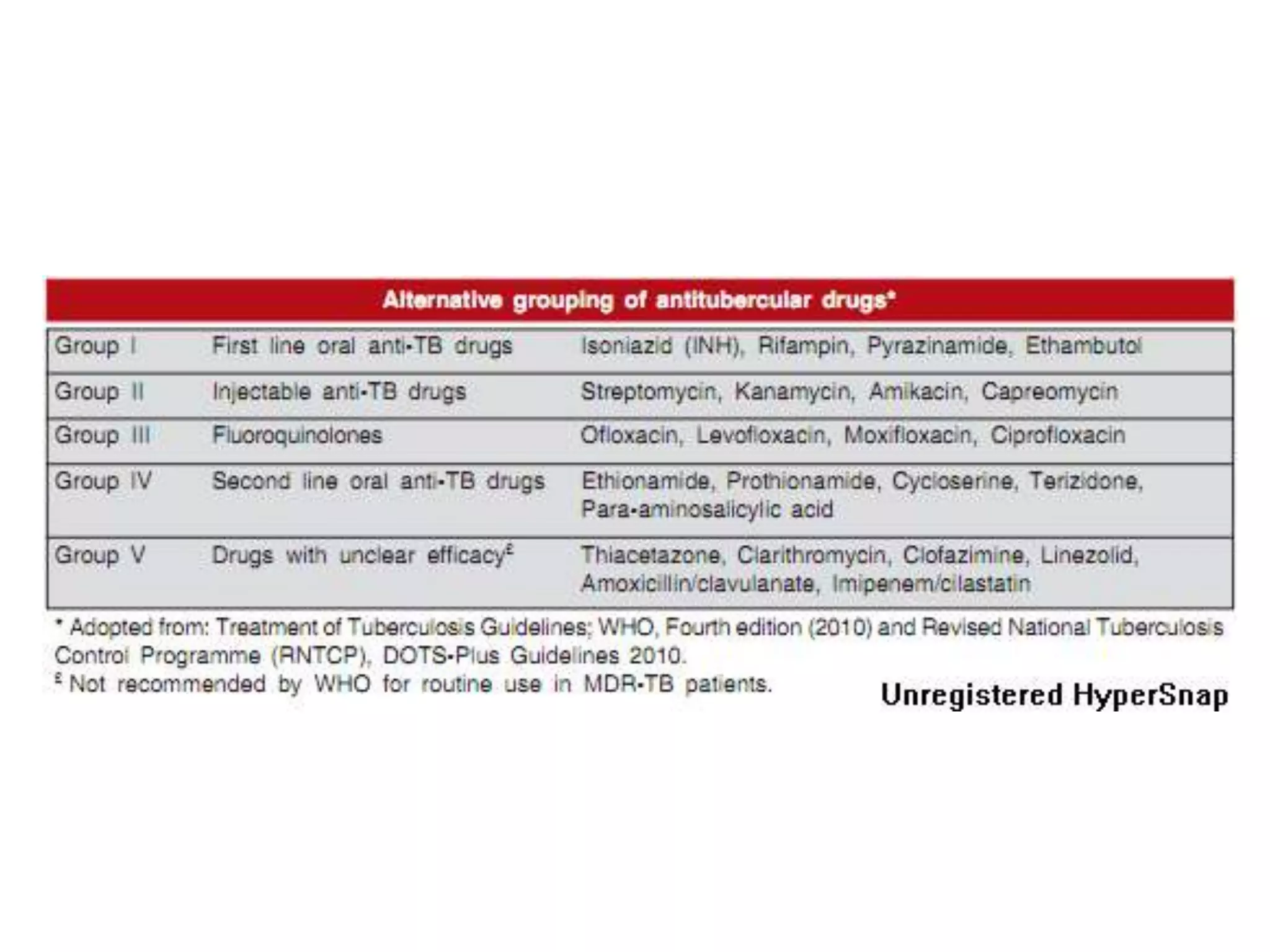
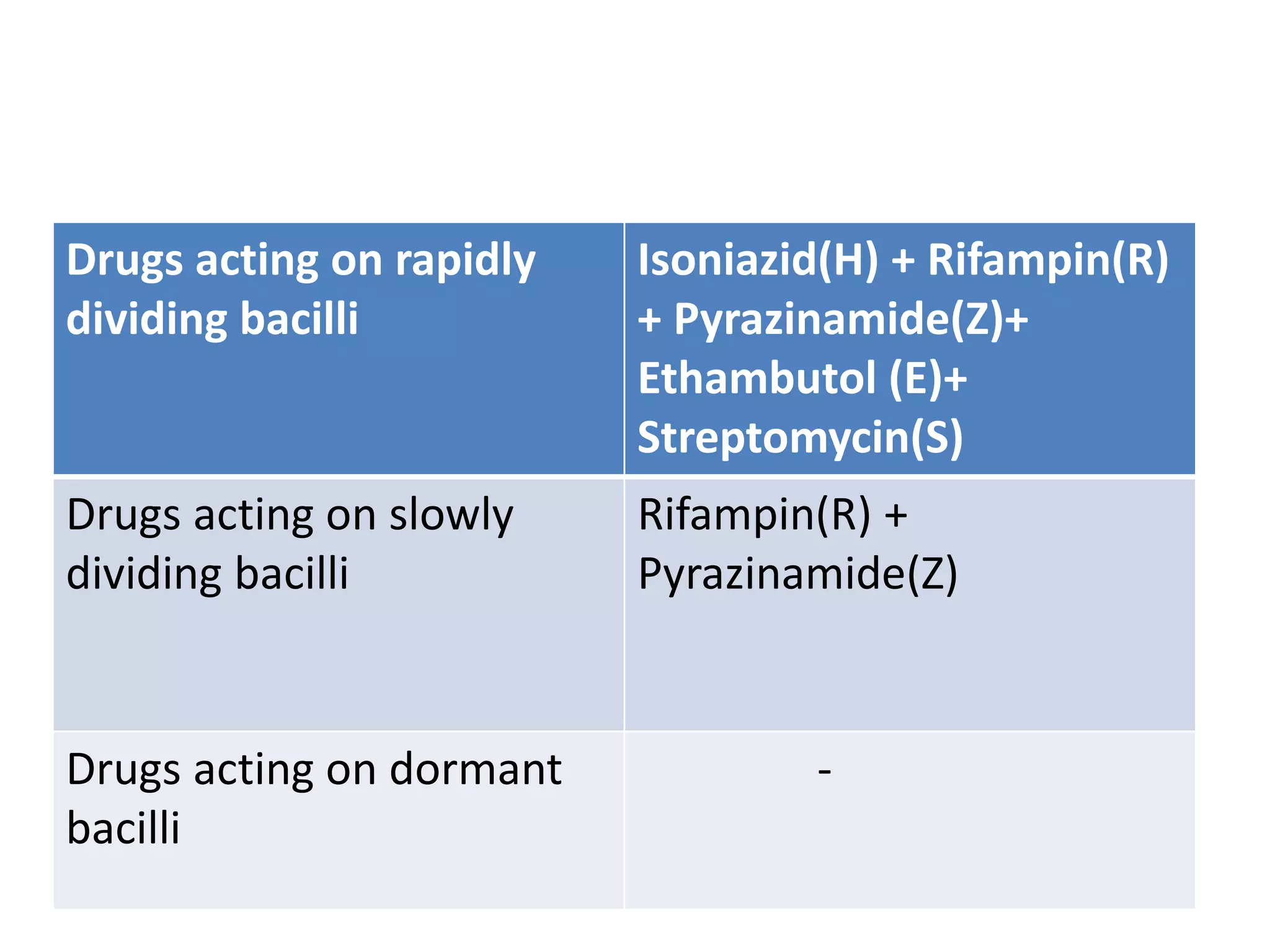
This document provides information on antitubercular drugs used to treat tuberculosis. It discusses first-line drugs like isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, ethambutol and streptomycin that are routinely used. It also discusses second-line drugs used when first-line drugs are ineffective or cannot be tolerated. The document describes the mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, resistance mechanisms and adverse effects of various antitubercular drugs. It also discusses treatment considerations for special populations like pregnant women, HIV patients and for chemoprophylaxis.