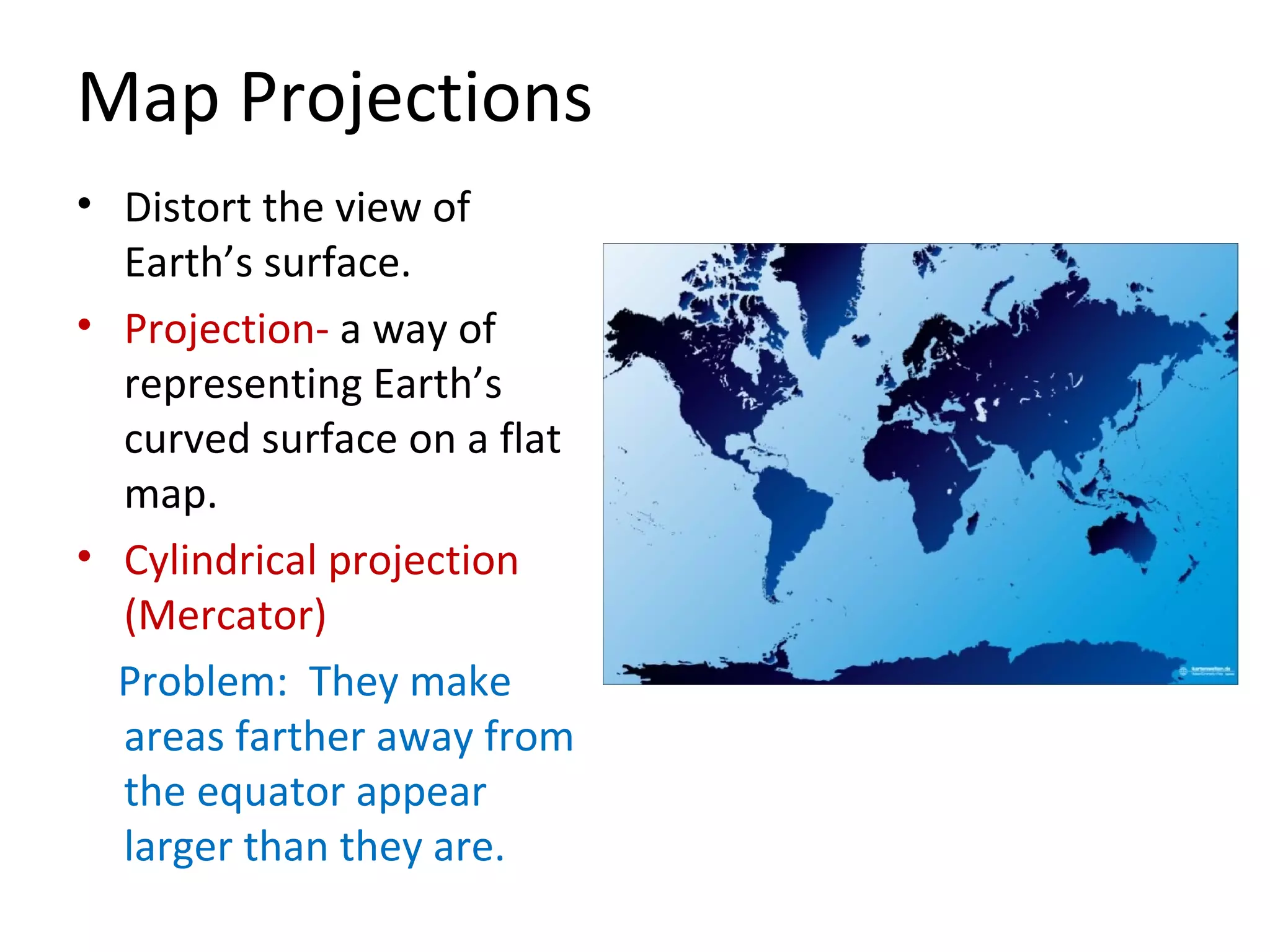
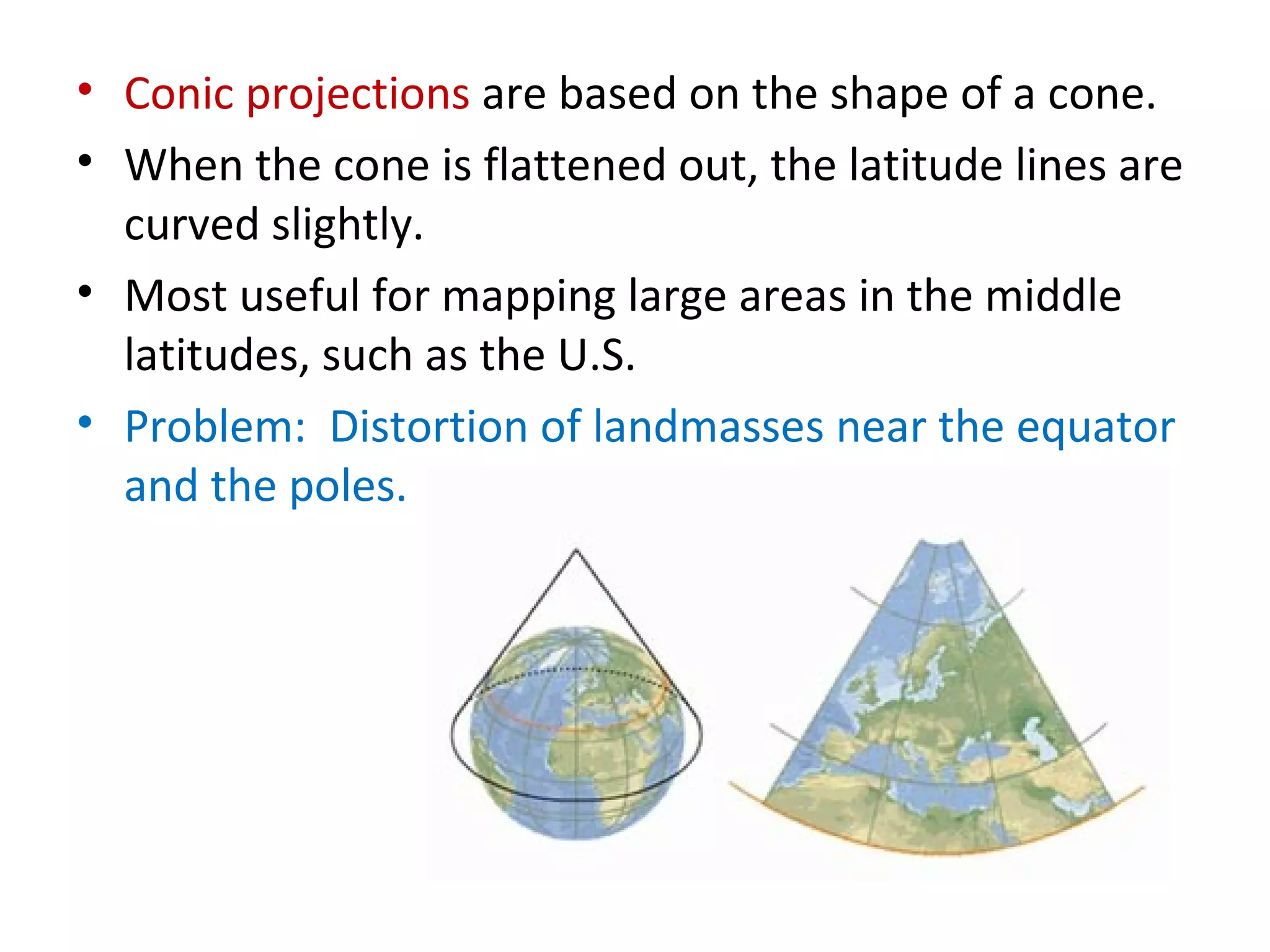
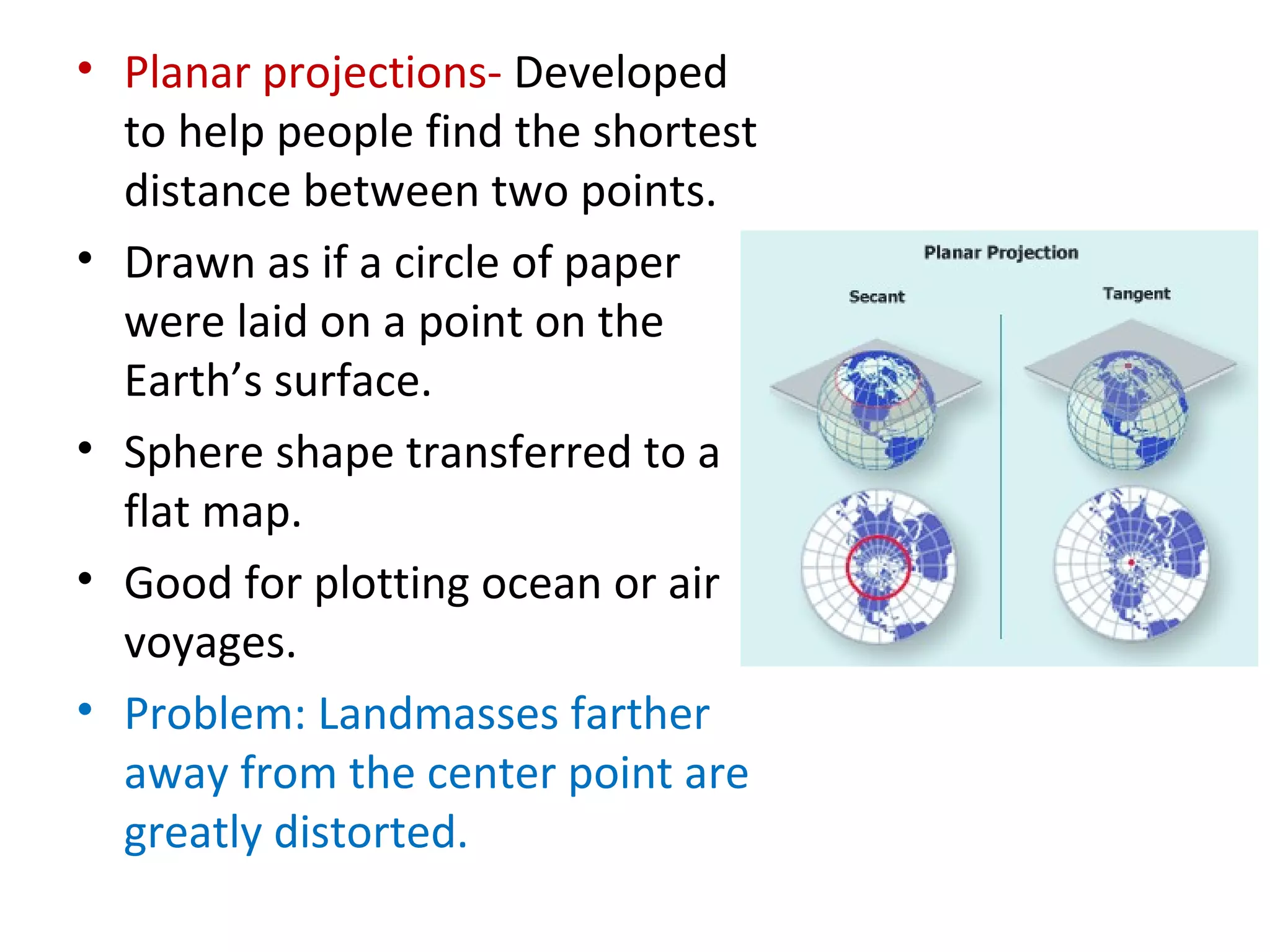
1. Maps and globes are models that represent features on Earth's surface. Maps show natural and human features from an above view, while globes show Earth as seen from space with accurate sizes and shapes.
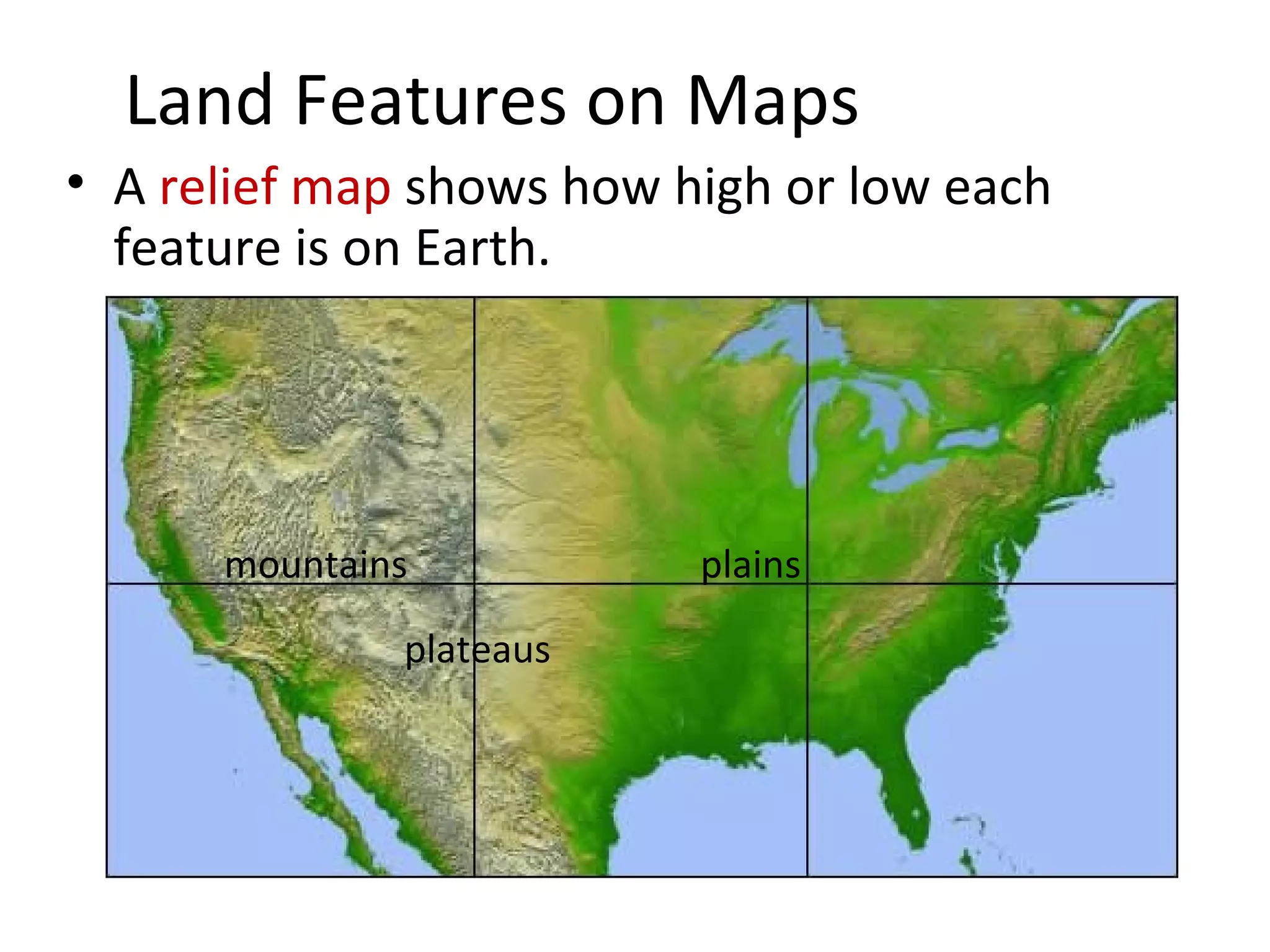
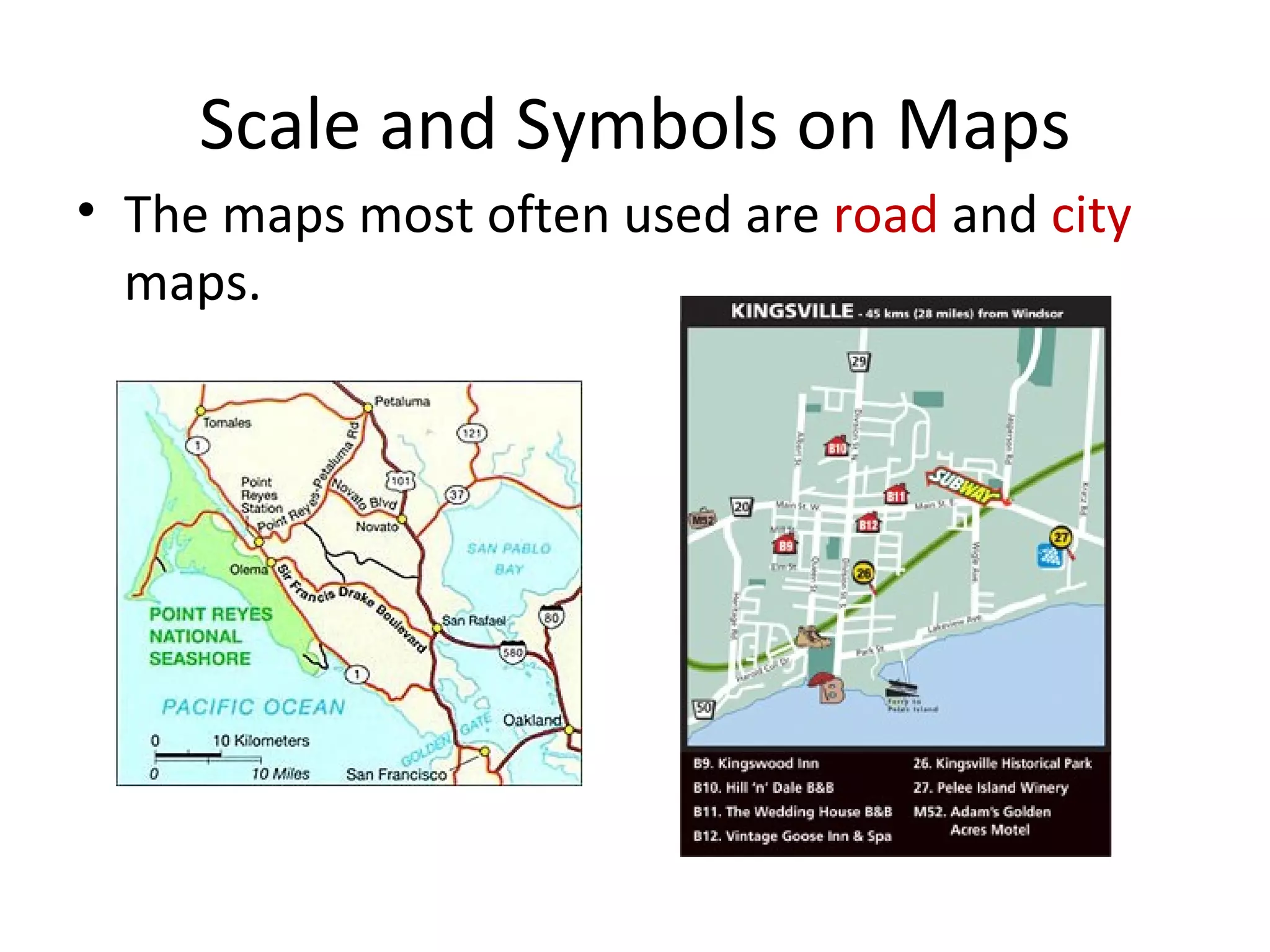
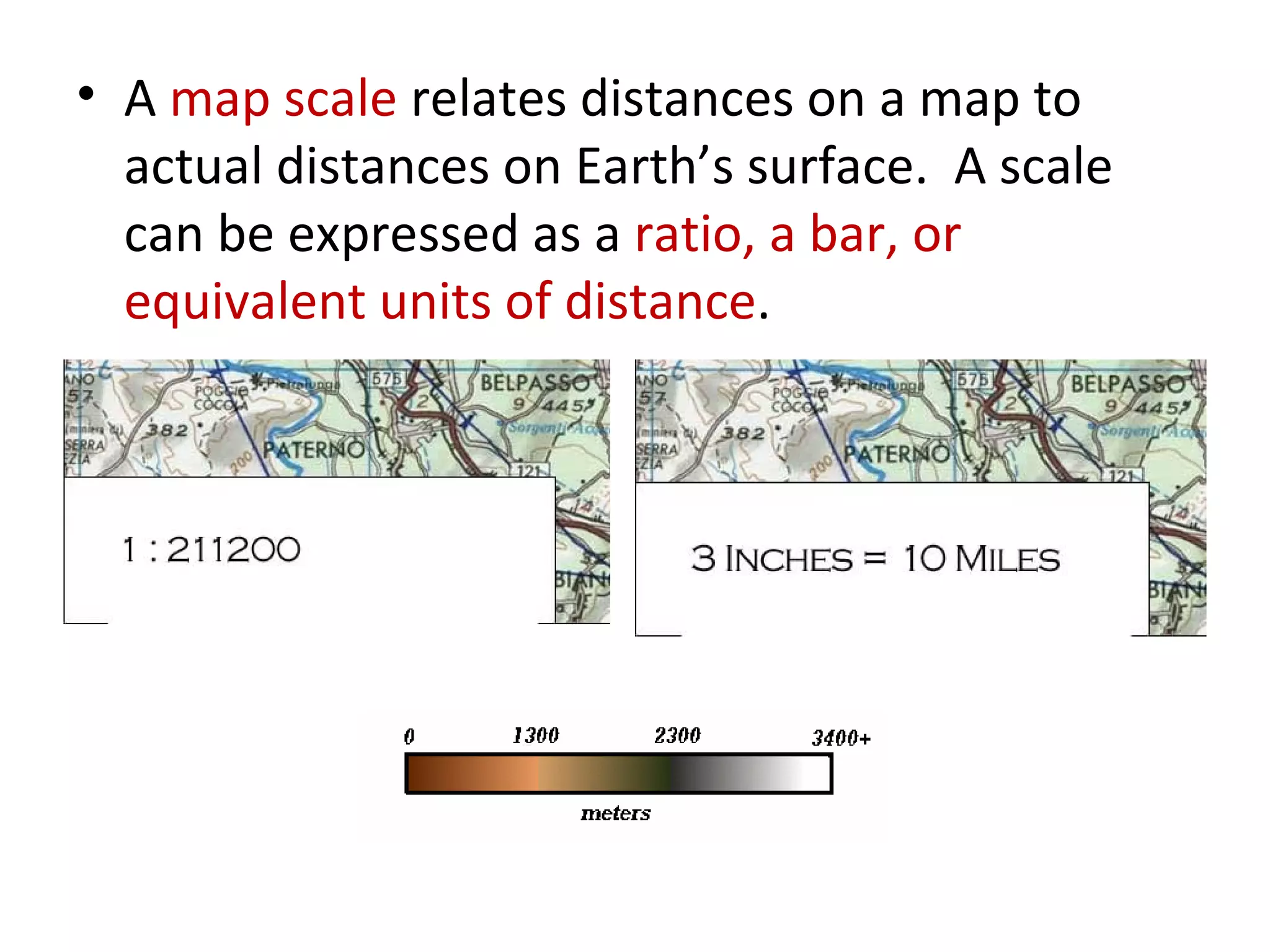
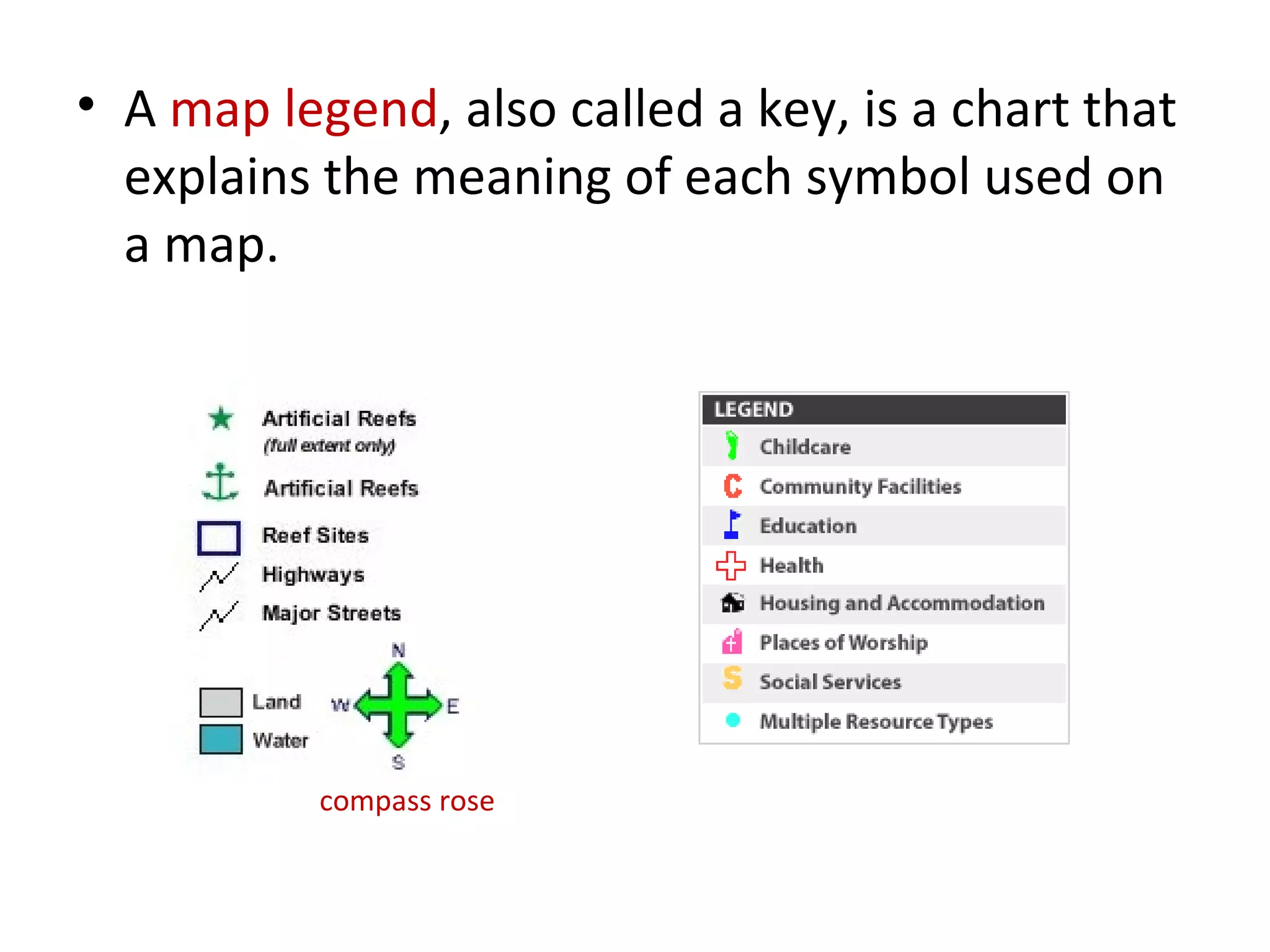
2. Maps use symbols to indicate different land features such as mountains, plateaus, and plains. They also use scales and legends to relate distances on maps to actual distances and explain symbols.
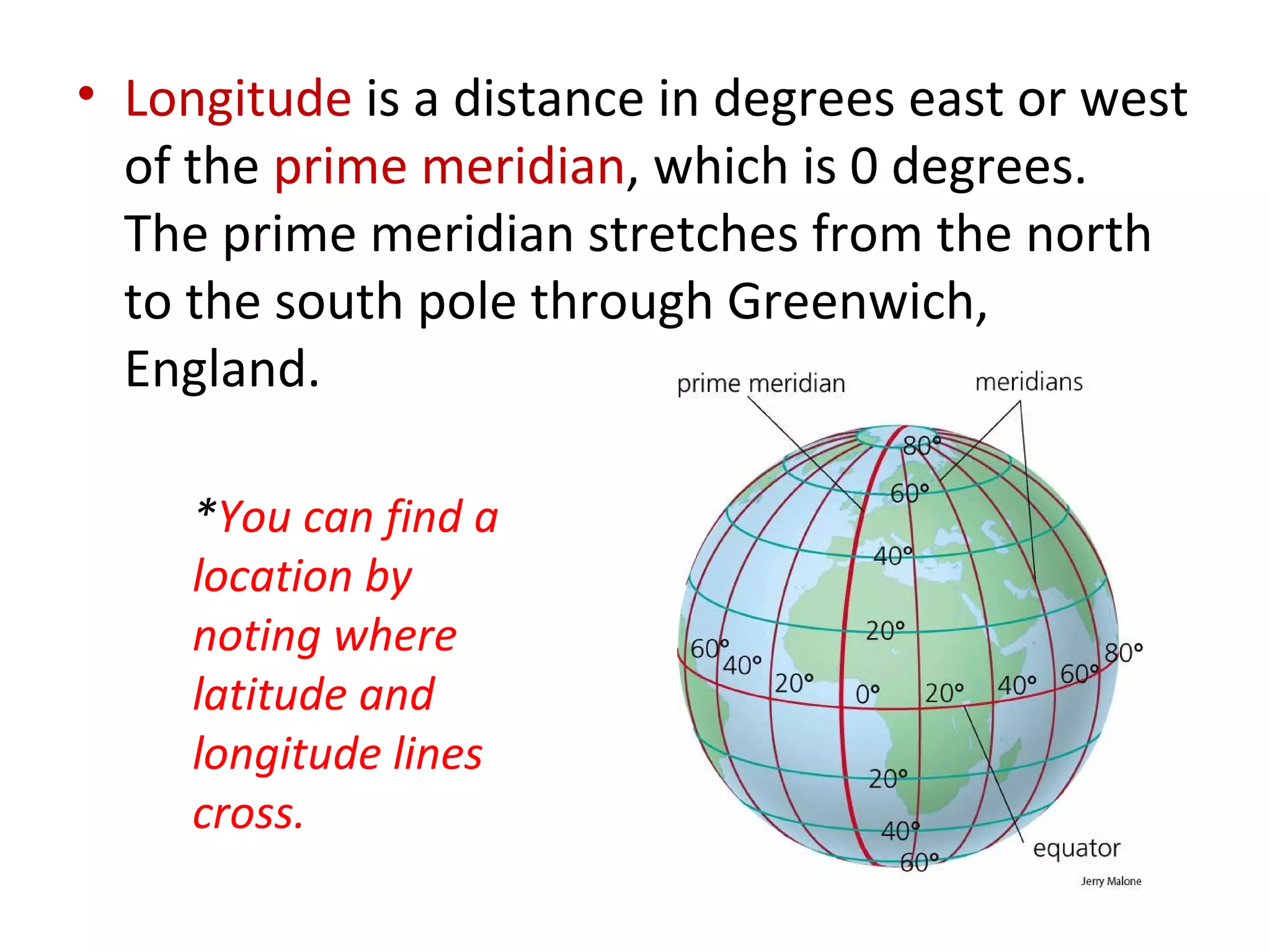
3. Latitude and longitude lines are used to locate positions on Earth, with latitude measuring distances north and south of the equator and longitude measuring distances east and west of the prime meridian.