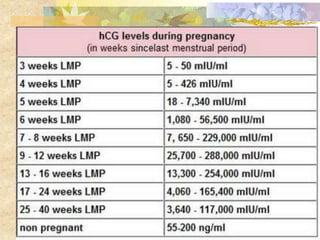
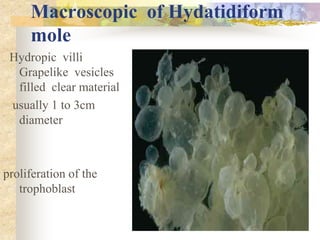
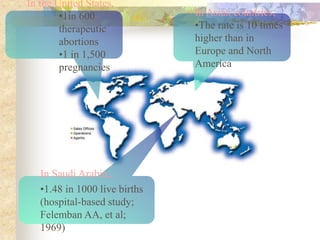
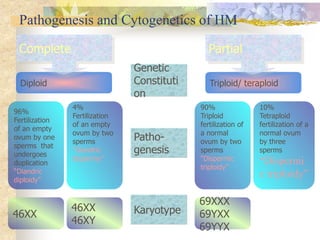
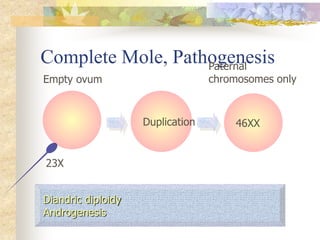
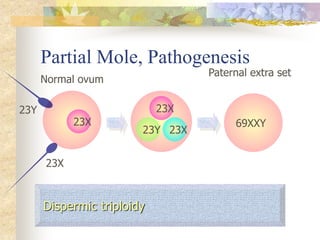
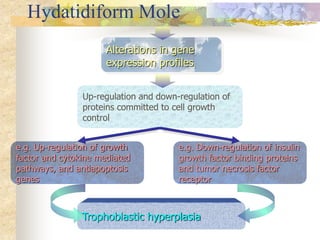
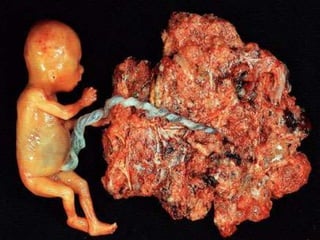
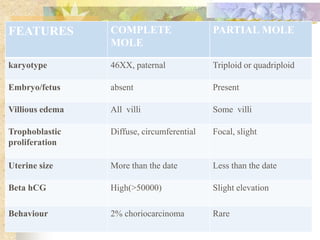
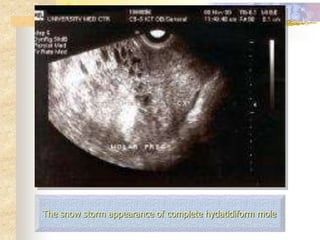
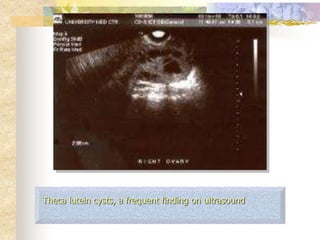
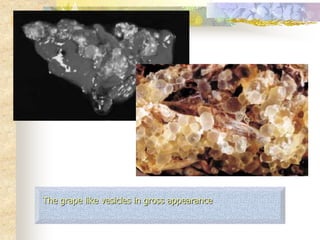
This document discusses molar pregnancy, also known as hydatidiform mole. It begins by classifying gestational trophoblastic disease as either benign, premalignant, or malignant. It then discusses the characteristics of complete and partial moles. Complete moles have no fetal tissue and are caused by fertilization of an empty ovum, while partial moles contain some fetal tissue and are usually triploid. Symptoms of a complete mole include vaginal bleeding, hyperemesis gravidarum, and a uterus larger than dates. Diagnosis involves ultrasound showing a "snowstorm" pattern, elevated hCG levels, and pathological examination of tissue. Complications can include theca-lutein cysts, pre