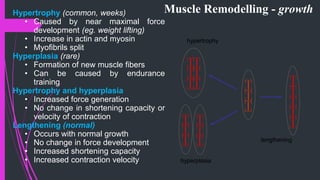
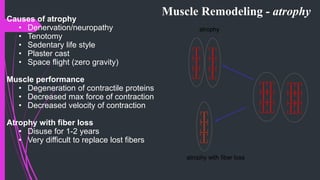
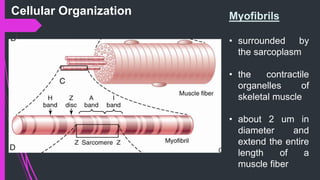
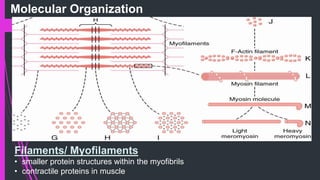
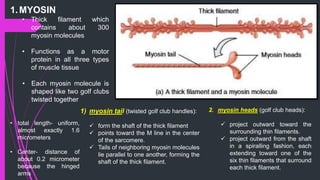
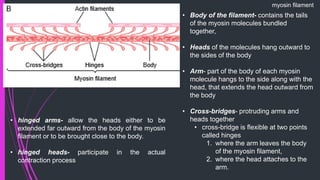
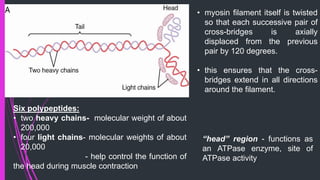
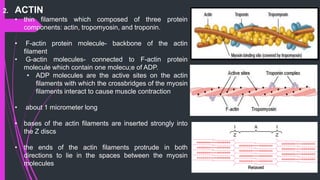
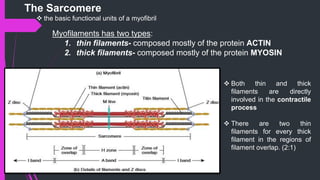
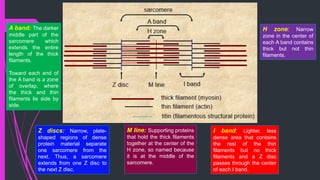
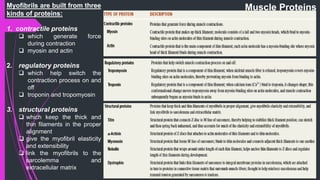
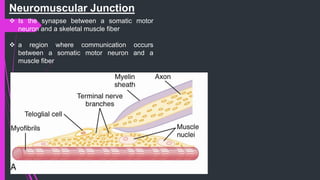
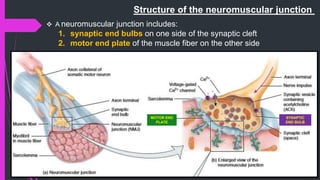
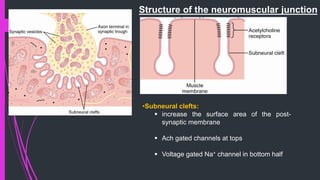
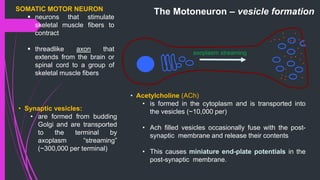
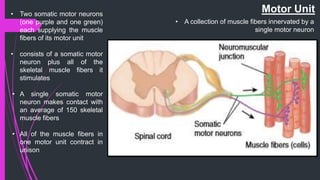
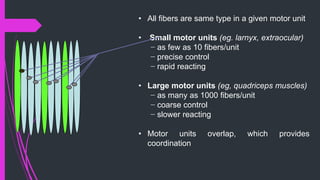
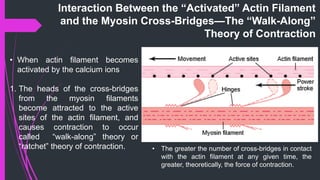
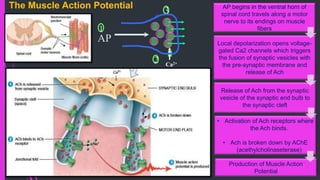
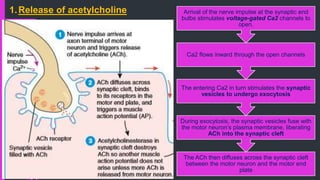
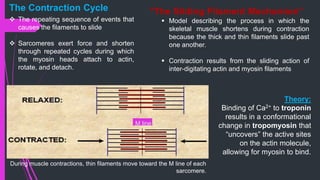
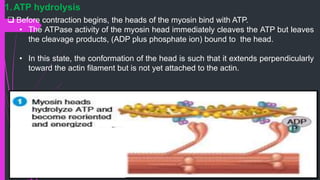
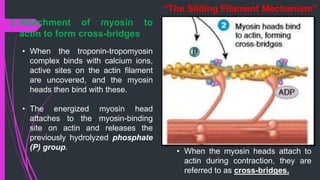
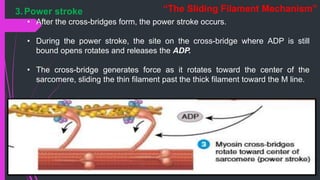
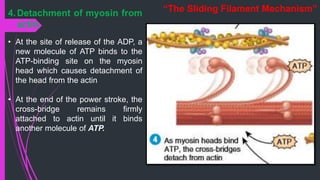
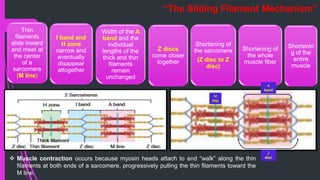
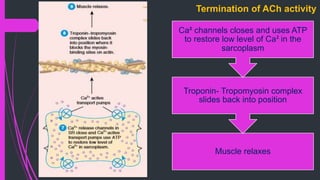
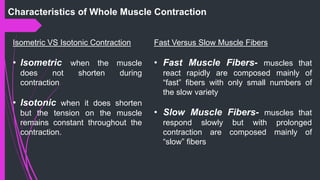
The document provides an in-depth overview of muscle contraction at the molecular level, detailing the structure and function of myofibrils, myofilaments, and the role of proteins like myosin, actin, troponin, and tropomyosin. It explains the neuromuscular junction's function in muscle action potential generation and the sliding filament mechanism that leads to muscle shortening during contraction. The regulation of contraction by calcium ions and the ATP's role in energizing the contraction cycle are emphasized throughout.



















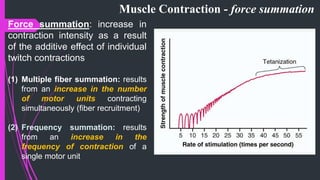
![Frequency Summation of Twitches and Tetanus
Myoplasmic [Ca2+]
Force
AP
Time (1 second)
Fused tetanus
• Myoplasmic Ca2+ falls (initiating relaxation) before development of maximal
contractile force
• If the muscle is stimulated before complete relaxation has occurred the new
twitch will sum with the previous one etc.
• If action potential frequency is sufficiently high, the individual contractions are
not resolved and a ‘fused tetanus’ contraction is recorded.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3musclephysiopart2-171002140913/85/MUSCLE-PHYSIOLOGY-1-51-320.jpg)