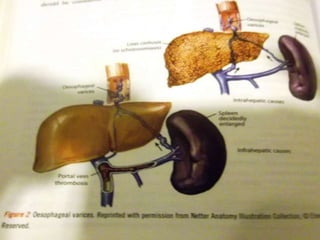
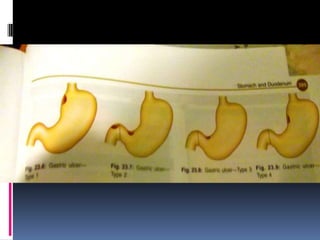
Haematemesis in pregnancy can be caused by conditions affecting the esophagus, stomach, or duodenum. Common causes include Mallory-Weiss tears from forceful vomiting, gastroesophageal reflux and hiatal hernias, peptic ulcers which may be associated with H. pylori infection, and acute gastritis from NSAID use. Less common causes can include esophageal or gastric varices from liver disease, angiodysplasia, or disorders of haemostasis from medications like warfarin. Treatment involves resuscitation, endoscopy if needed, and treating the underlying condition.