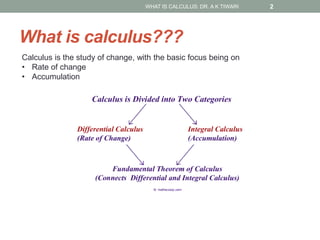
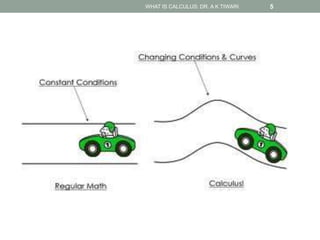
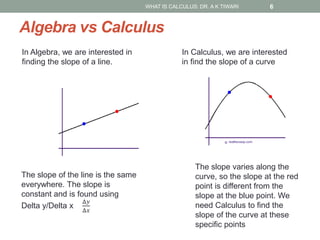
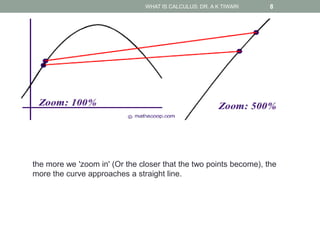
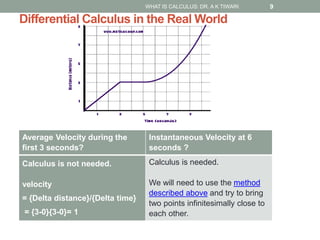
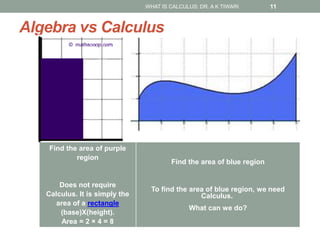
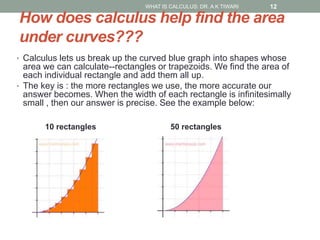
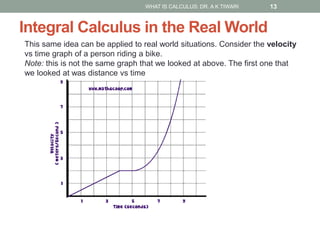
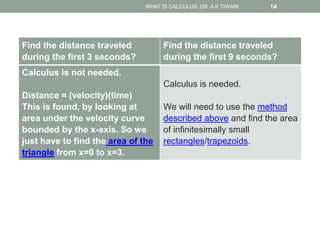
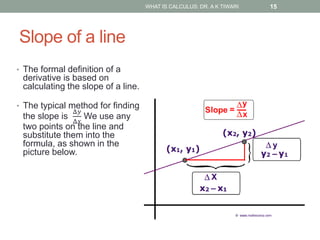
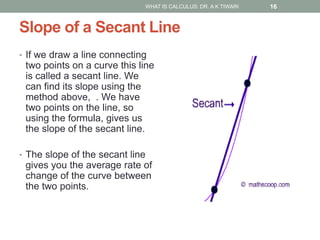
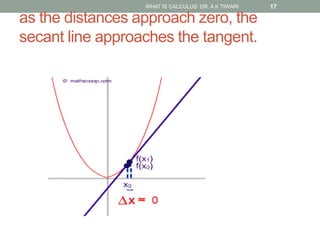
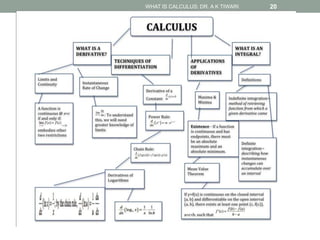
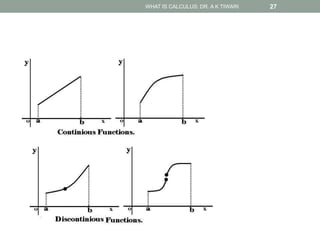
Calculus is the study of change, focusing on rates of change and accumulation. It extends concepts from algebra and geometry using limits, which allow studying what happens to points on a graph as their distance approaches zero. Calculus has two main branches:
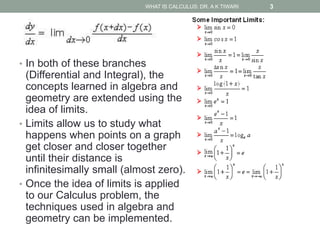
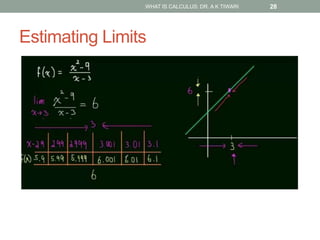
Differential calculus deals with rates of change and derivatives. Integral calculus concerns accumulation and finding areas under curves. Limits are a fundamental concept, defining a derivative as the slope of a tangent line as points approach each other infinitesimally. Calculus has many applications in physics, engineering, and other fields for problems involving curves, optimization, and rates of change.