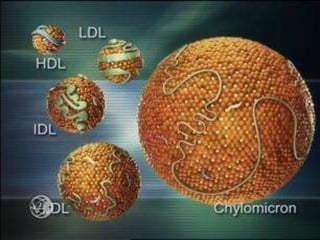
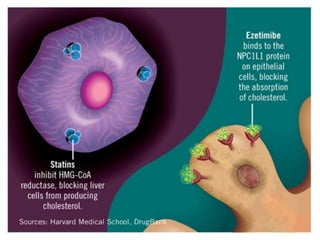
This document discusses hyperlipidemia and its treatment. It begins by explaining how elevated lipid levels can lead to atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease. It then outlines different classes of drugs that target endogenous and exogenous cholesterol, including statins, fibrates, nicotinic acid, ezetemibe, and bile acid sequestrants. The mechanisms of action, indications, and adverse effects are described for each drug class. Combination therapies are also discussed.