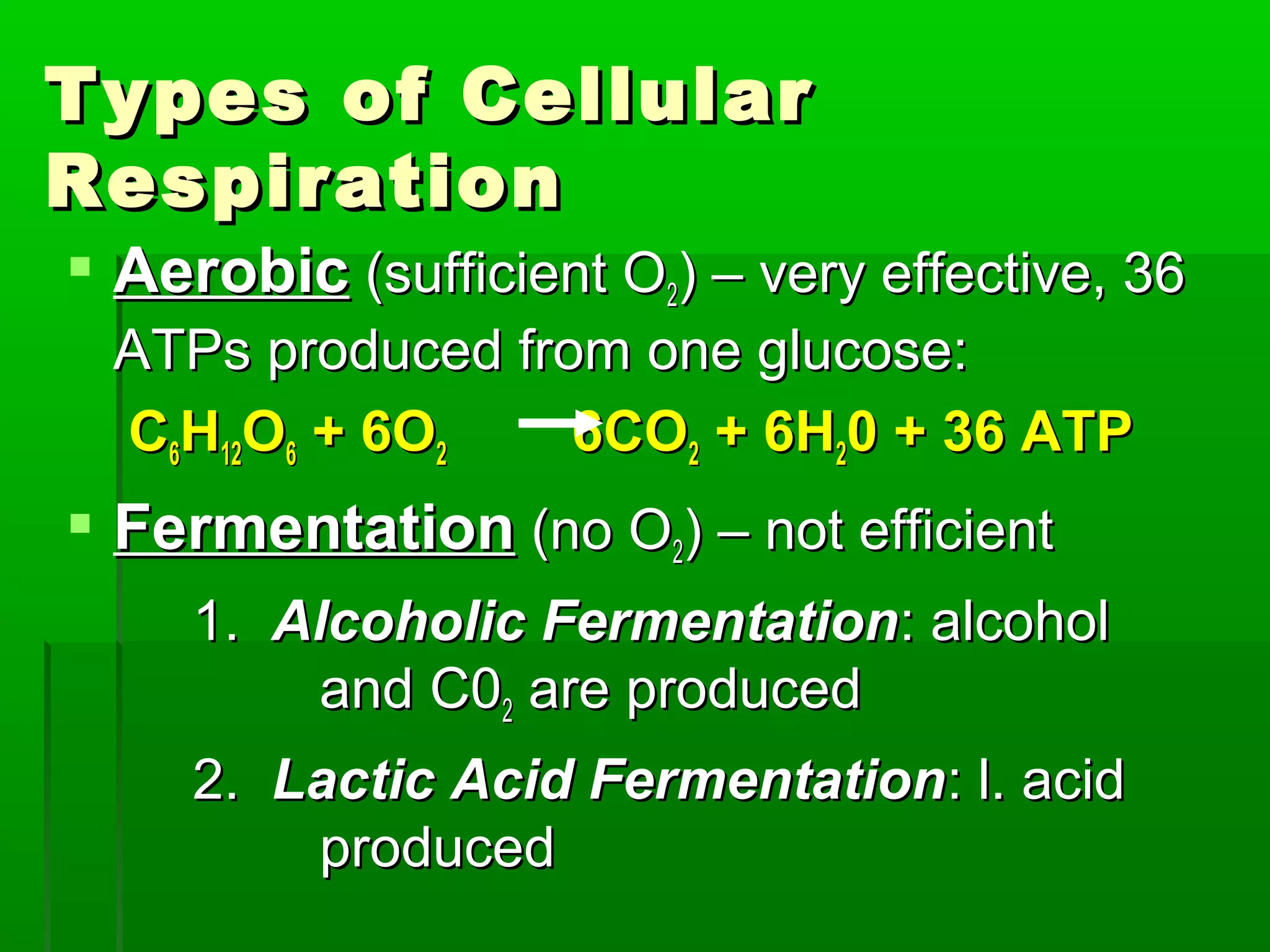
All cells need energy to function, which they obtain through glucose. Autotrophic cells produce their own glucose through photosynthesis using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. Heterotrophic cells obtain glucose through other means. Glucose is converted to ATP through cellular respiration, releasing energy. Photosynthesis uses chlorophyll and other pigments to convert sunlight, carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen through a series of chemical reactions in chloroplasts. Cellular respiration breaks down glucose and oxygen in mitochondria to produce water, carbon dioxide, and ATP.