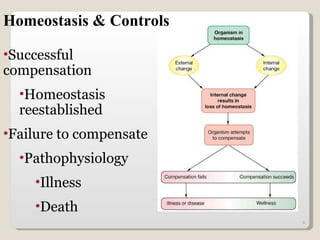
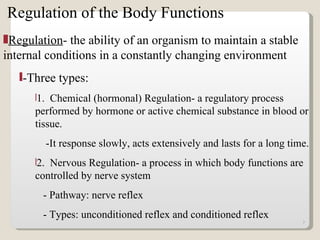
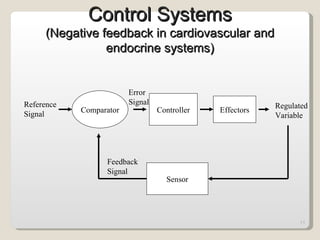
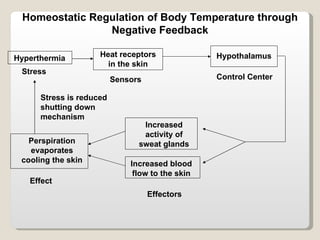
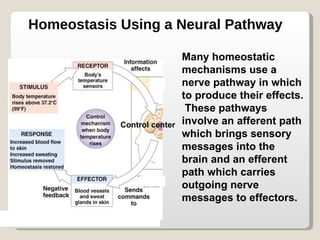
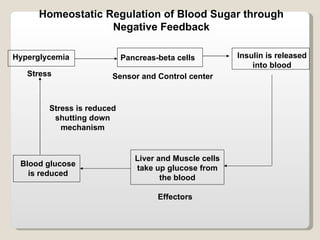
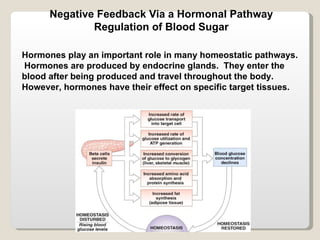
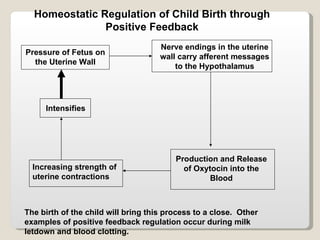
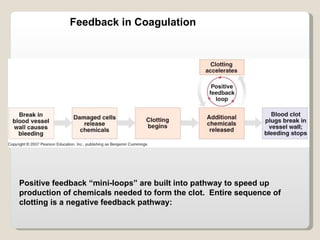
Homeostasis refers to the maintenance of relatively constant internal conditions in the body despite changes in the external environment. There are three main types of regulation that work together to achieve homeostasis: chemical/hormonal regulation, nervous regulation, and autoregulation of tissues and organs. Homeostatic mechanisms use either negative or positive feedback loops. Negative feedback loops work to reduce any imbalance, while positive feedback loops intensify an initial stimulus over a short period of time, such as during childbirth.