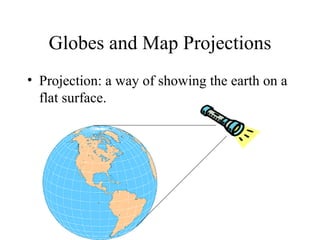
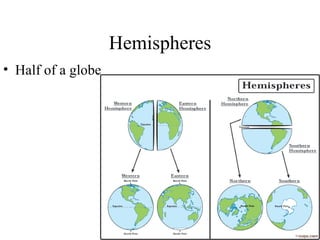
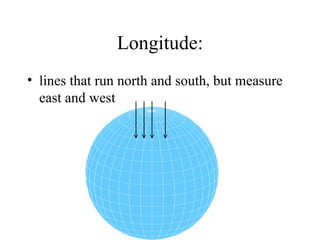
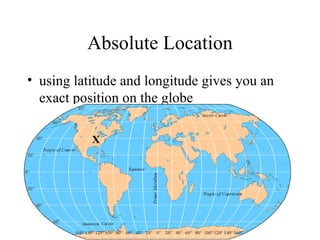
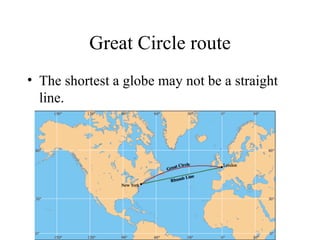
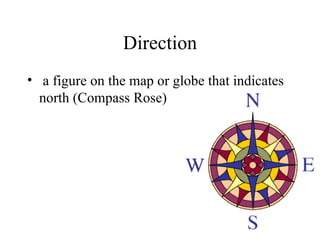
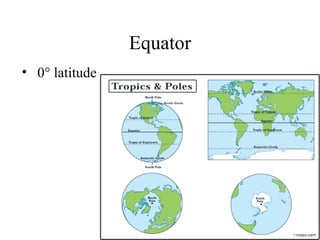
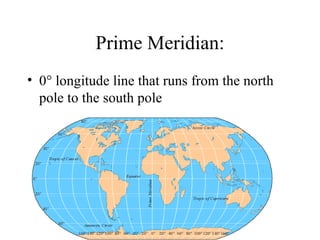
There are several types of map projections that are used to represent the spherical Earth on a flat surface. All map projections involve some degree of distortion of shapes, sizes, or distances. The Mercator projection increasingly distorts distances the farther one moves from the equator, while the Robinson and Goode's interrupted projections aim to minimize distortion of landmasses. Other map features discussed include hemispheres, latitude and longitude grid systems, directions, scales, and different types of thematic maps.