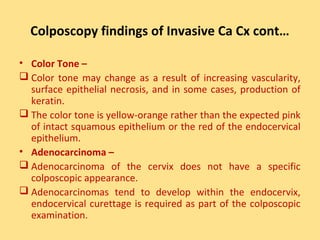
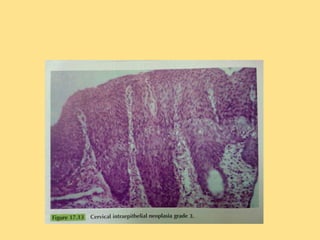
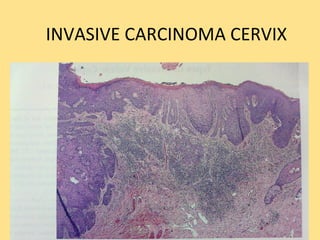
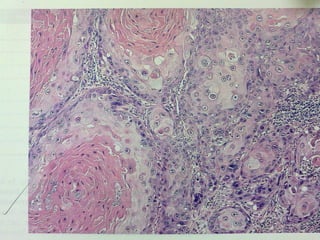
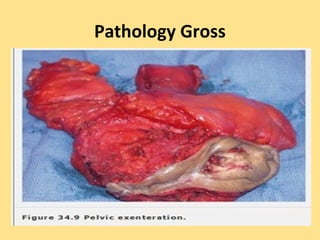
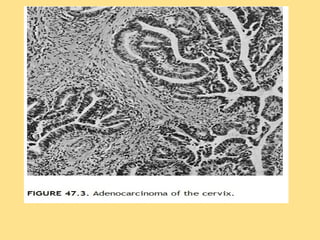
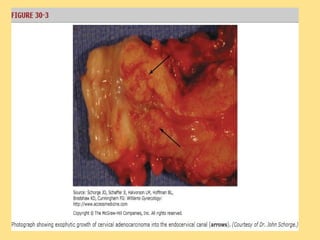
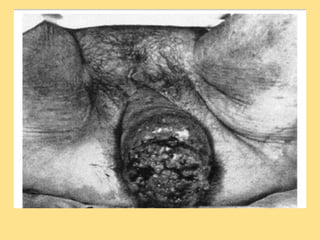
This document discusses cervical cancer, including its epidemiology, risk factors, mechanisms, evaluation, staging, treatment options, and prognosis. Key points include:
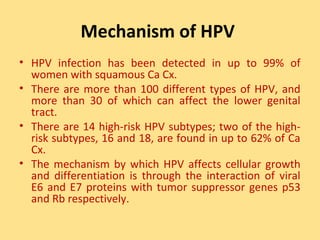
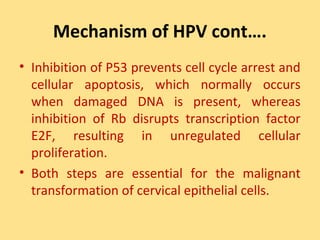
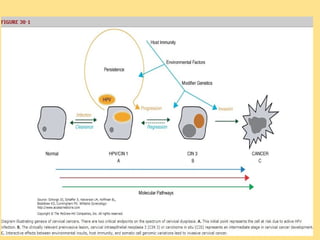
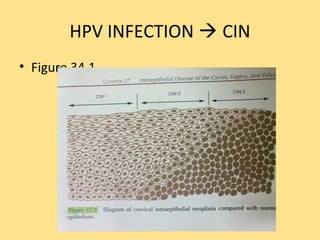
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is the main risk factor and causal agent for cervical cancer. High-risk HPV subtypes 16 and 18 are responsible for most cases.
- Early detection through Pap screening can prevent 30% of cases in developed countries and up to 60% in developing countries. Symptoms often include abnormal bleeding.
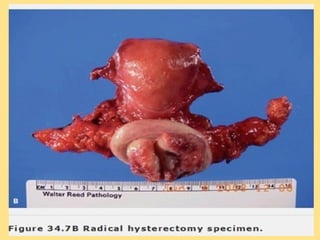
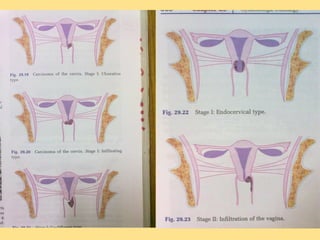
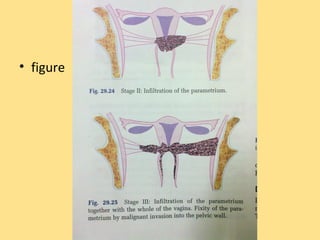
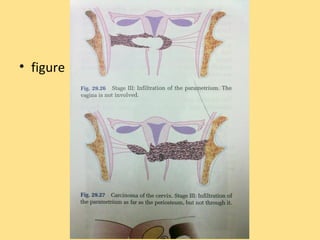
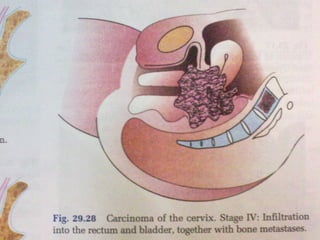
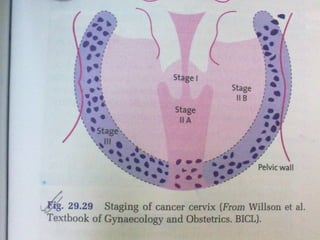
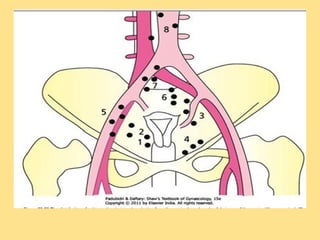
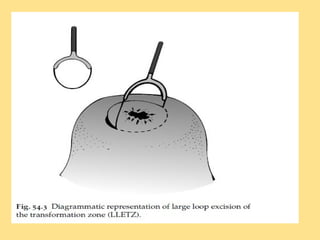
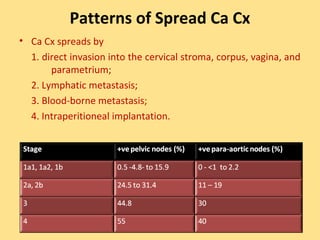
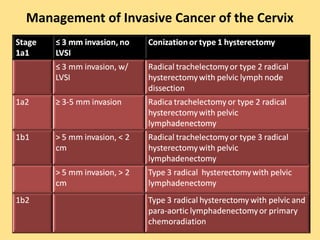
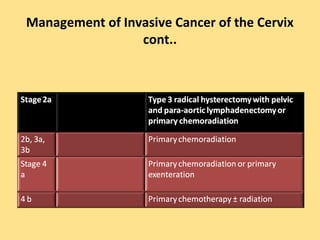
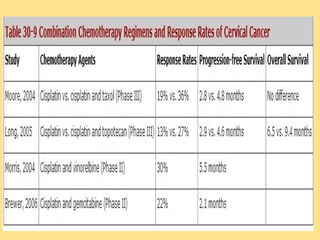
- Staging follows the FIGO system and determines prognosis and treatment. Surgery (e.g. radical hysterectomy), radiotherapy, and chemotherapy are common treatment options.
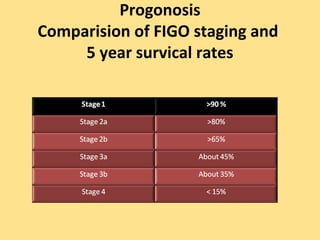
- Prognosis