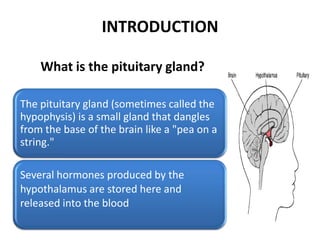
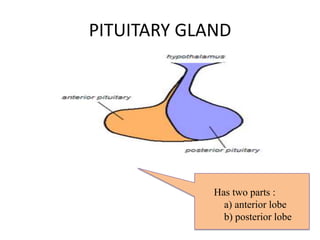
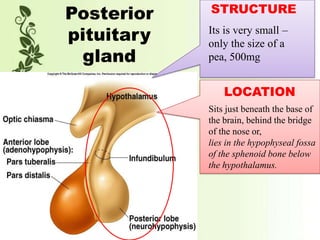
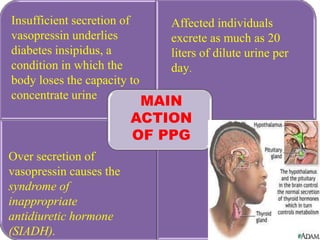
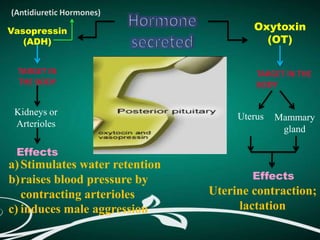
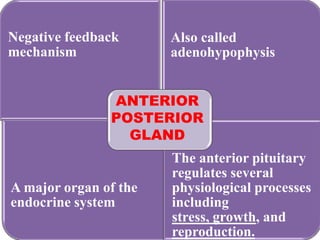
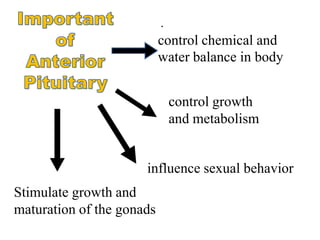
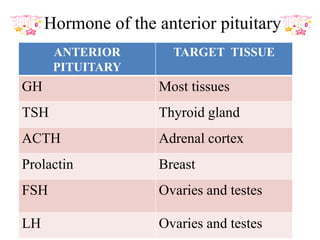
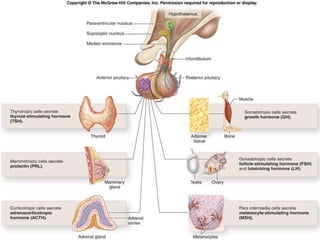
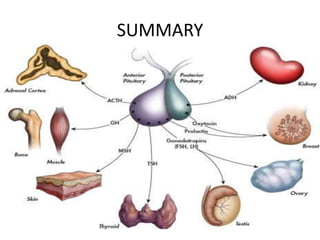
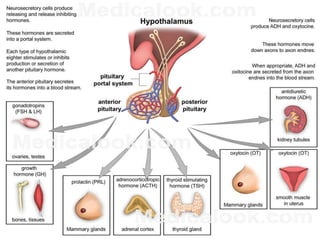
The pituitary gland, also known as the hypophysis, is a small pea-sized gland located at the base of the brain. It has two lobes - the anterior and posterior lobes. The anterior lobe regulates growth, metabolism, stress responses, reproduction and lactation by producing hormones that stimulate other glands. The posterior lobe helps control water balance in the body. The pituitary gland is often called the "master gland" as it controls many other glands.