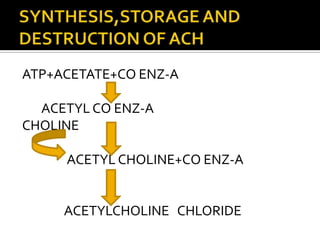
Acetylcholine (ACh) is a major neurotransmitter synthesized from choline and acetyl-CoA. It exists in two types: muscarinic and nicotinic. Muscarinic receptors are selectively stimulated by muscarine and blocked by atropine, while nicotinic receptors are activated by nicotine and blocked by tubocurarine. ACh acts on muscarinic receptors in the CNS, smooth muscles, and glands to produce various effects like tremors, contraction, increased secretion, and accommodation. It acts on nicotinic receptors in the CNS and neuromuscular junction. Cholinergic agonists like ACh and carbachol mimic the actions of ACh