Embed presentation
Downloaded 272 times







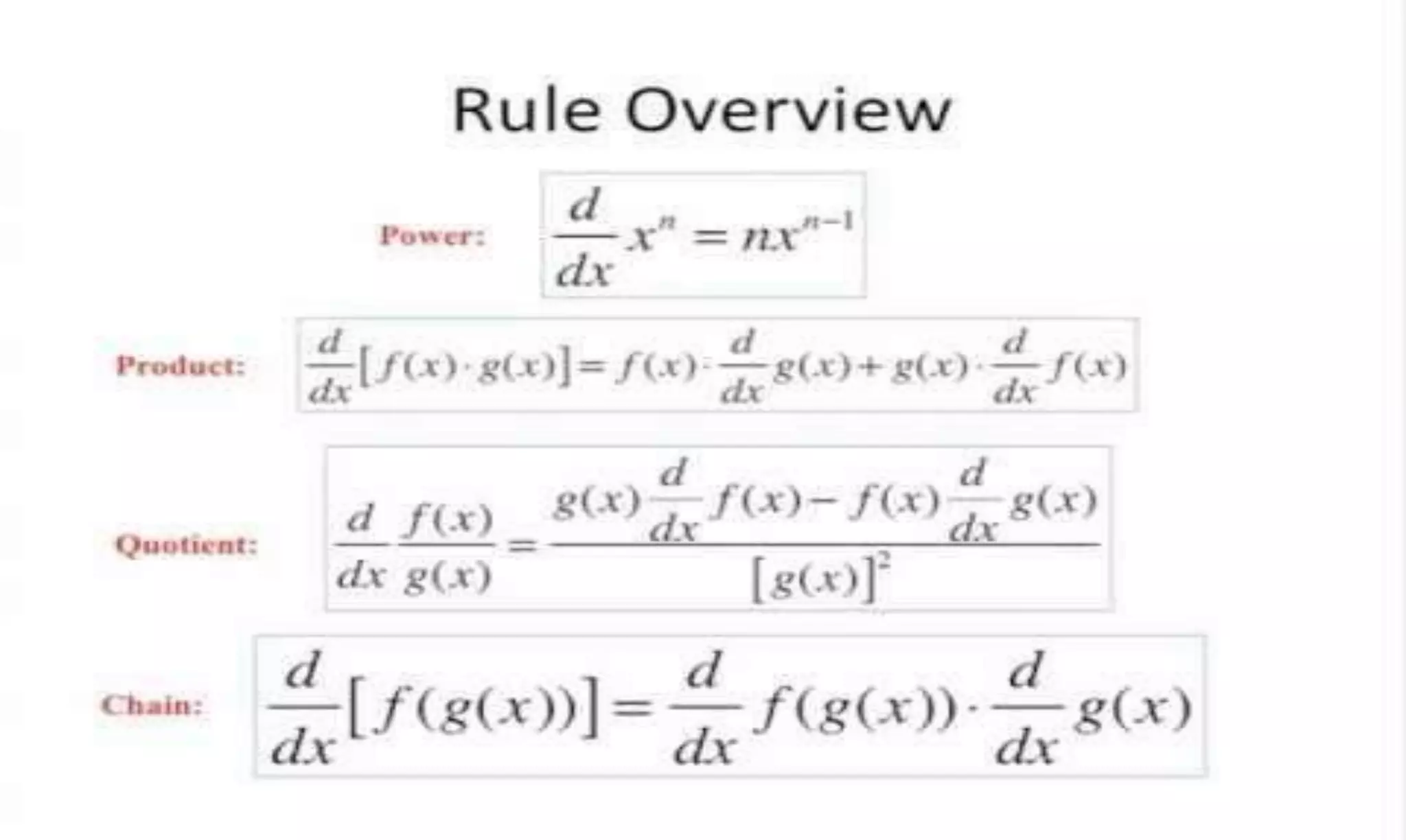


The document provides an overview of derivatives and differentiation in basic calculus, defining derivatives as measures of sensitivity to changes in function inputs. It discusses the derivative of a function with an example and explains the relationship between continuity and differentiability, stating that a differentiable function must be continuous. Additionally, it includes rules for differentiation such as the inverse function rule and reciprocal rule.














Explores the concept of derivatives and their significance in measuring the sensitivity of functions to changes in inputs.
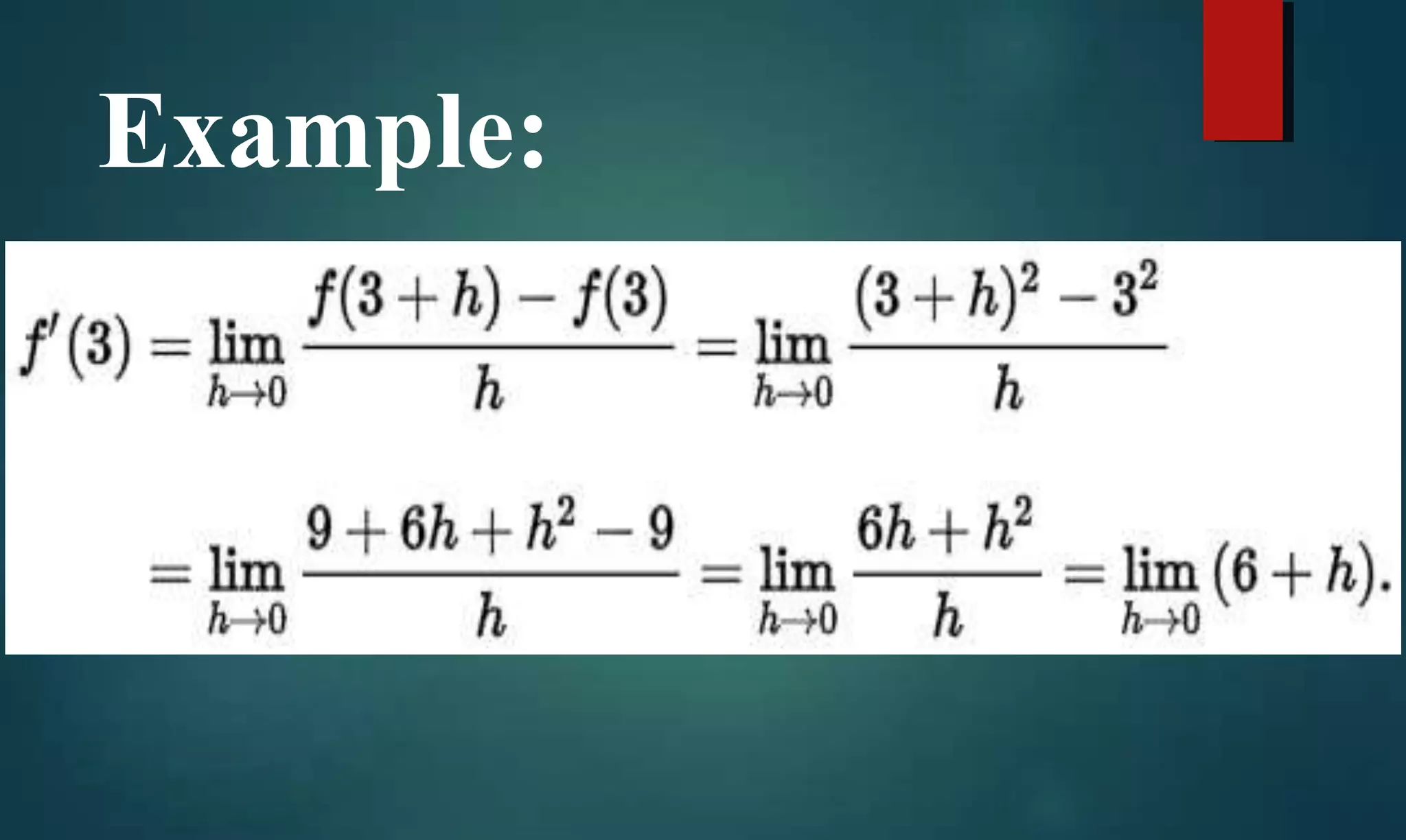
Defines differentiation as the process of computing derivatives, emphasizing the mathematical definition of a derivative.
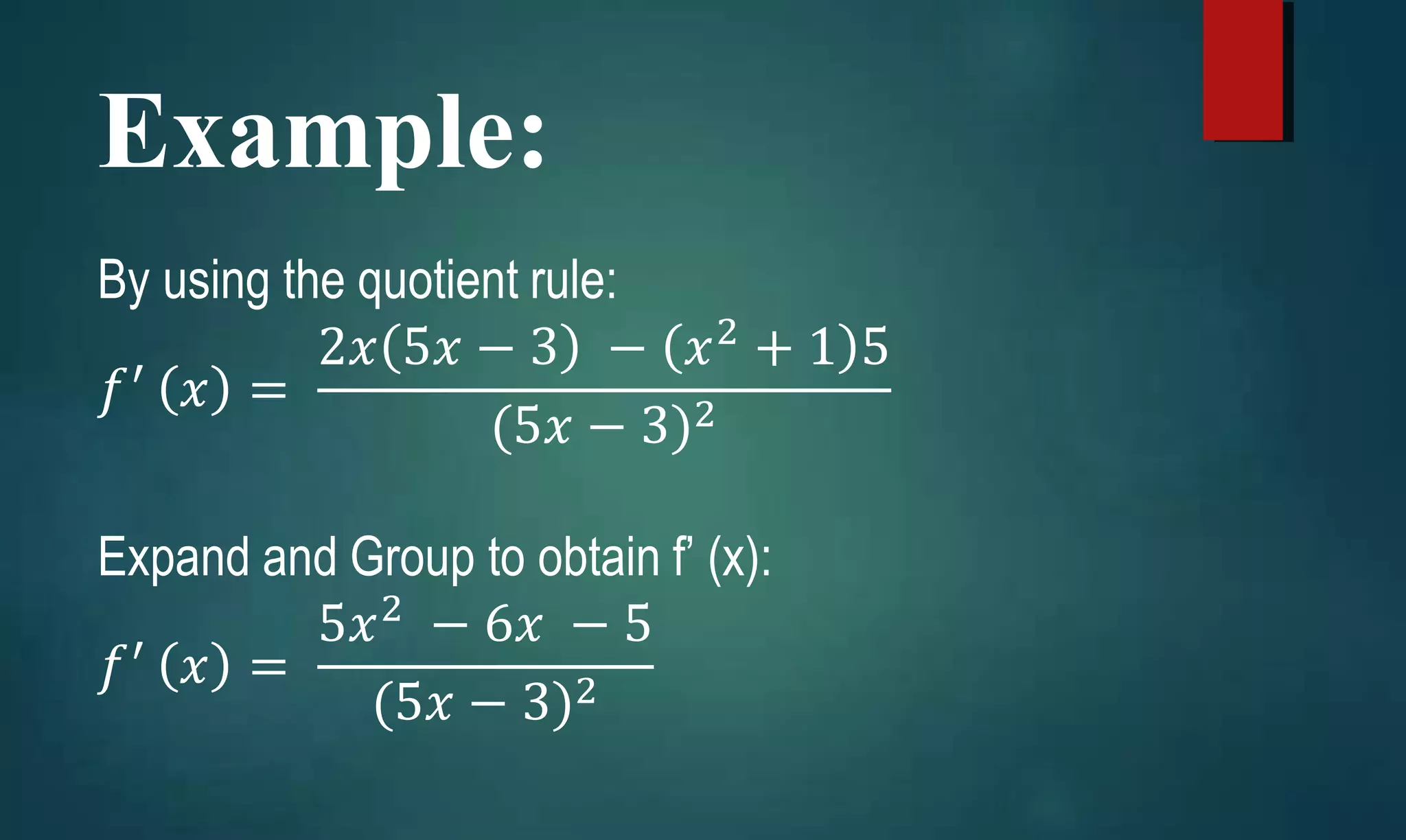
Presents a practical example of a derivative calculation using the quotient rule with specific functions.
Discusses the concept that differentiability implies continuity at a point within a function's domain.
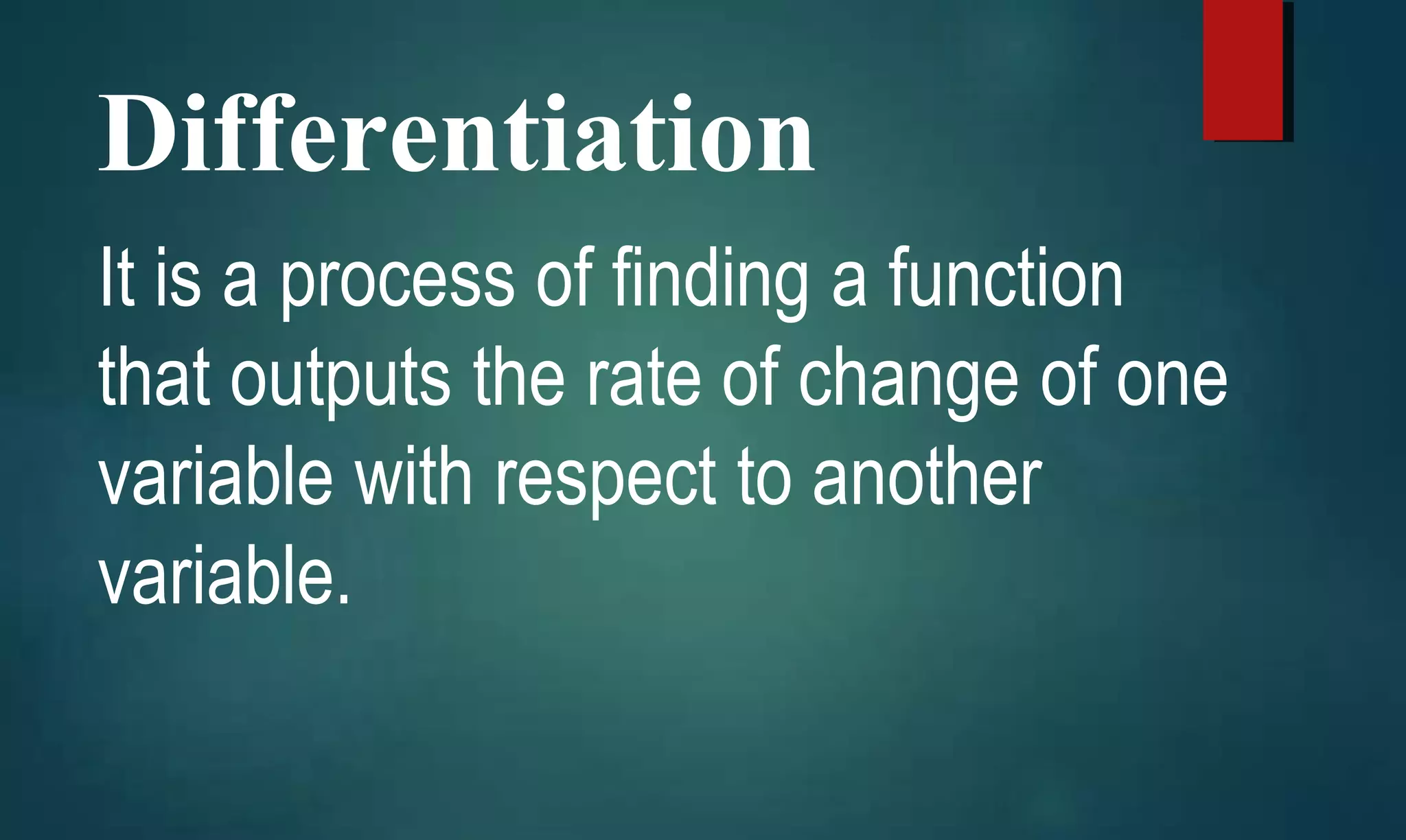
Introduces rules in differentiation, explaining the process of finding rates of change between variables.
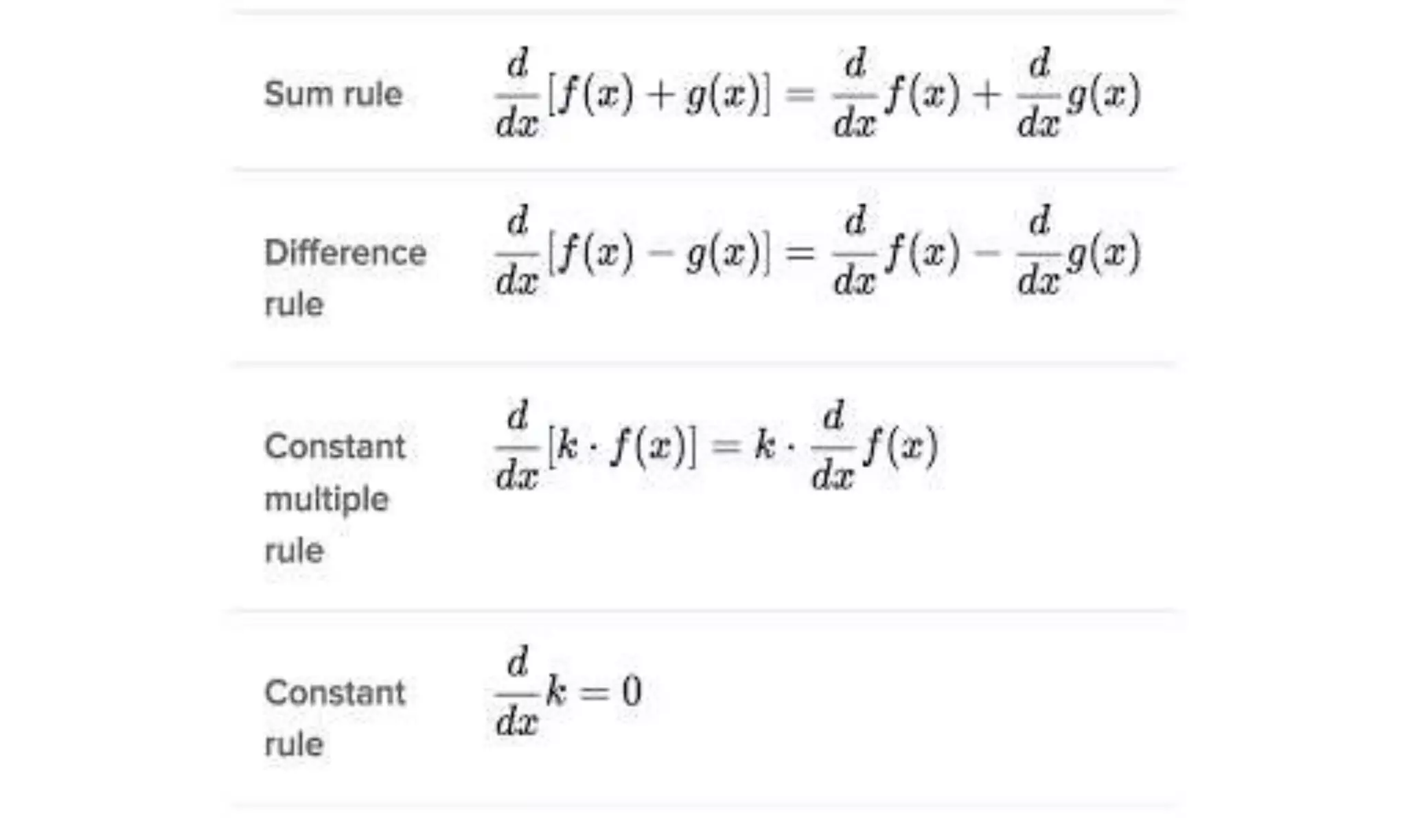
Introduces specific differentiation rules like the Inverse Function Rule and Reciprocal Rule to aid in calculations.