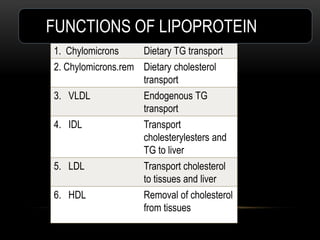
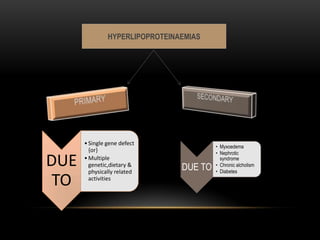
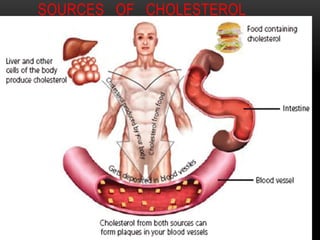
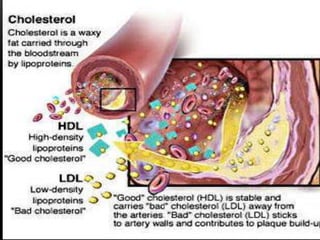
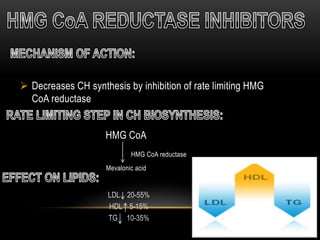
This document discusses lipoproteins and drugs that lower lipid levels. It begins by defining lipoproteins and how they transport lipids in blood, classifying them into six groups. It then discusses the functions of different lipoproteins and causes of hyperlipoproteinemias. The document focuses on statins, how they work by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, and their effects on cholesterol, LDL, HDL, and triglyceride levels. It covers the pharmacokinetics of statins, their adverse effects and uses. Other drug classes discussed include bile acid sequestrants, fibrates, nicotinic acid and their mechanisms and uses for treating different lipid abnormalities.