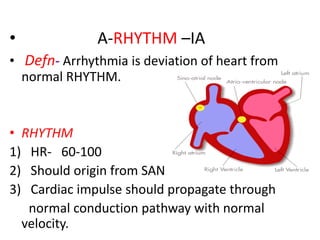
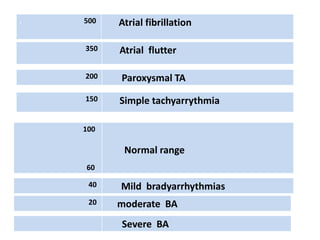
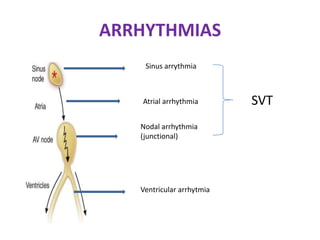
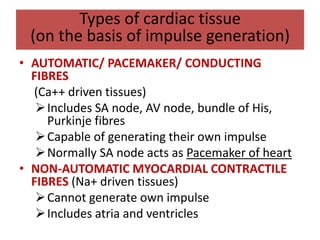
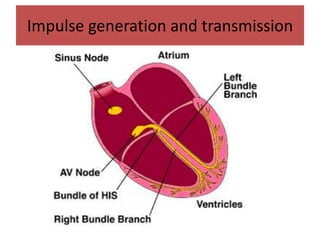
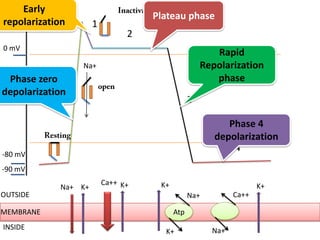
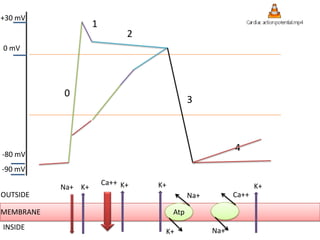
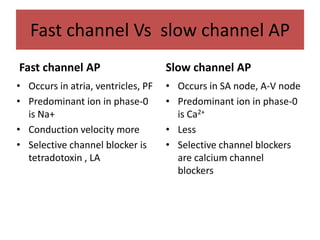
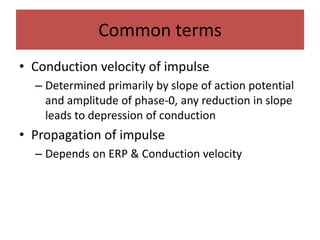
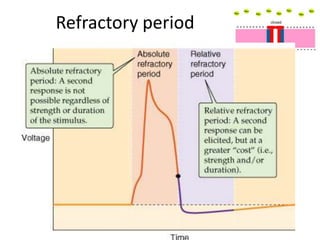
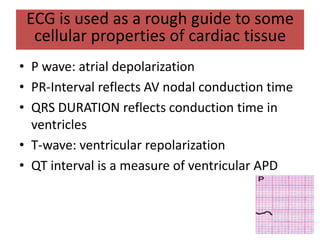
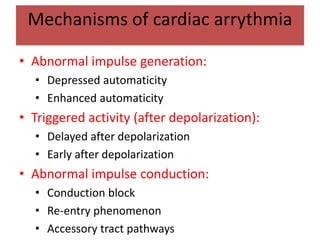
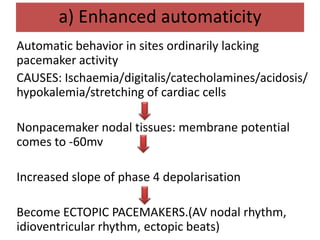
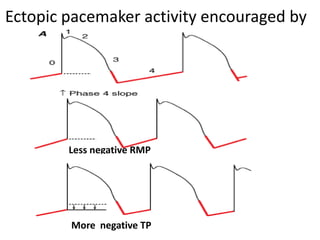
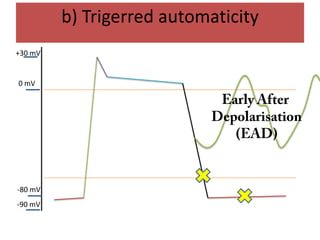
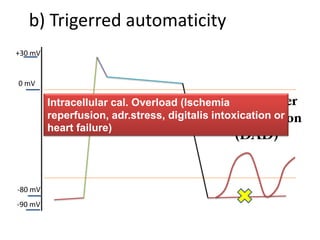
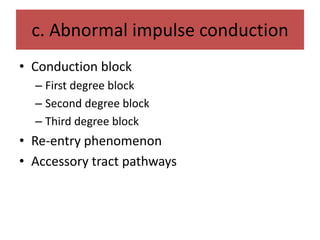
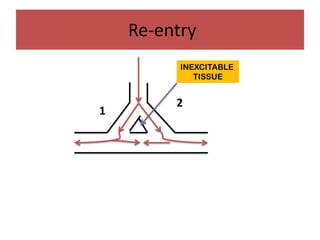
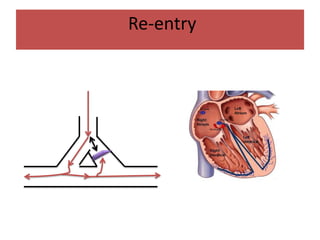
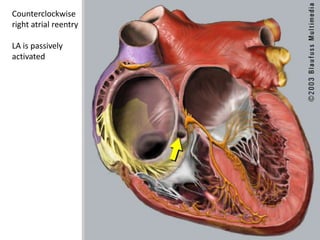
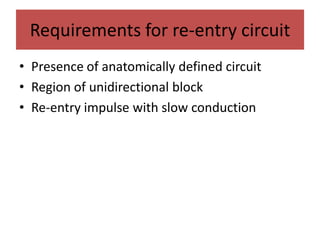
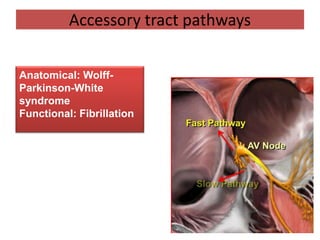
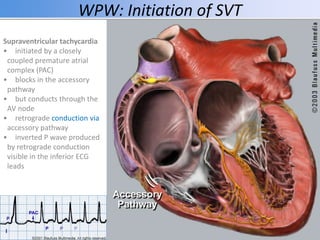
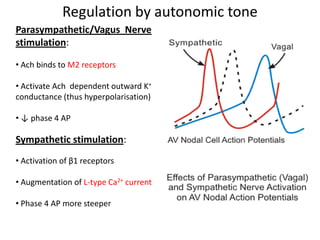
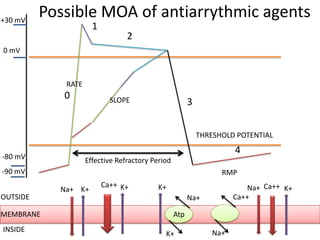
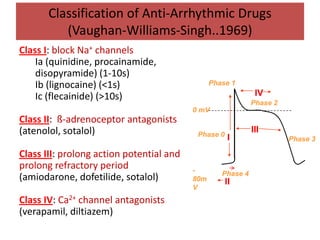
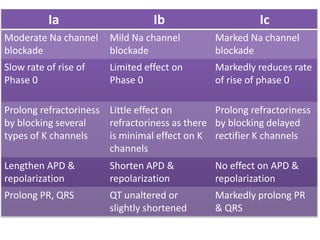
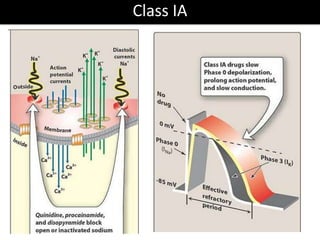
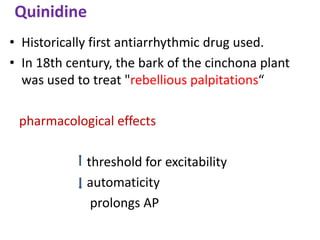
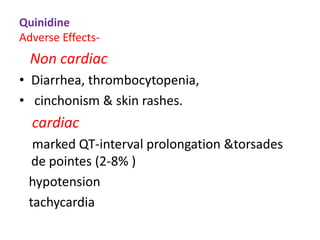
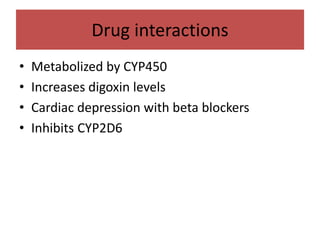
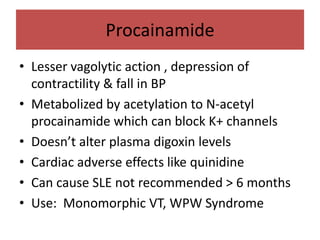
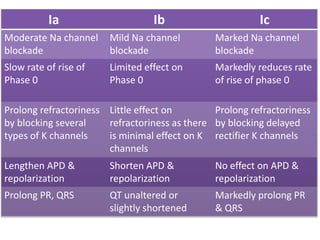
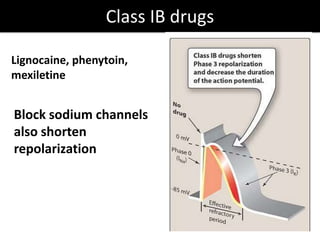
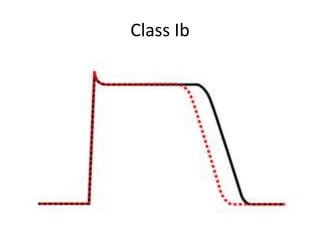
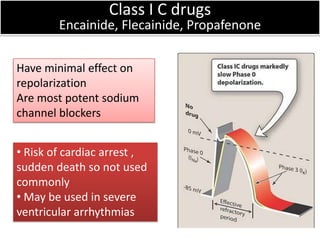
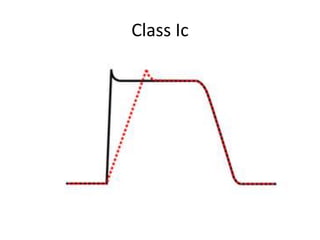
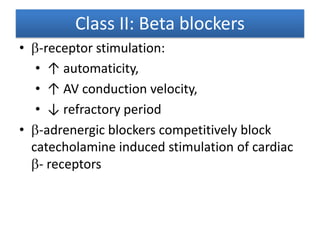
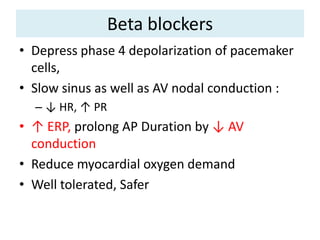
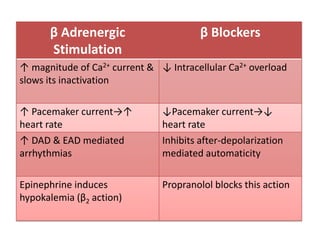
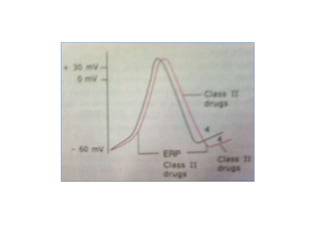
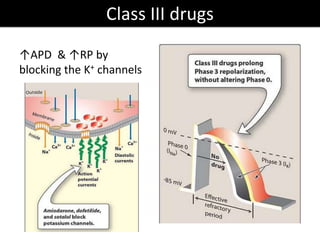
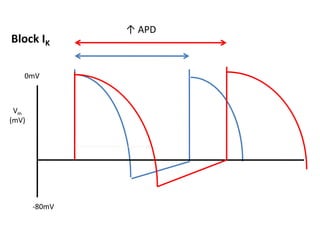
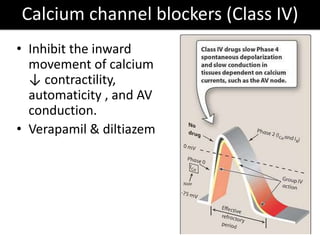
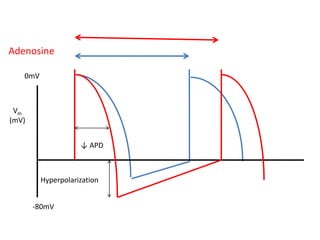
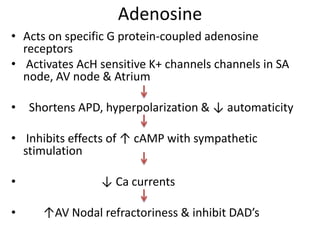
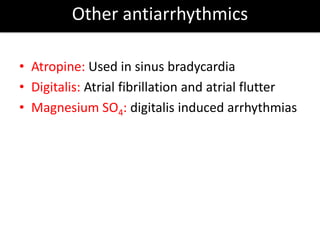
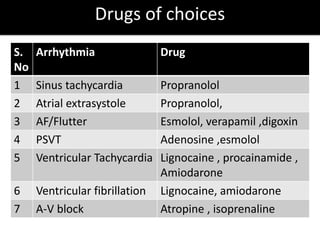
This document discusses antiarrhythmic drugs and their mechanisms of action. It begins by classifying arrhythmias and describing the electrophysiology of the heart. It then classifies antiarrhythmic drugs into four classes based on their mechanisms of action - sodium channel blockers (Class I), beta blockers (Class II), drugs that prolong the action potential (Class III), and calcium channel blockers (Class IV). Specific Class I drugs are discussed in detail, including quinidine, procainamide, and lignocaine. Their effects on cardiac sodium channels, action potentials, and refractory periods are summarized. Adverse effects and clinical uses are also briefly mentioned for key drugs.