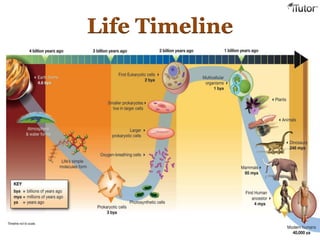
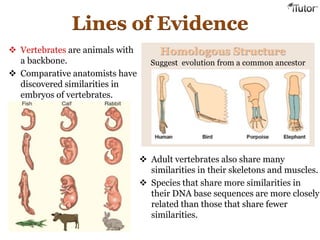
Evolution is the process by which organisms acquire adaptations over time. There are several lines of evidence that support the theory of evolution, including:
- Comparative anatomy, which looks at anatomical similarities between species and finds homologous structures that suggest a common ancestor.
- DNA analysis, where closer genetic relationships are found between species that share more similarities in their DNA sequences.
- The fossil record, where fossils in older rock layers tend to resemble more ancient organisms, while fossils in newer layers more closely resemble present-day species.