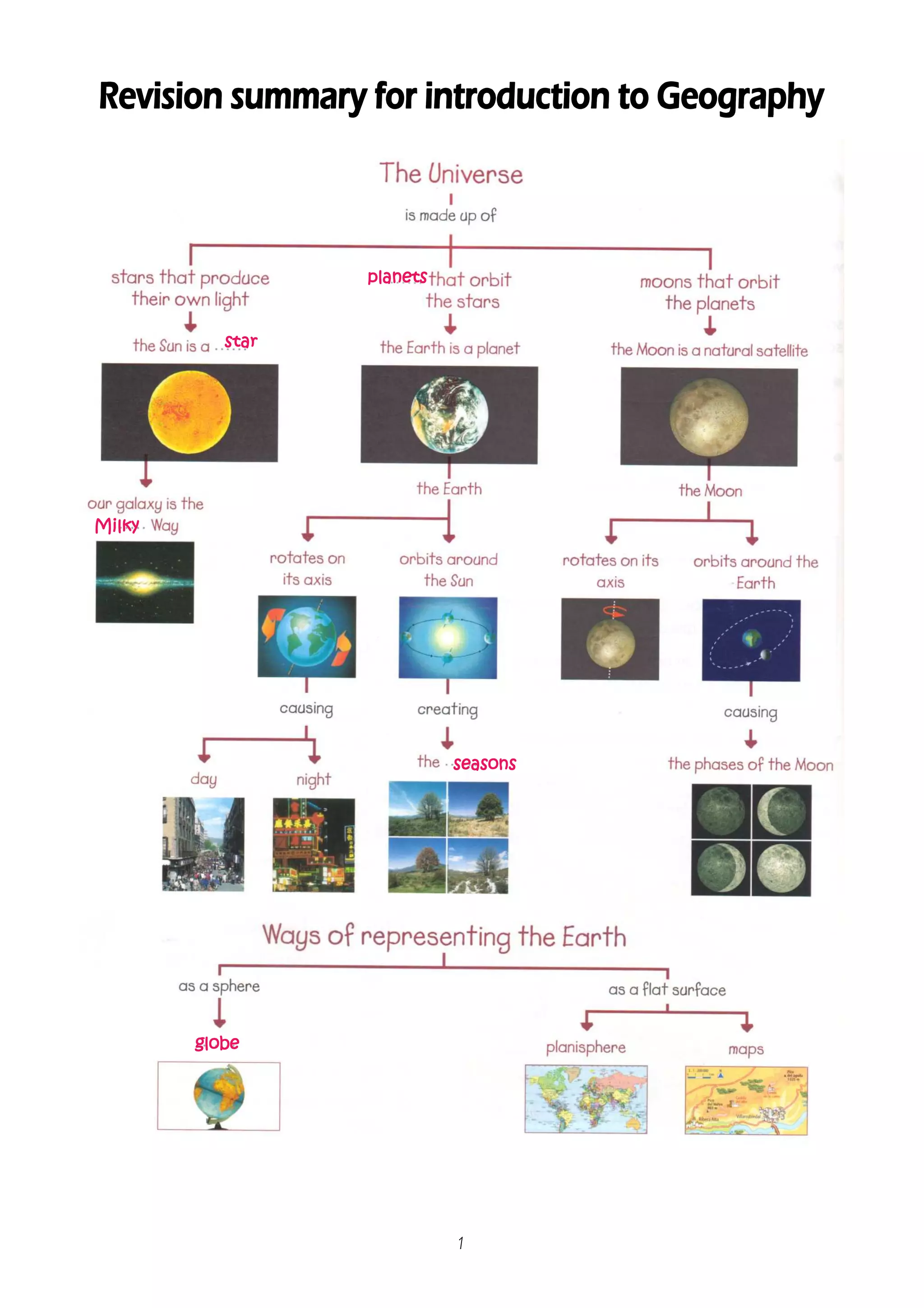
The document discusses key concepts about maps including:
1) Maps use imaginary lines like latitude and longitude to show locations on Earth's surface.
2) The Earth rotates on its axis and orbits the sun, causing seasons and different amounts of sunlight in each hemisphere.
3) Maps are 2D representations of the 3D Earth, so various projections are used to depict its surface on a flat plane. Scale, symbols, and other elements help readers understand maps.