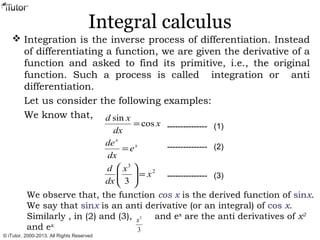
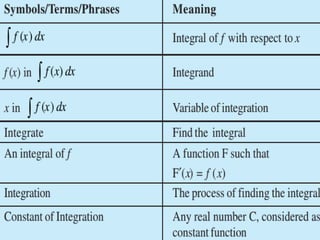
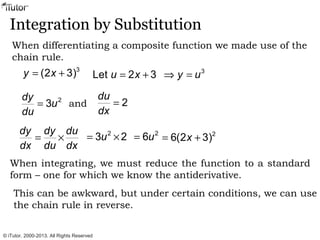
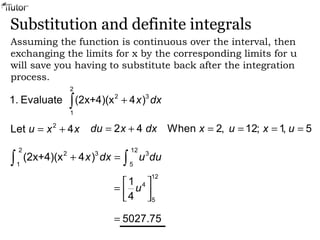
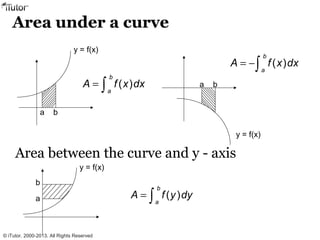
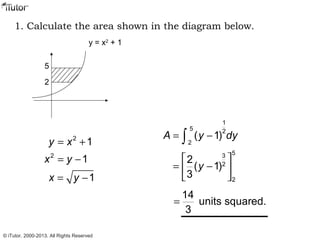
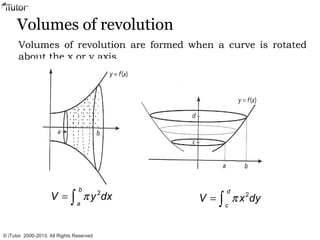
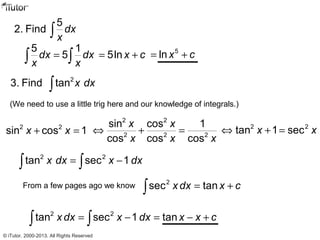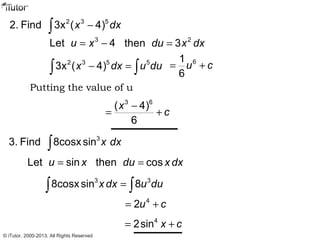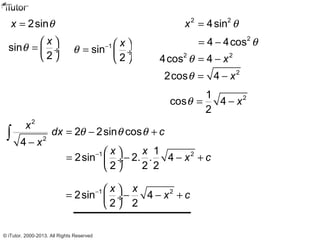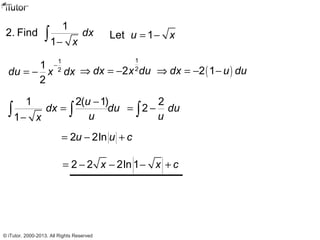This document discusses integration, which is the inverse process of differentiation. Integration allows us to find the original function given its derivative. Several integration techniques are explained, including substitution, integration by parts, and finding volumes of revolution. Standard integrals are presented along with examples of calculating areas under curves and volumes obtained by rotating areas about axes. Definite integrals are used to find the area between curves over a specified interval.