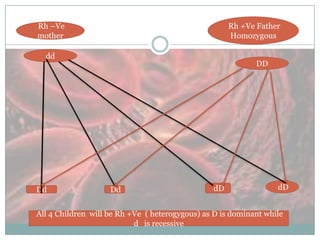
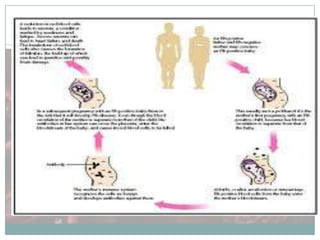
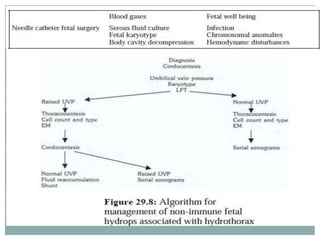
This document discusses immune and non-immune hydrops fetalis. It begins by defining hydrops fetalis as generalized fetal edema that can be detected on ultrasound. It then describes the two subtypes - immune and non-immune. Immune hydrops is more common in developing countries and results from Rh sensitization of the mother from a Rh-positive fetus. Non-immune hydrops has more varied underlying causes and is more common in developed countries. The document goes on to discuss the mechanisms, investigations, management and complications of both immune and non-immune hydrops fetalis.