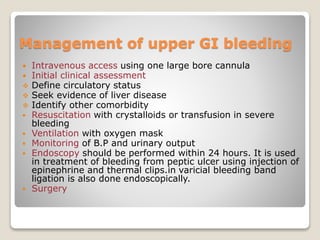
Upper GI tract bleeding can present with hematemesis (vomiting of blood) which resembles coffee grounds, indicating bleeding from the esophagus, stomach or duodenum. Common causes include peptic ulcers, esophageal varices, erosive gastritis, esophagitis, Mallory-Weiss syndrome, stomach cancer, and bleeding disorders. Peptic ulcers are caused by an increase in acid secretion or a decrease in mucosal resistance. Esophageal varices develop due to portal hypertension from liver cirrhosis. Management of upper GI bleeding involves intravenous fluids, monitoring, and endoscopy within 24 hours to control bleeding.