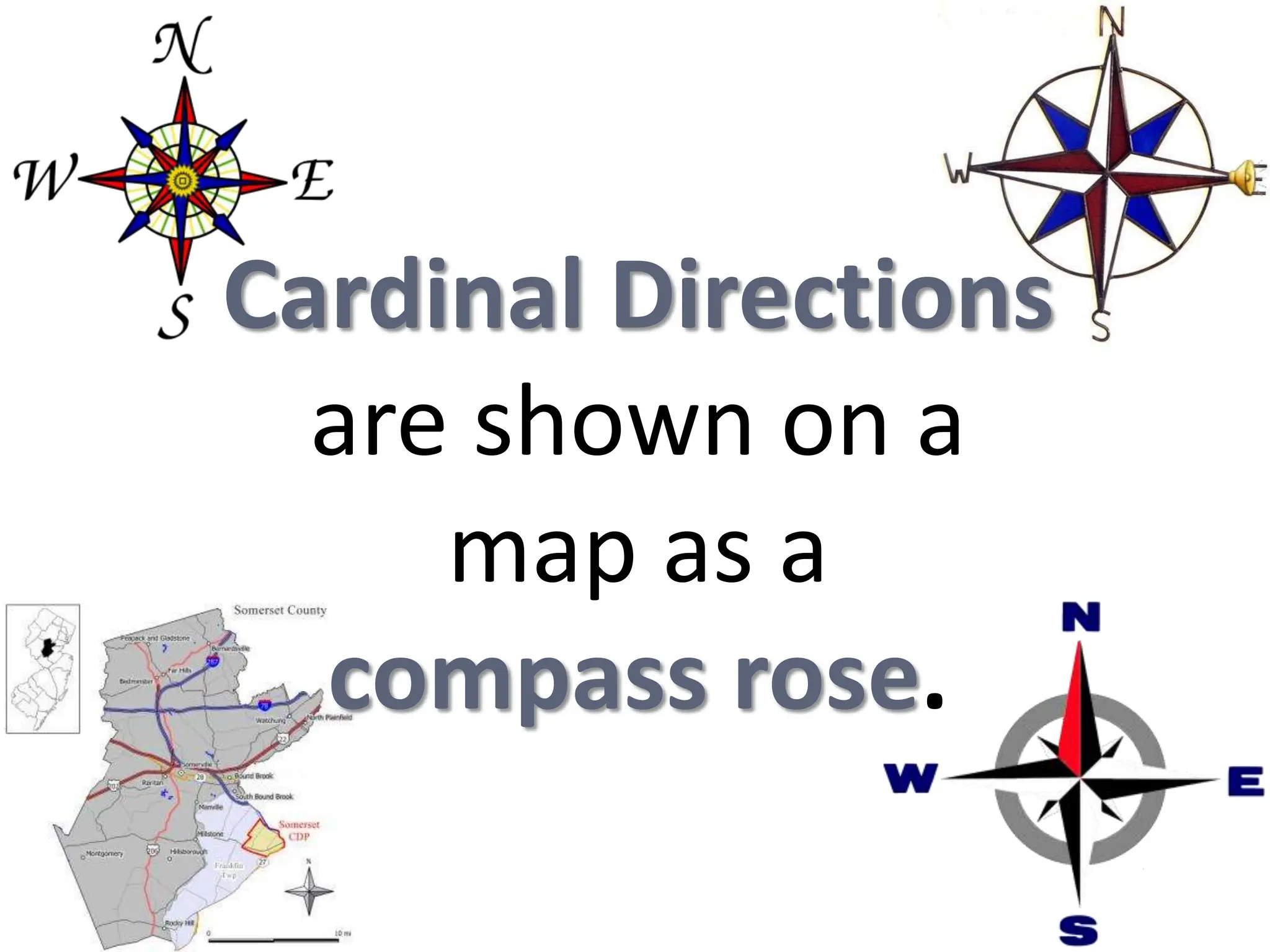
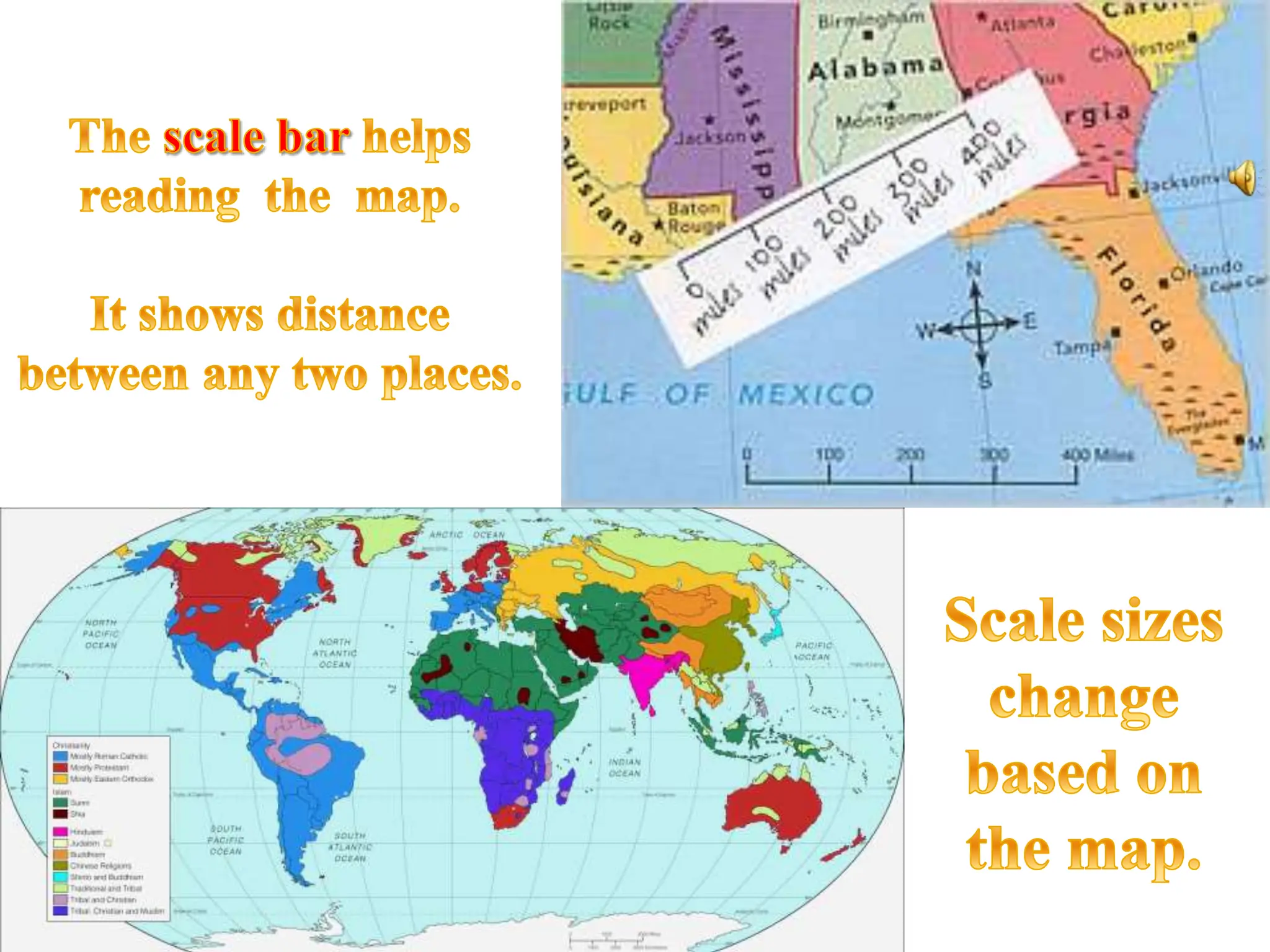
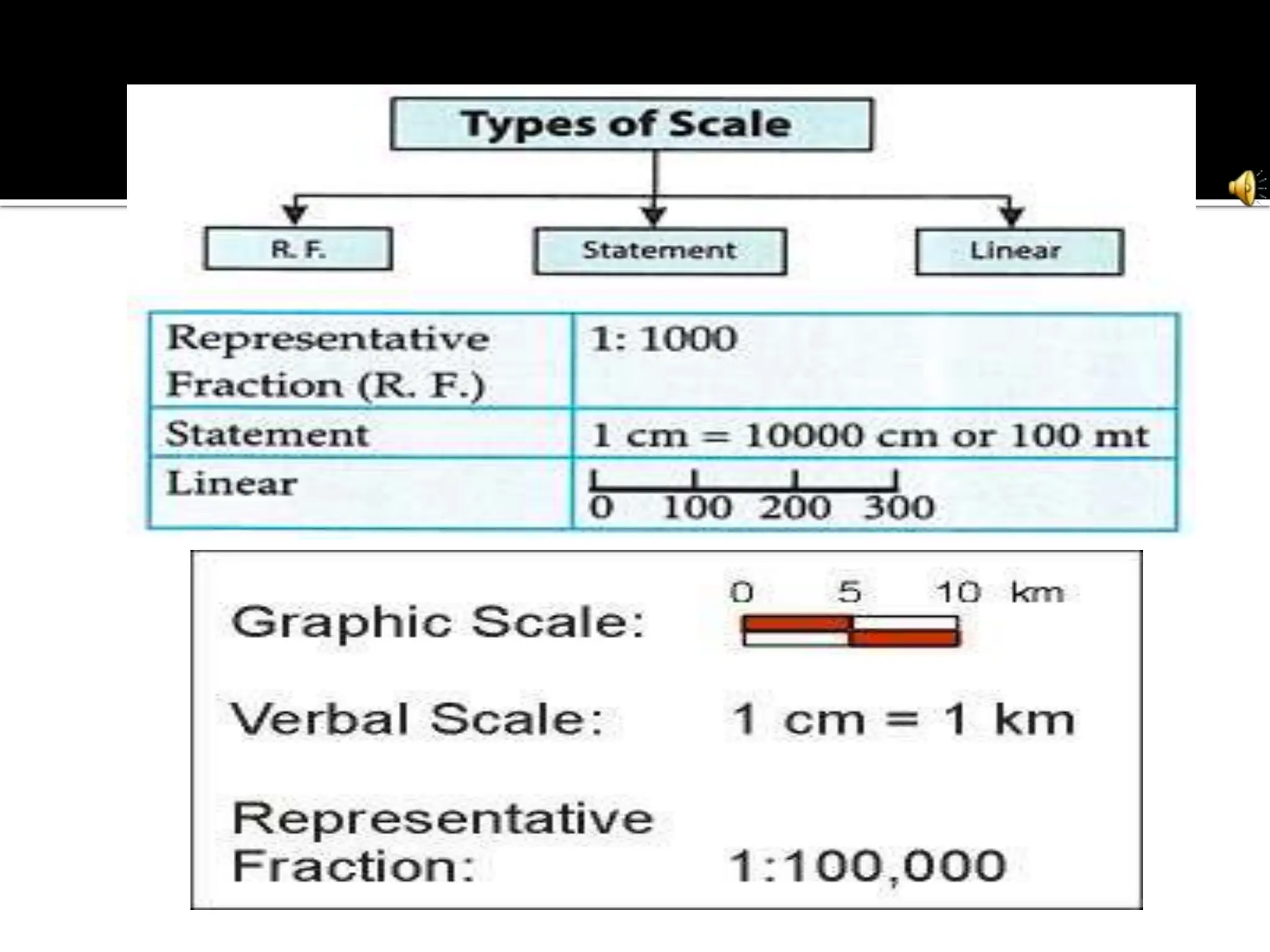
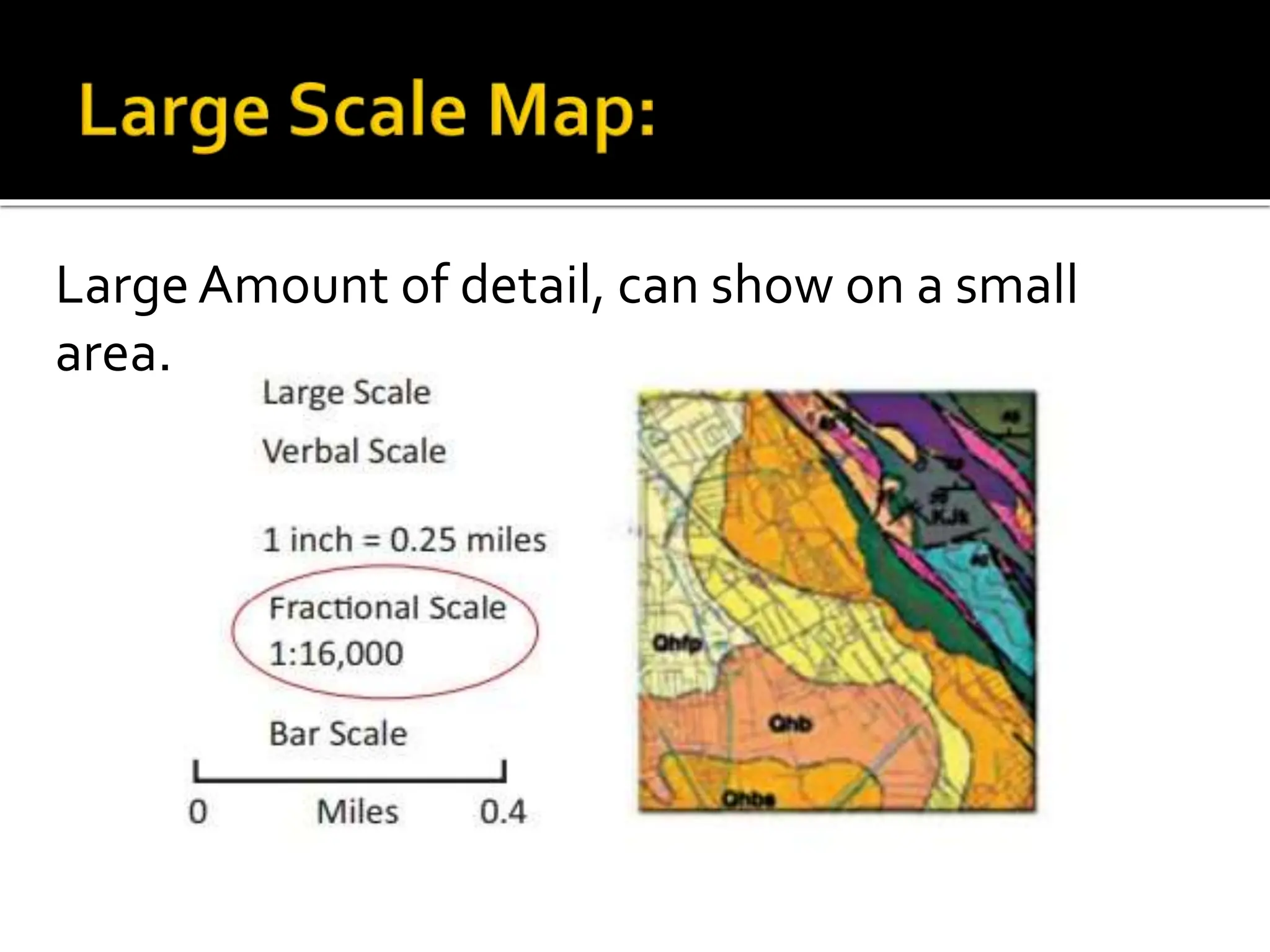
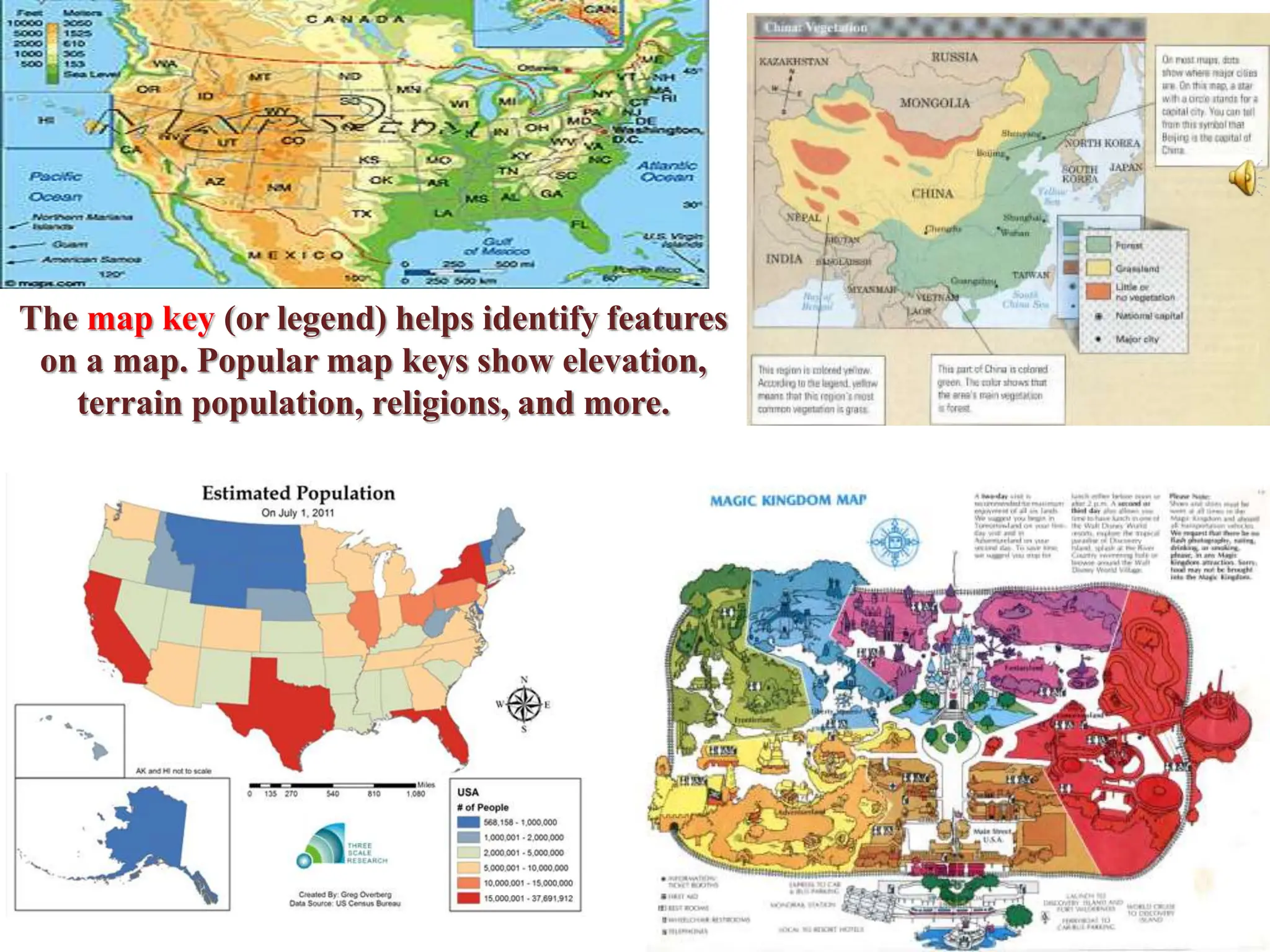
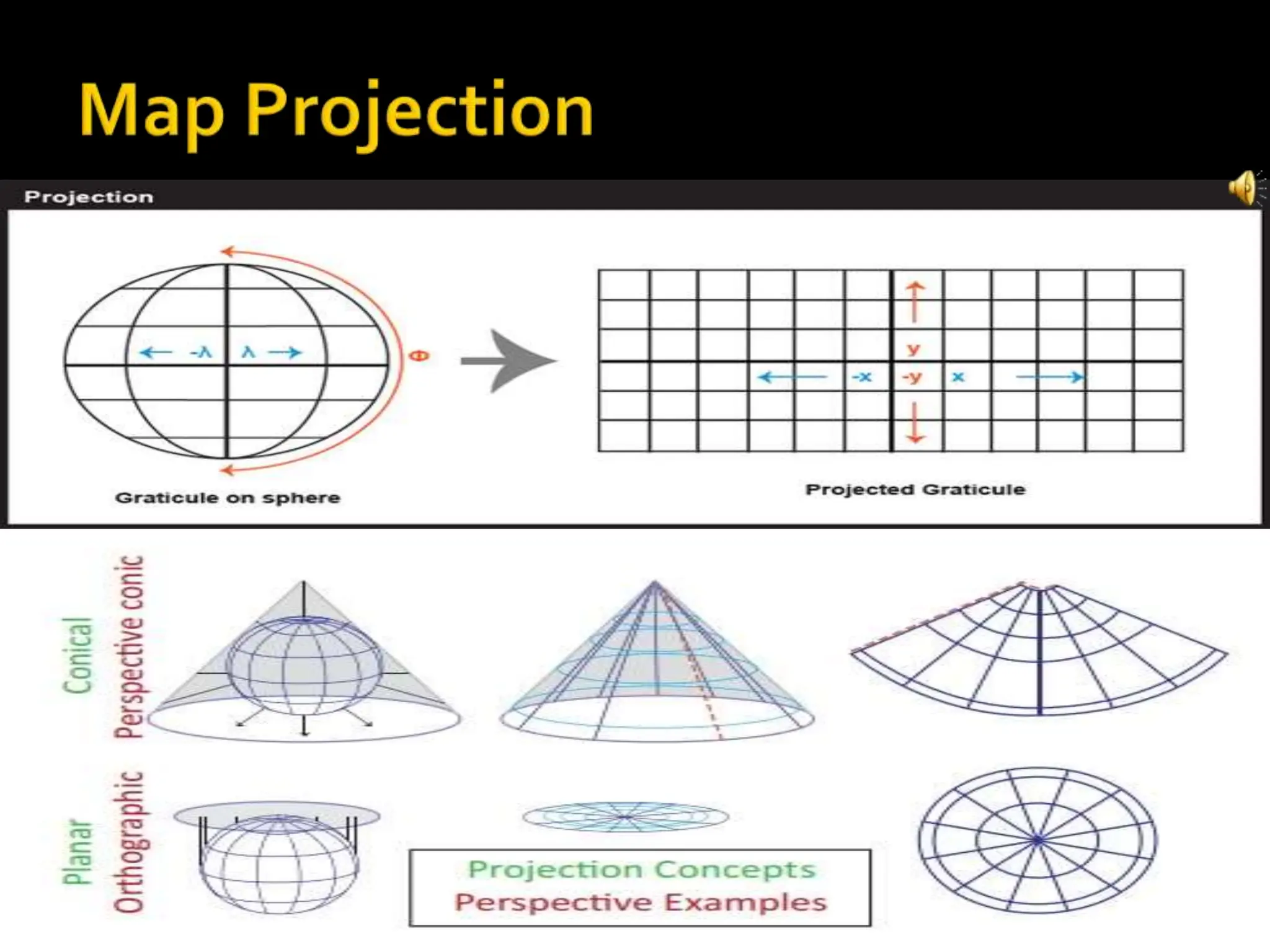
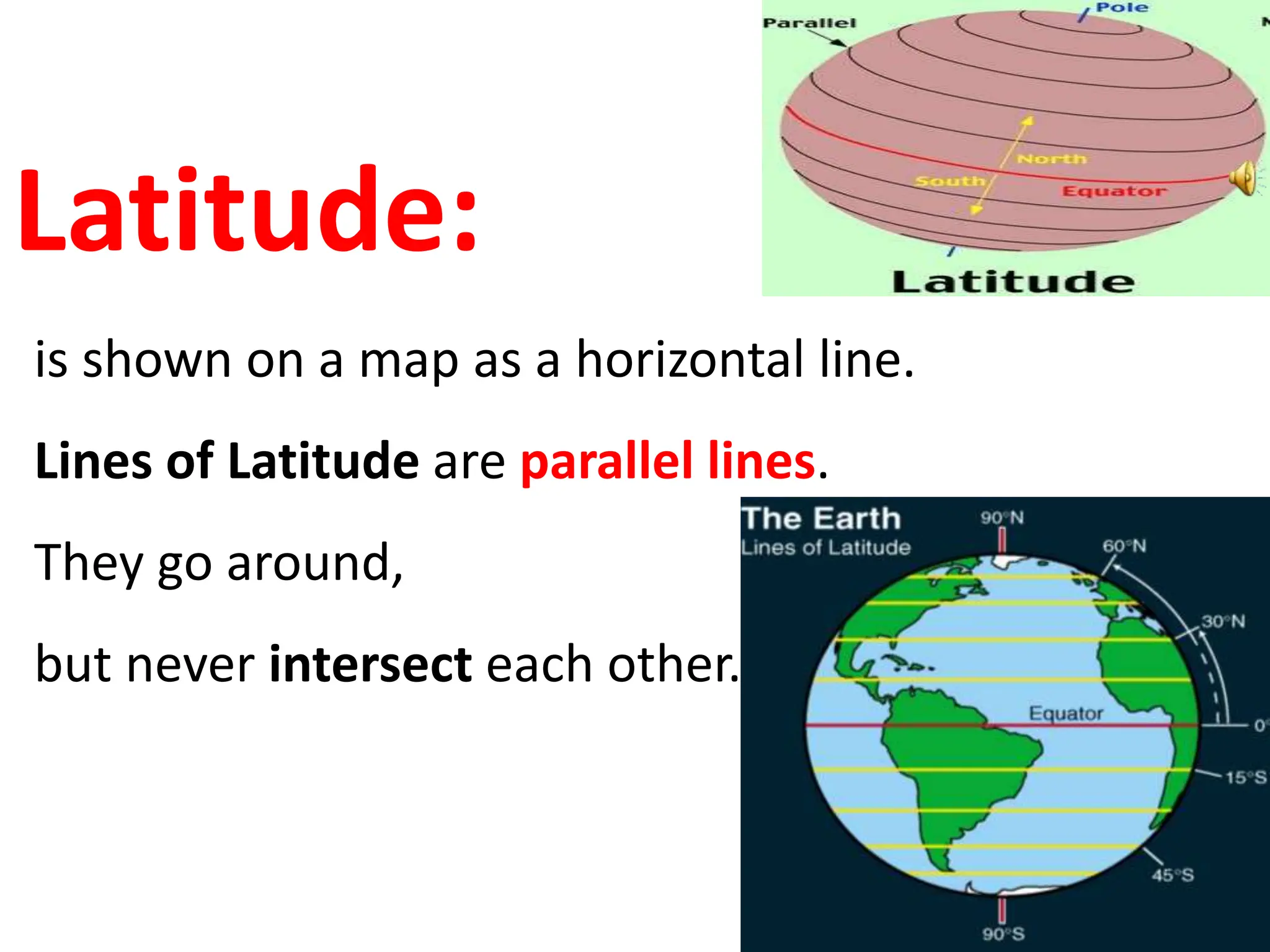
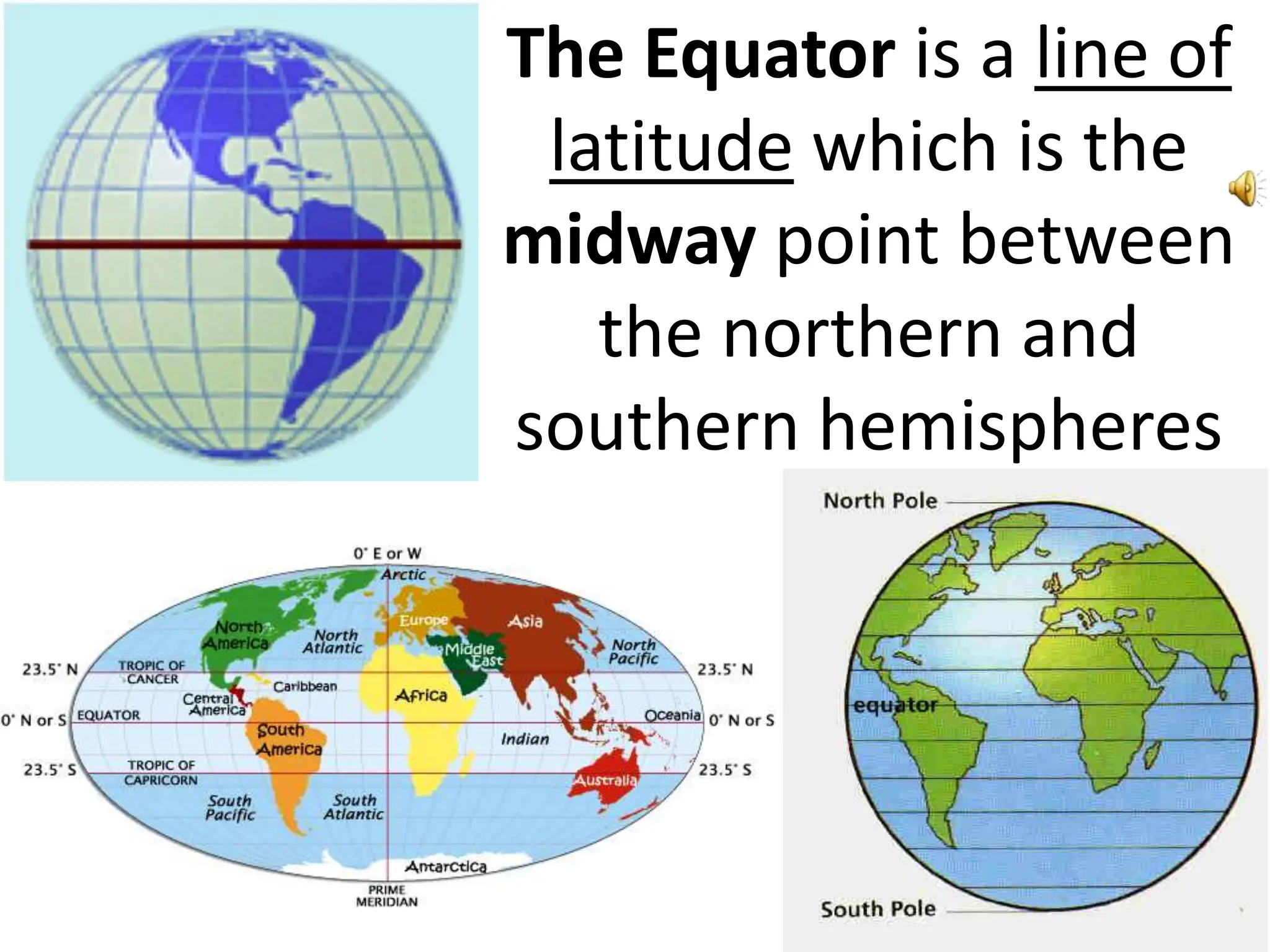
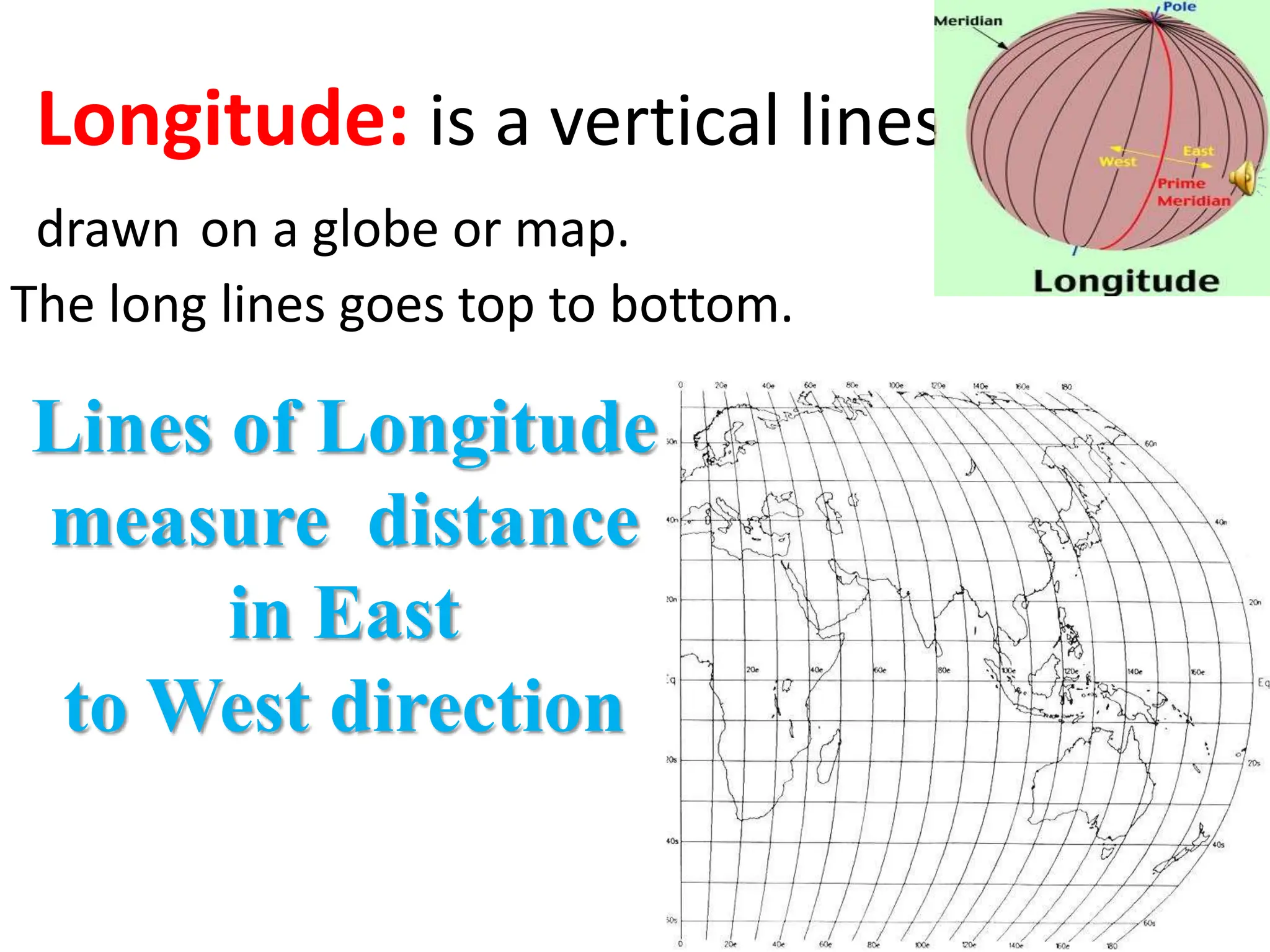
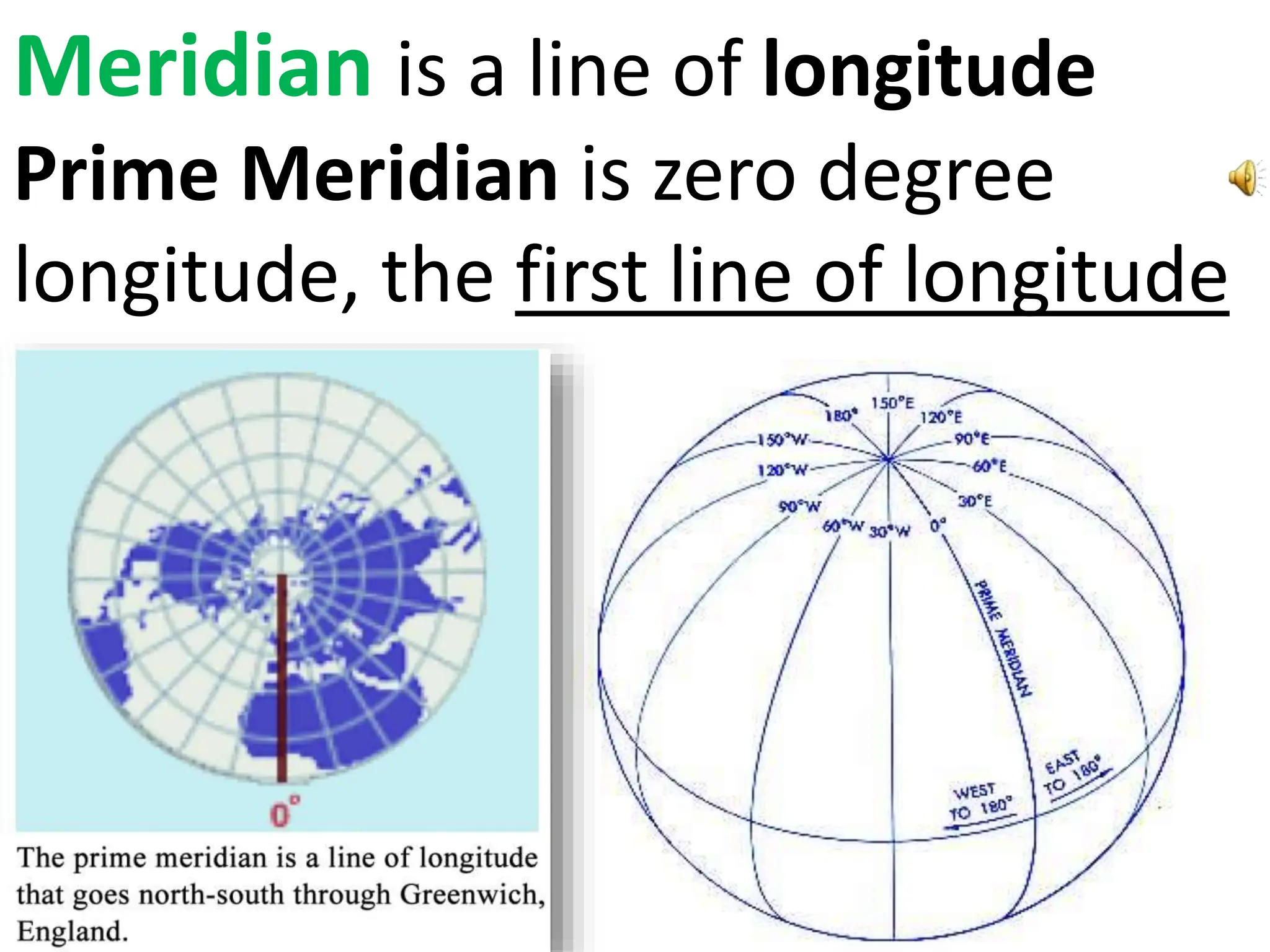
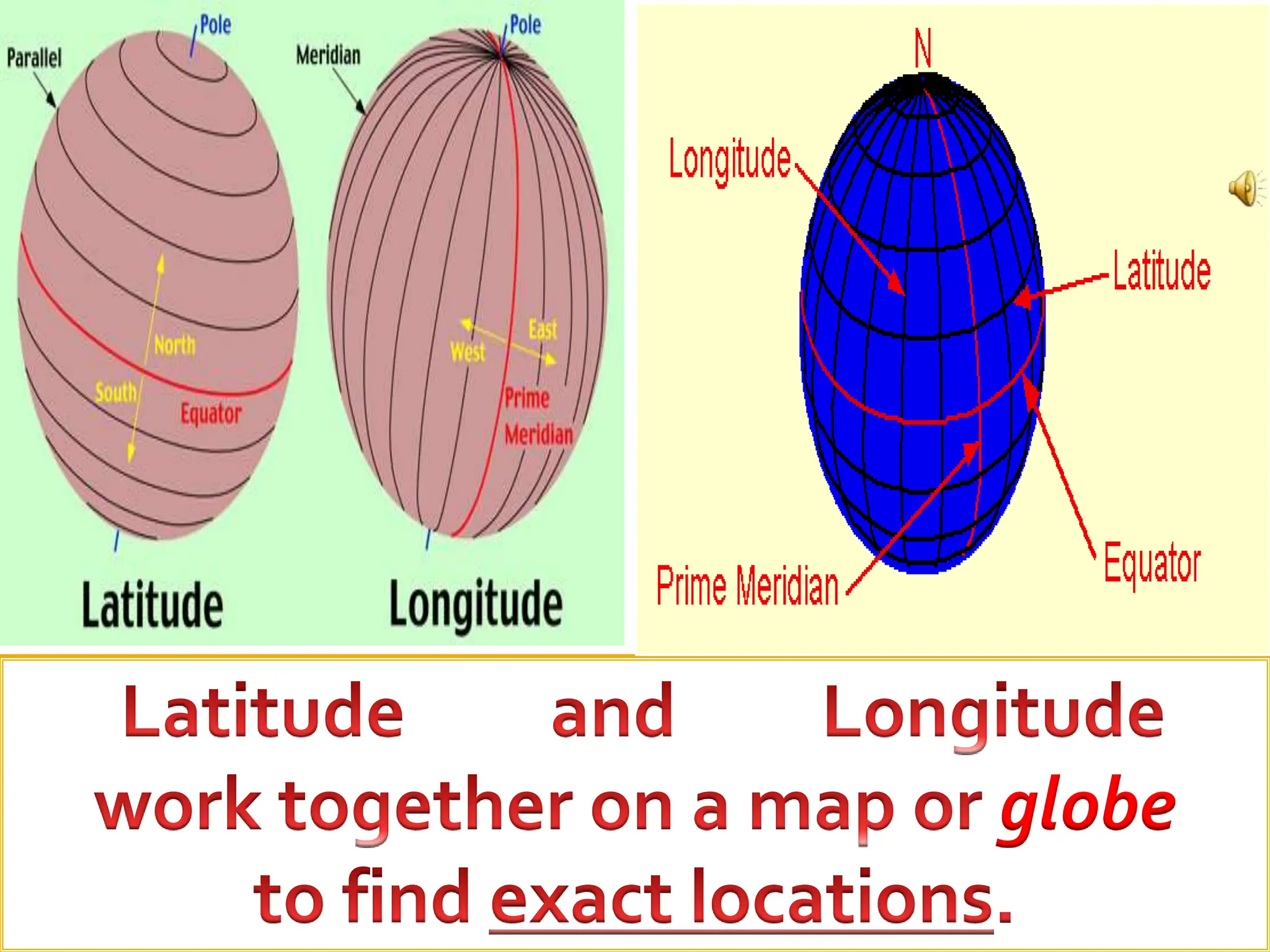
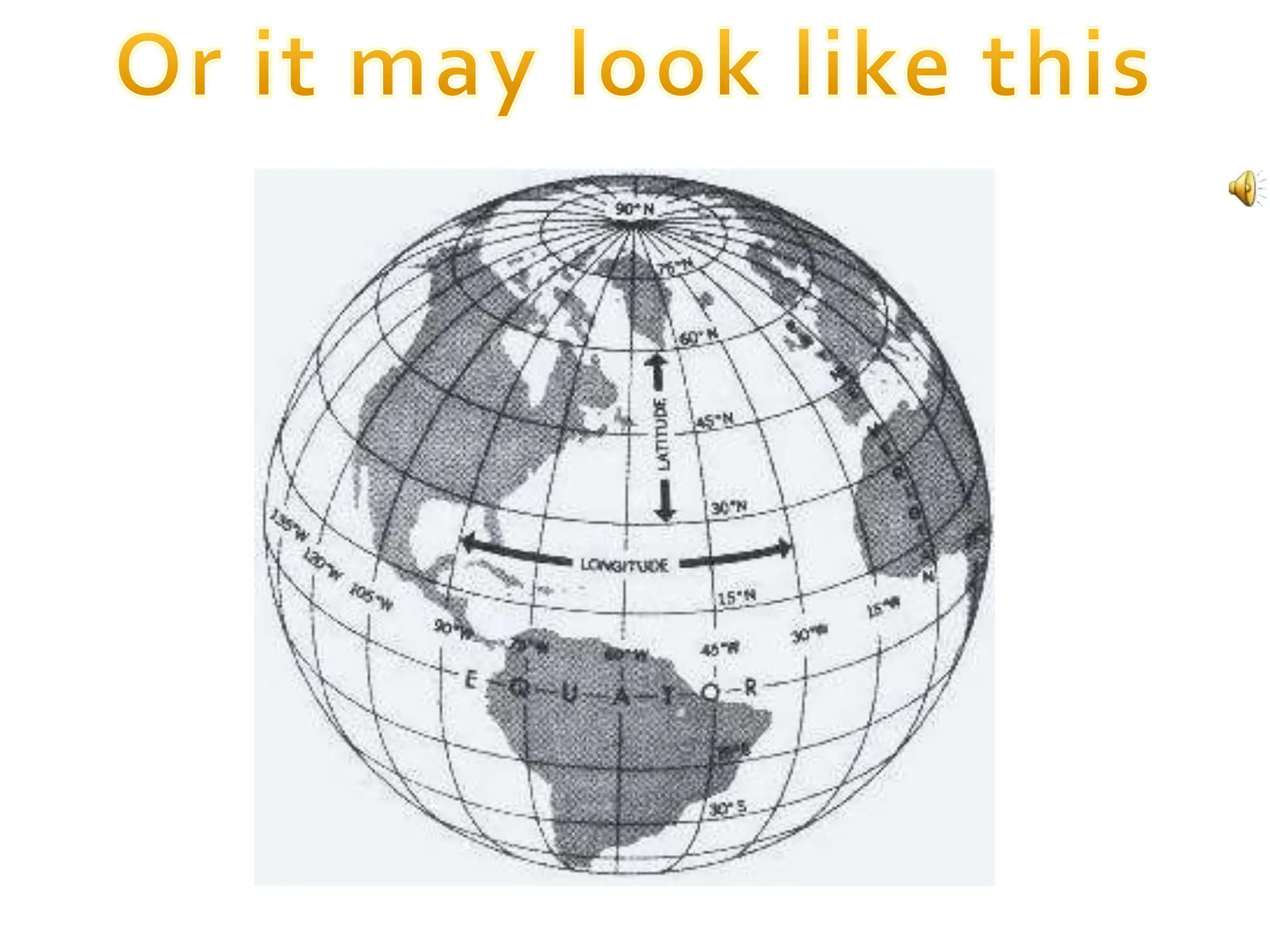
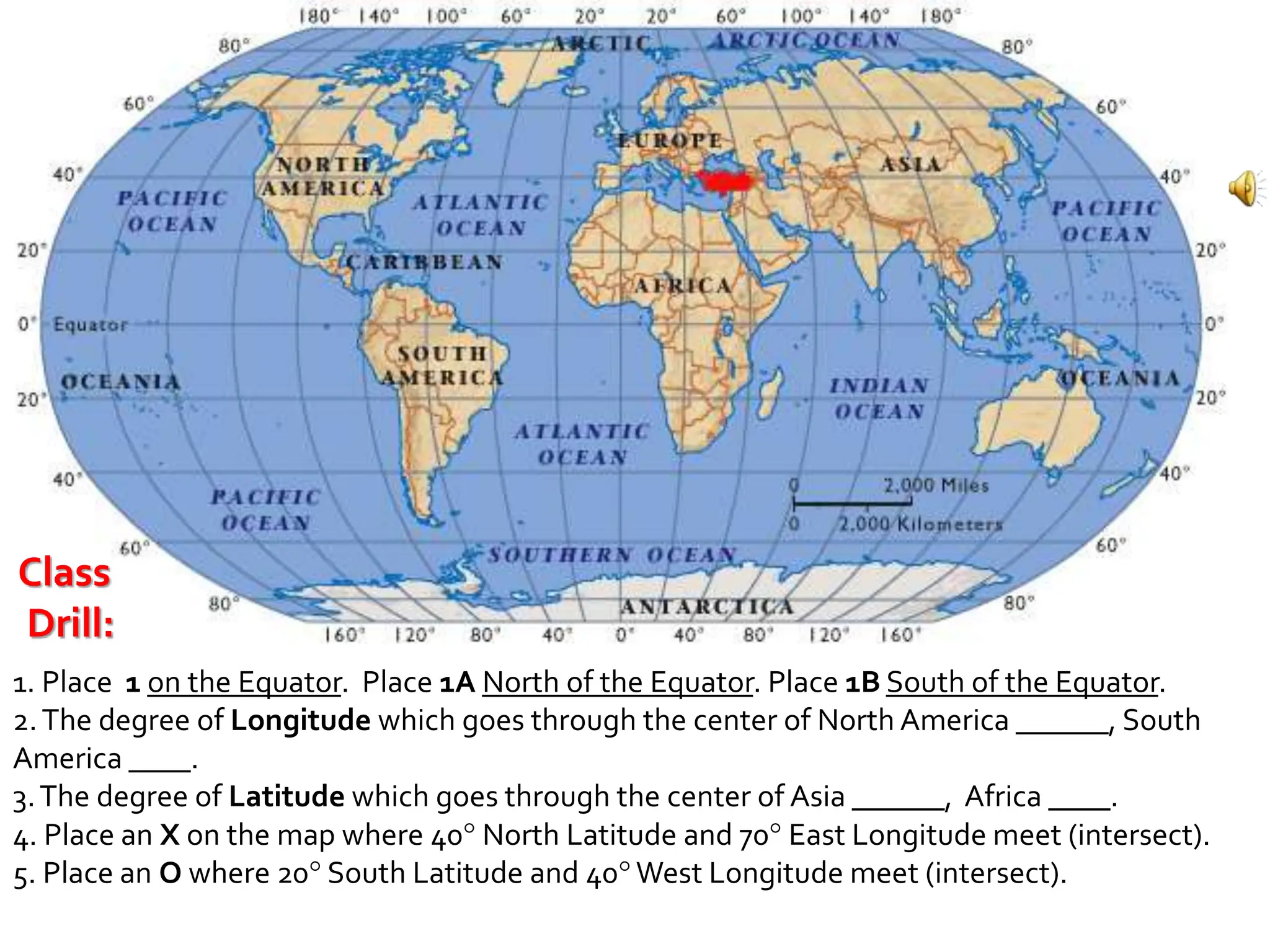
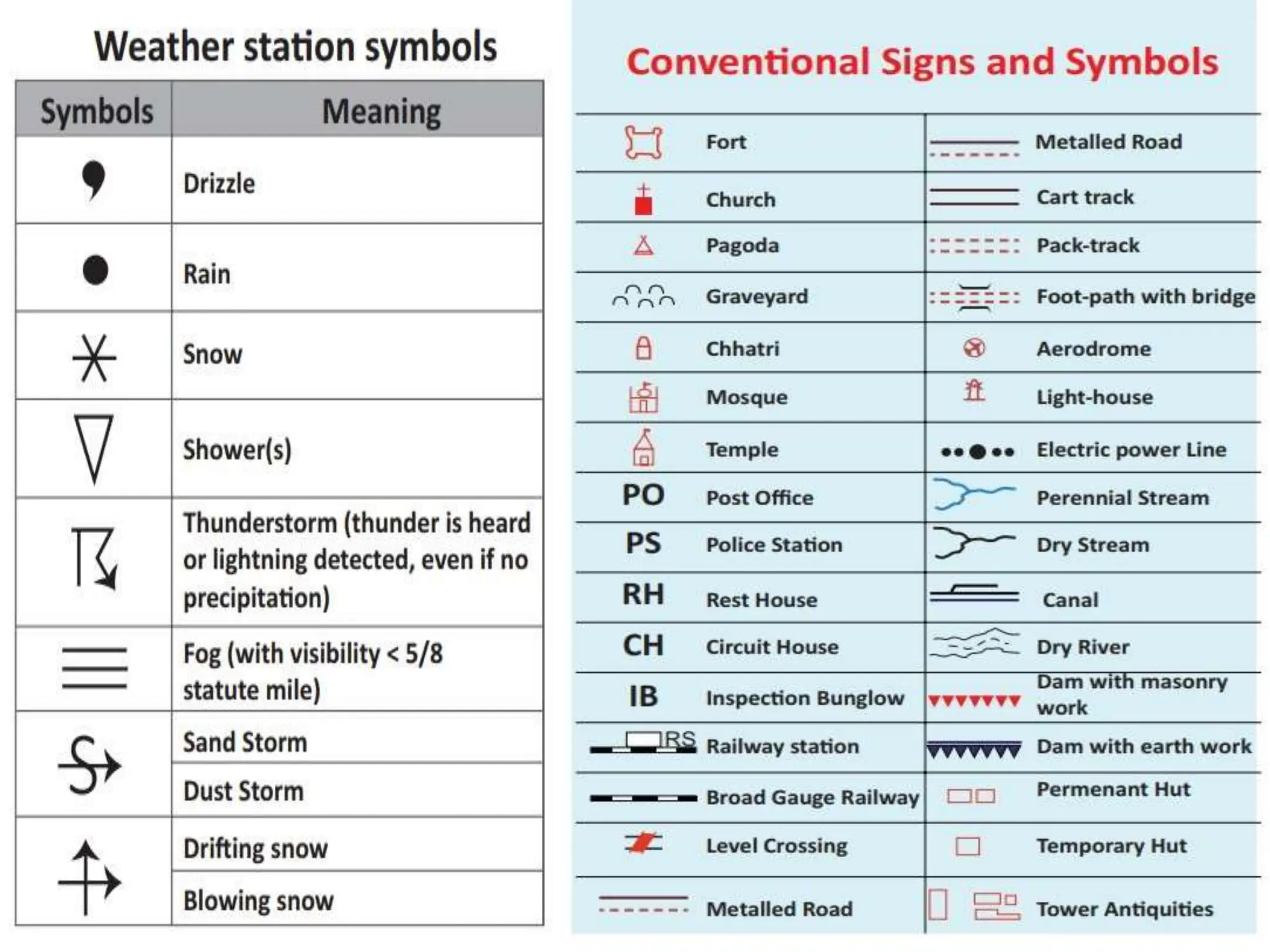
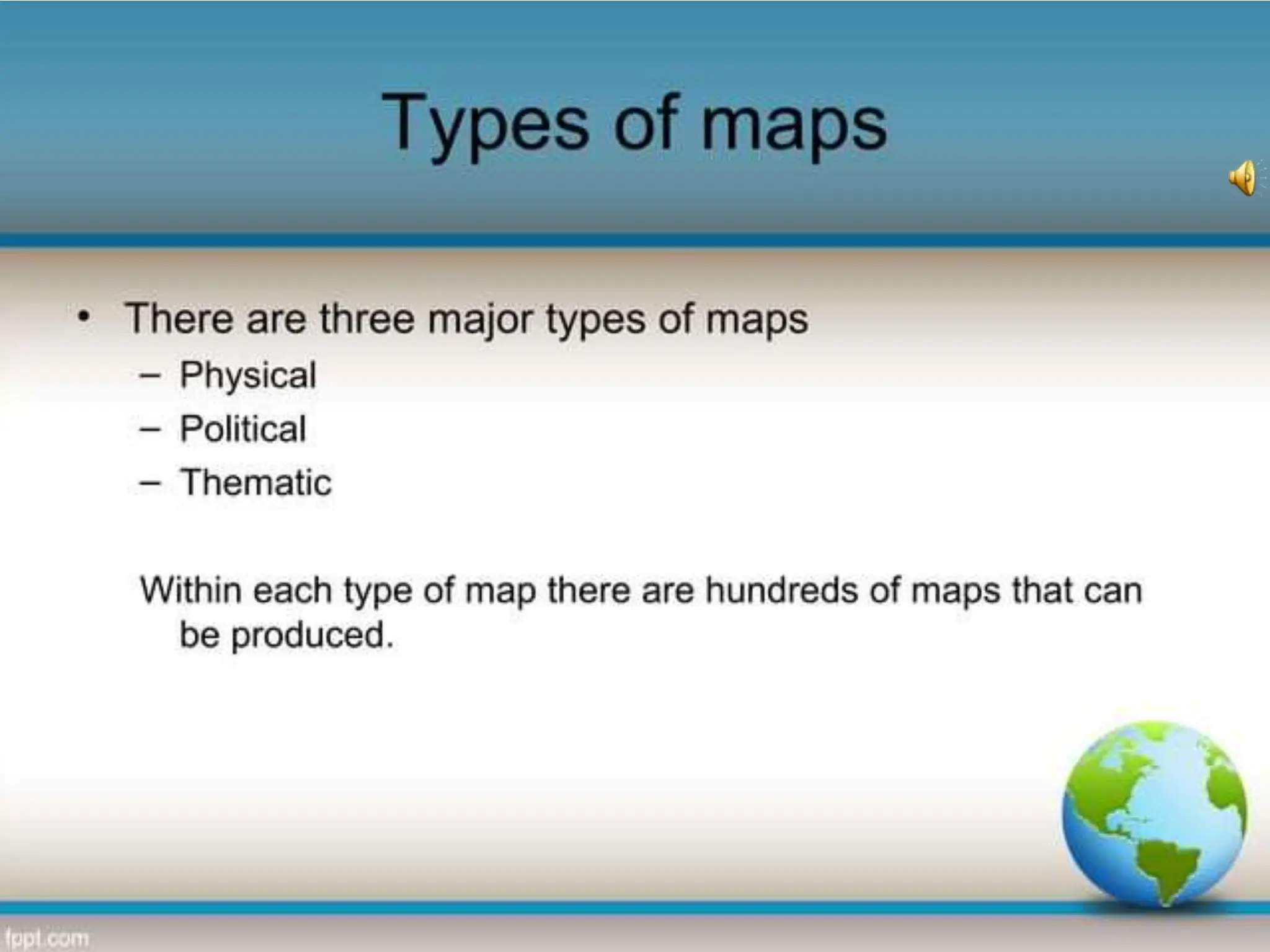
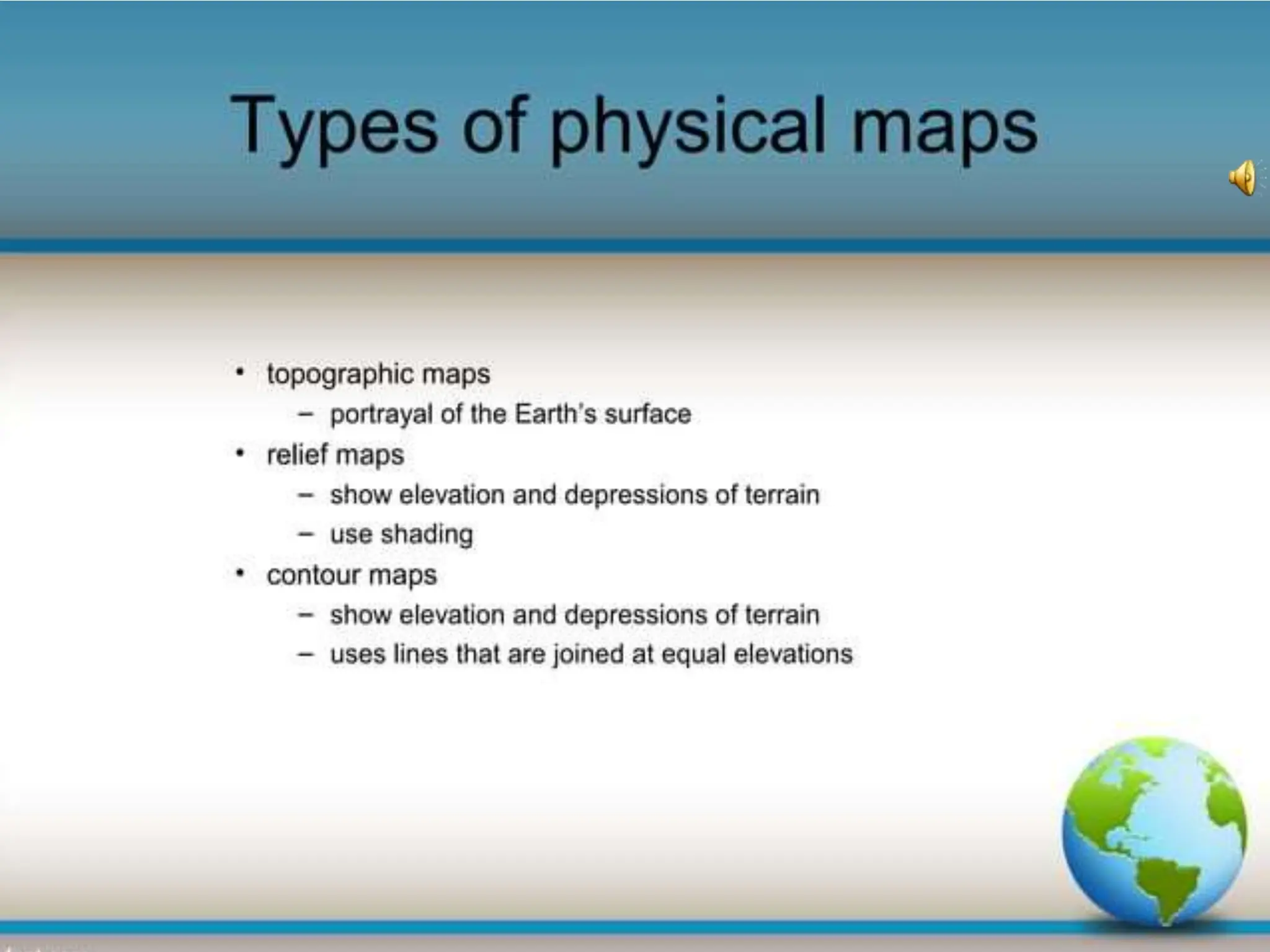
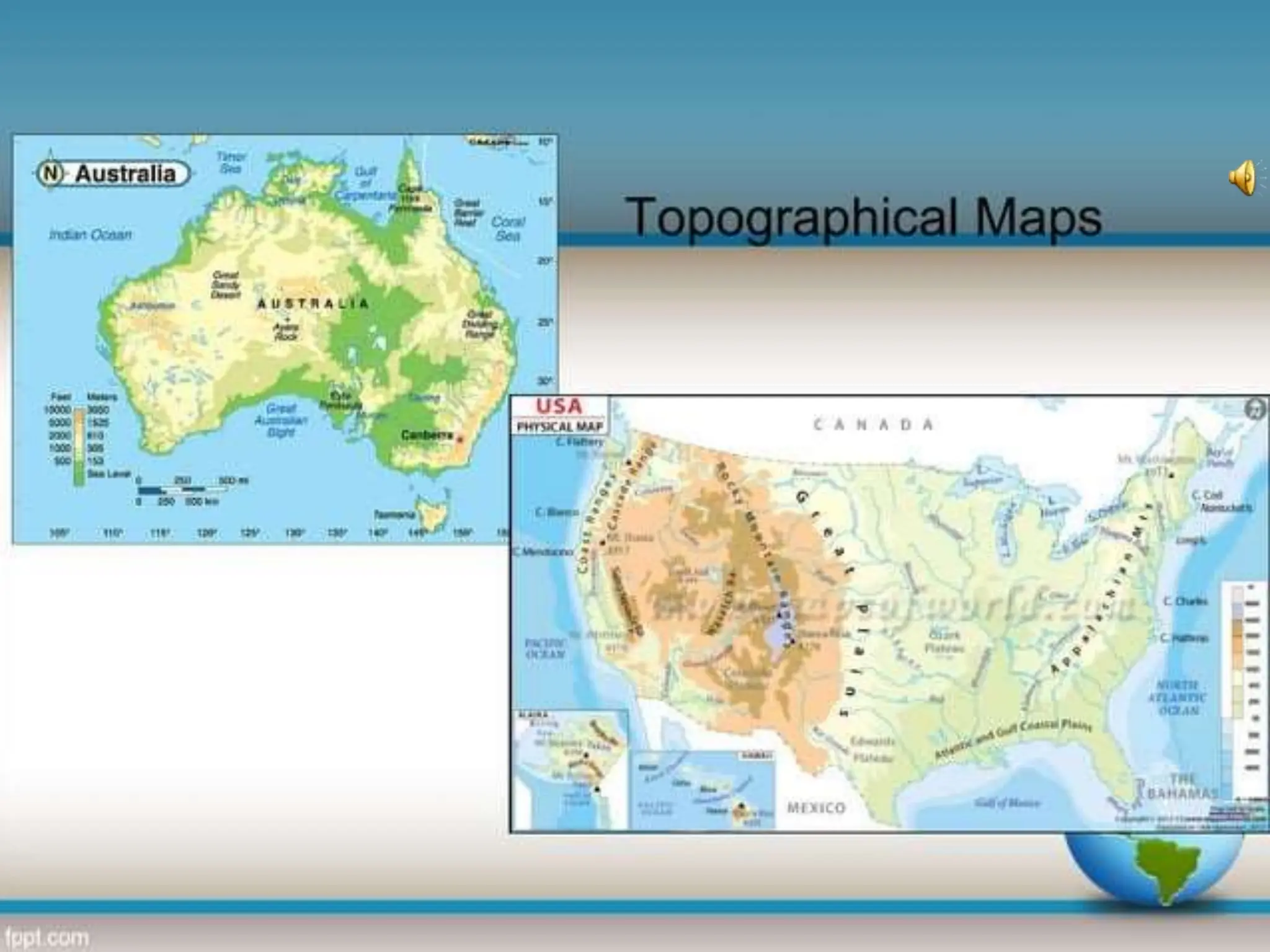
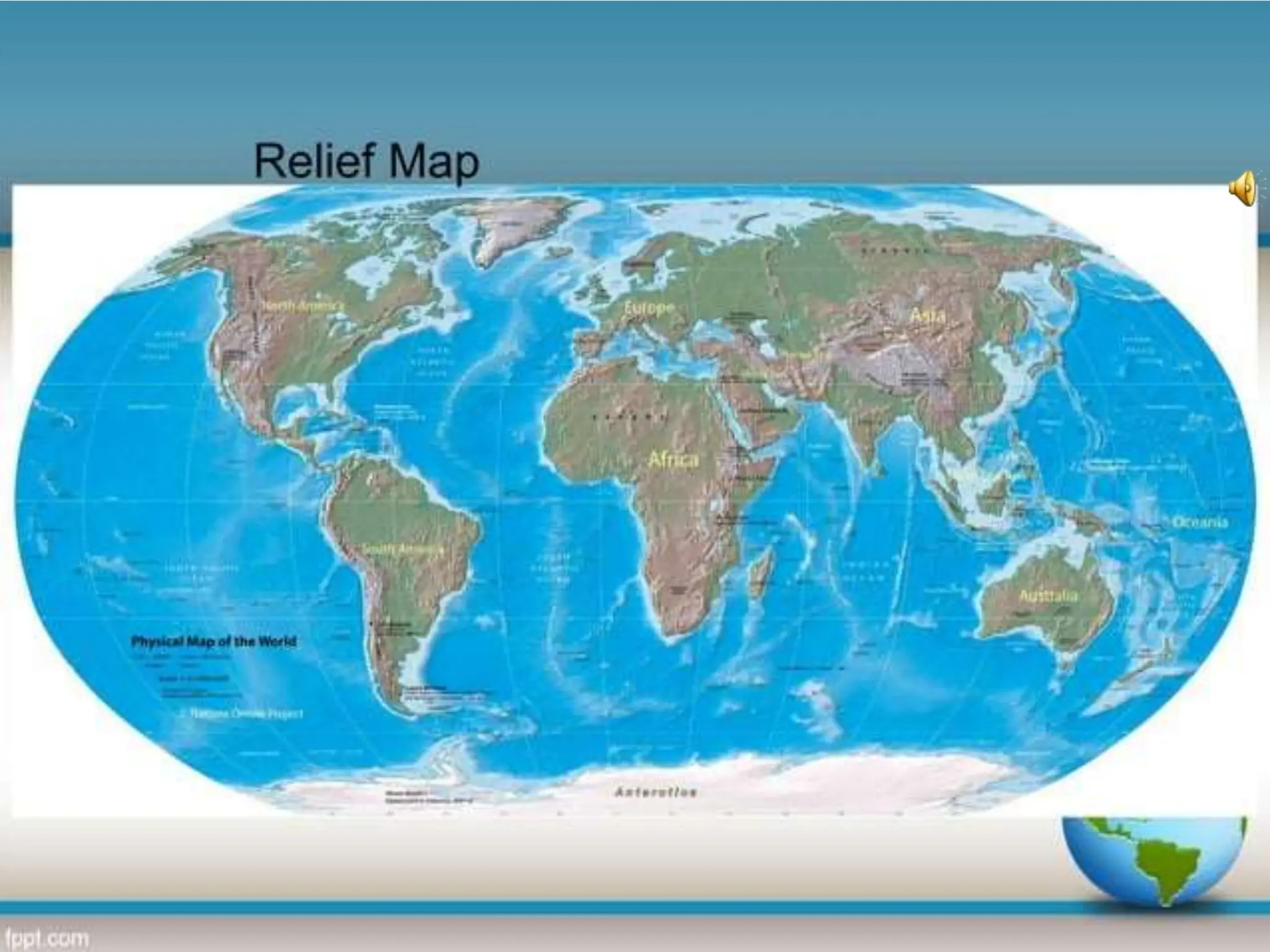
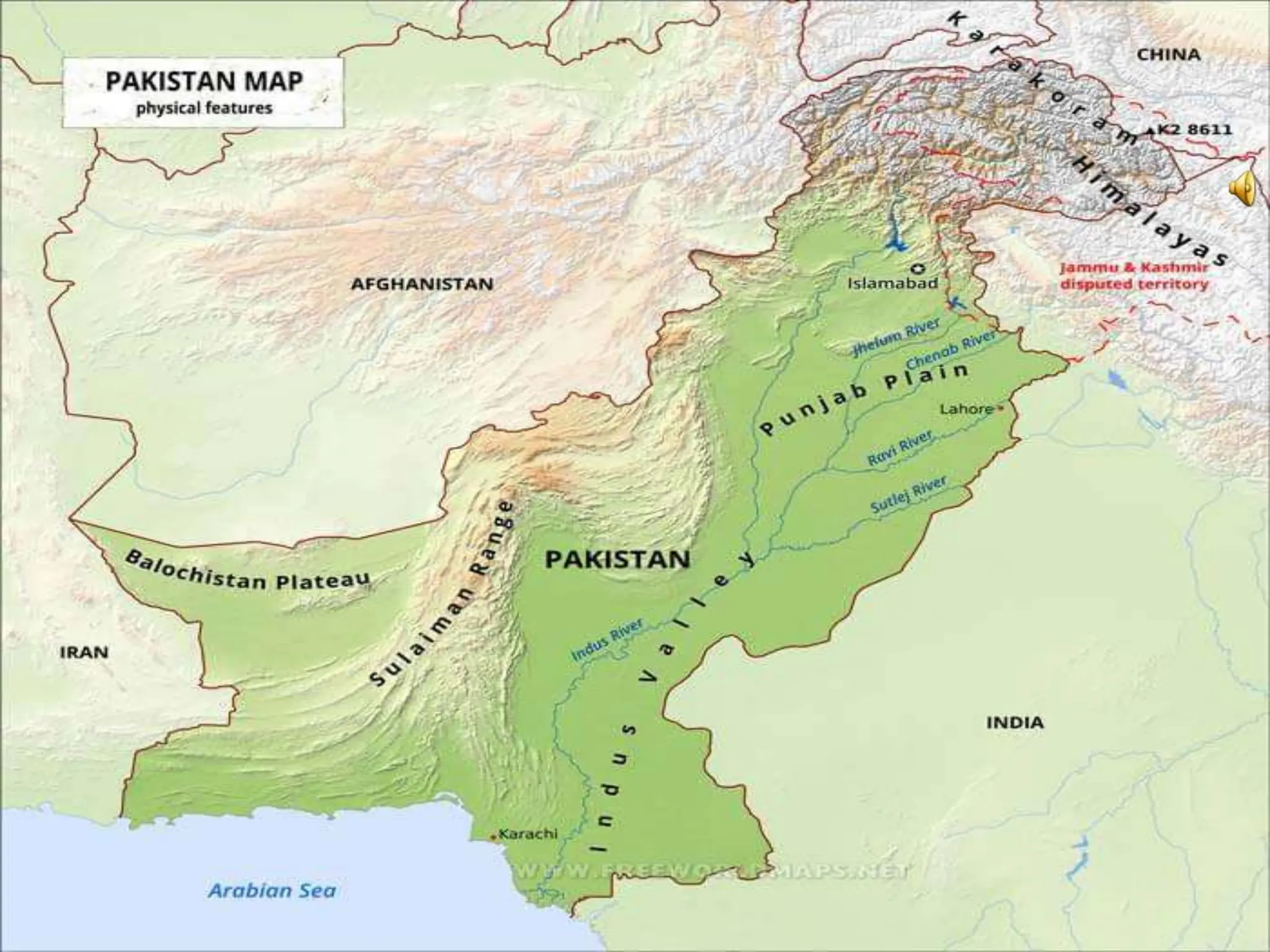
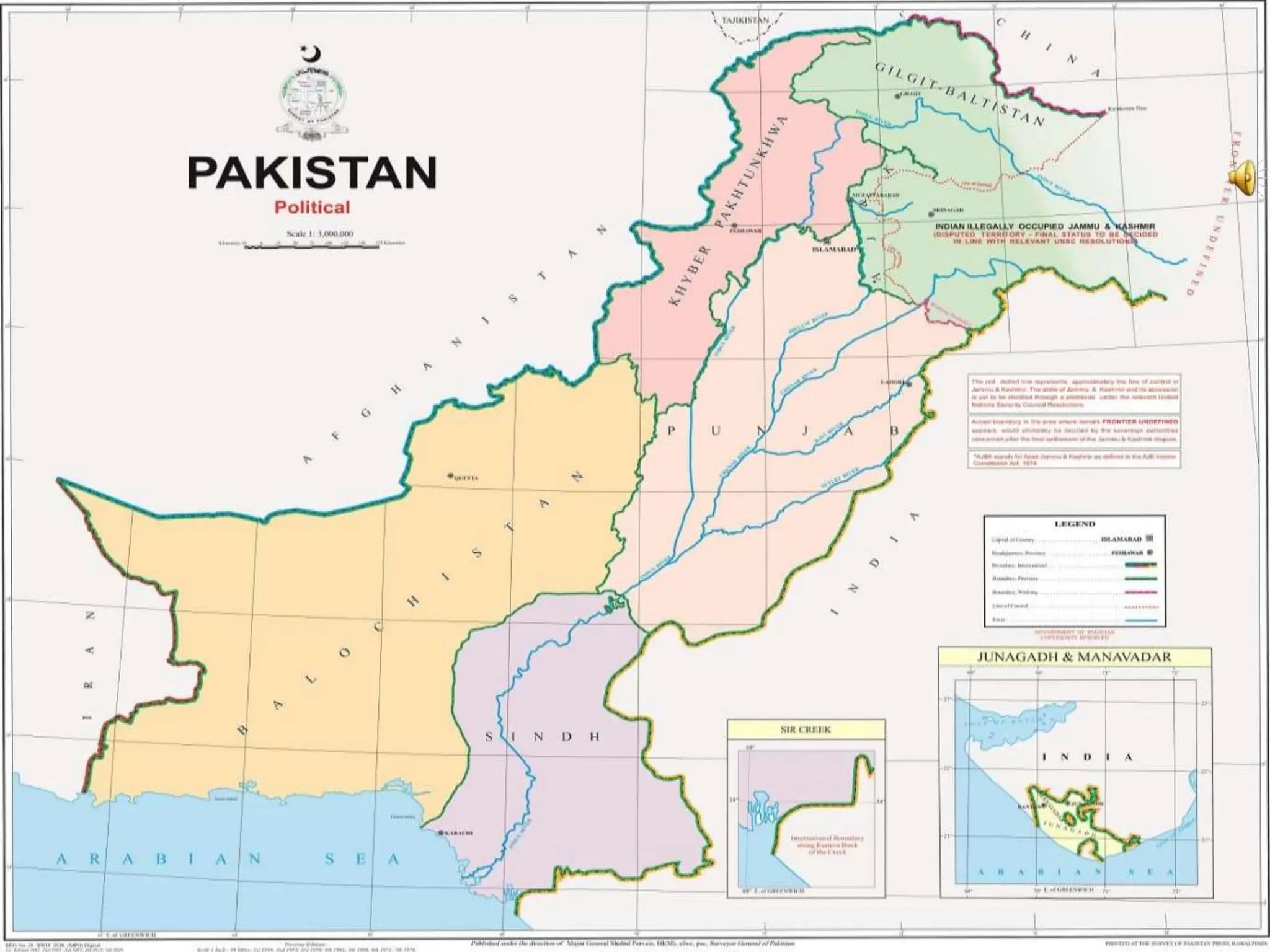
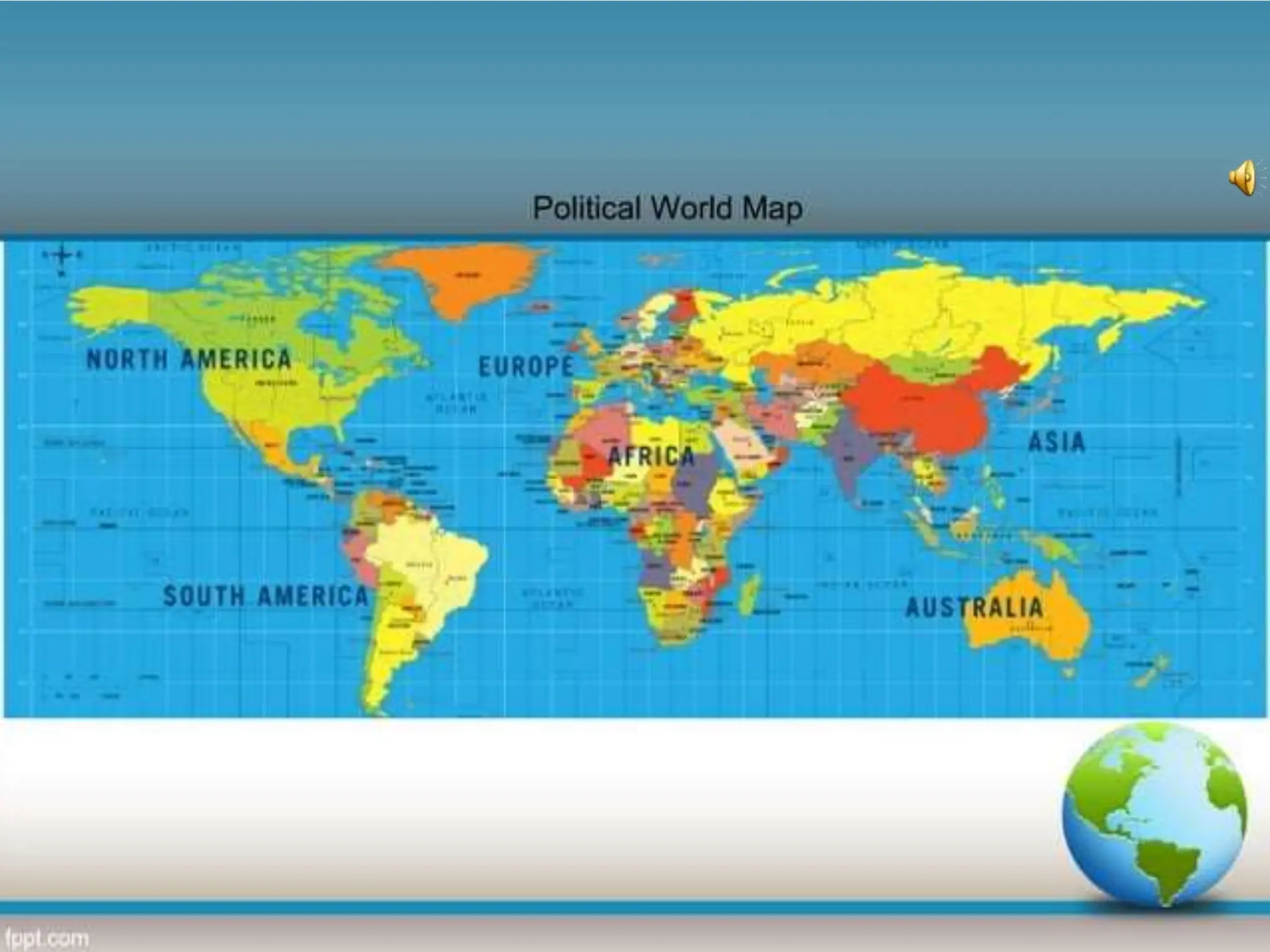
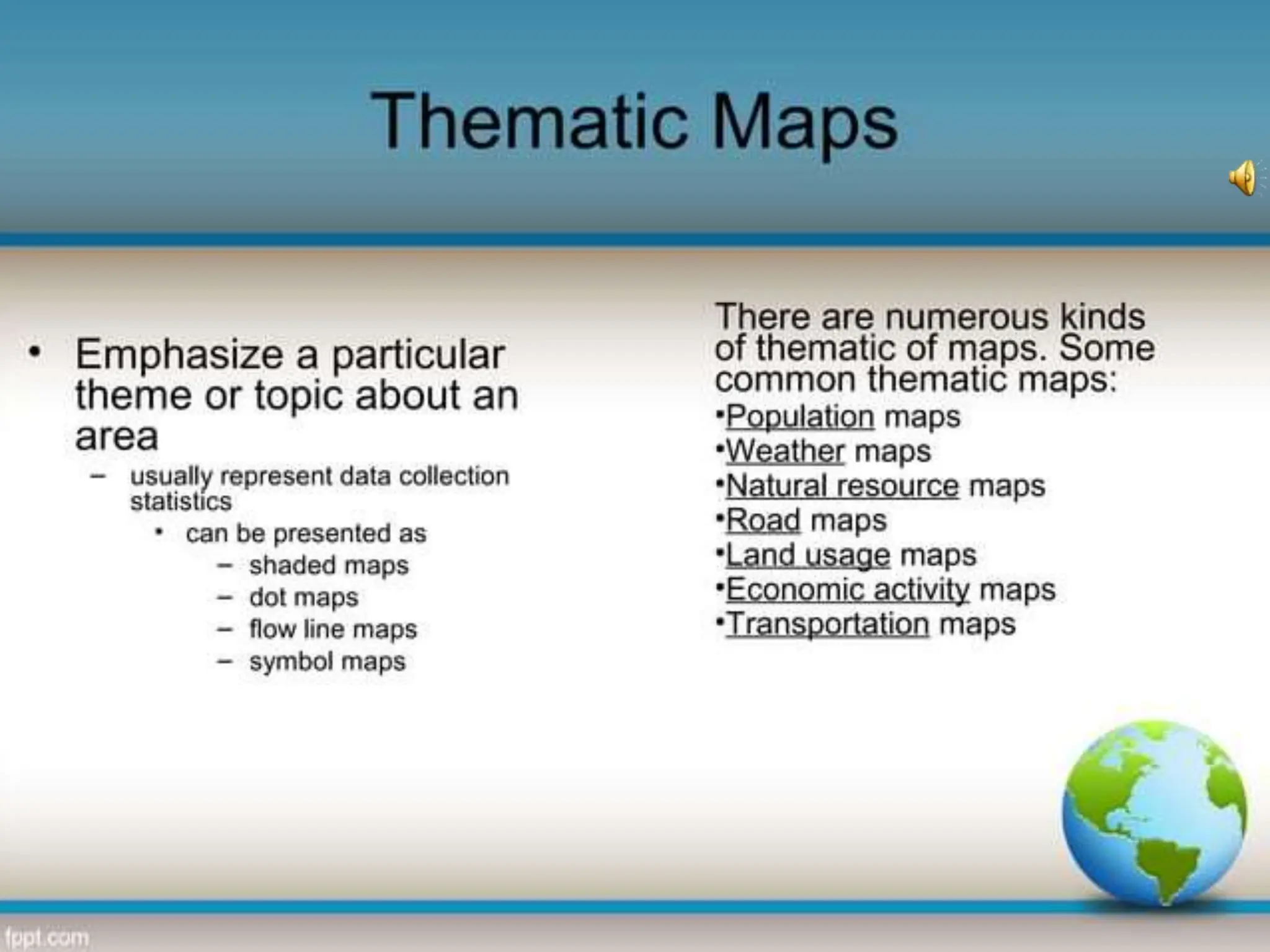
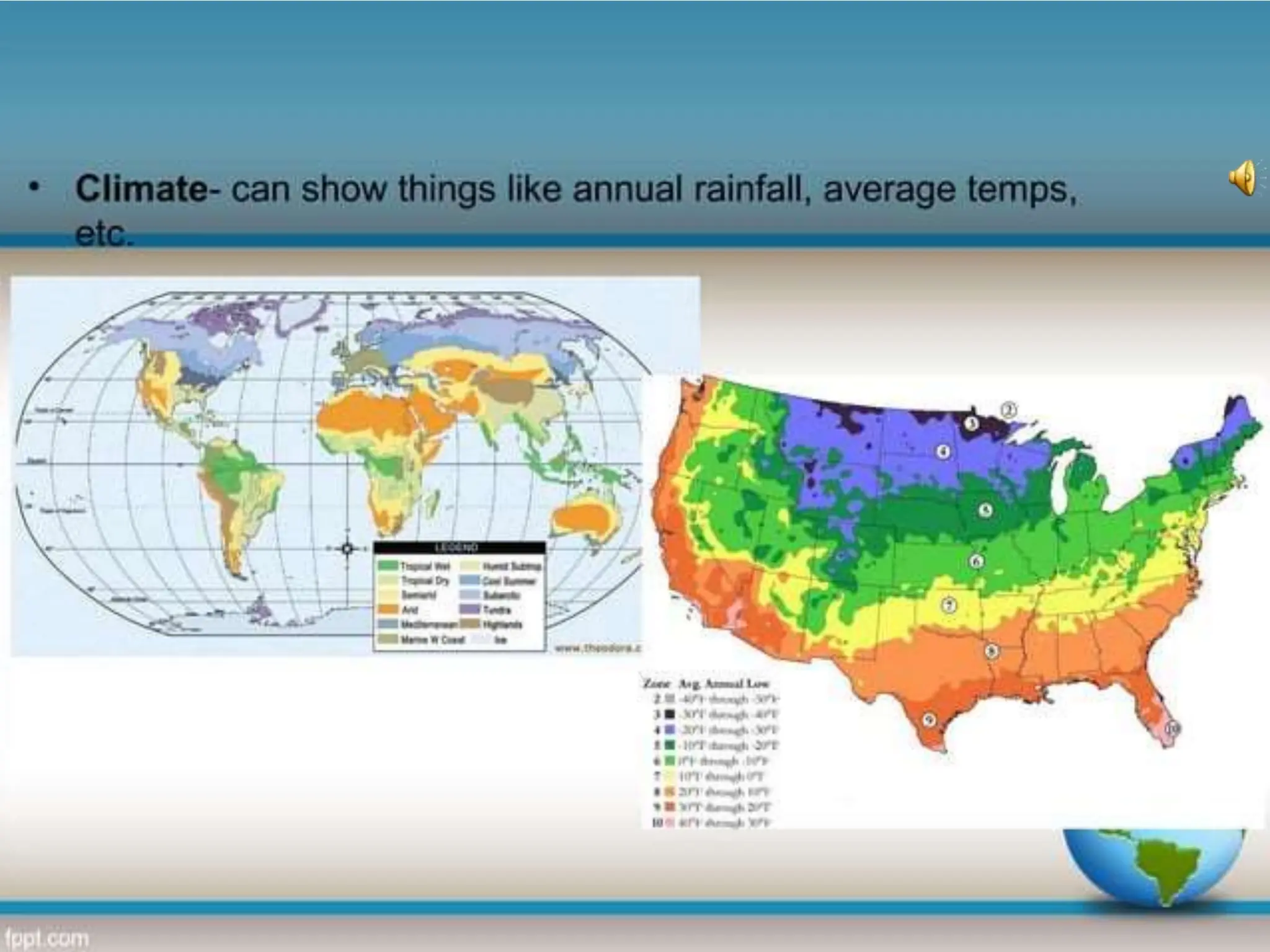
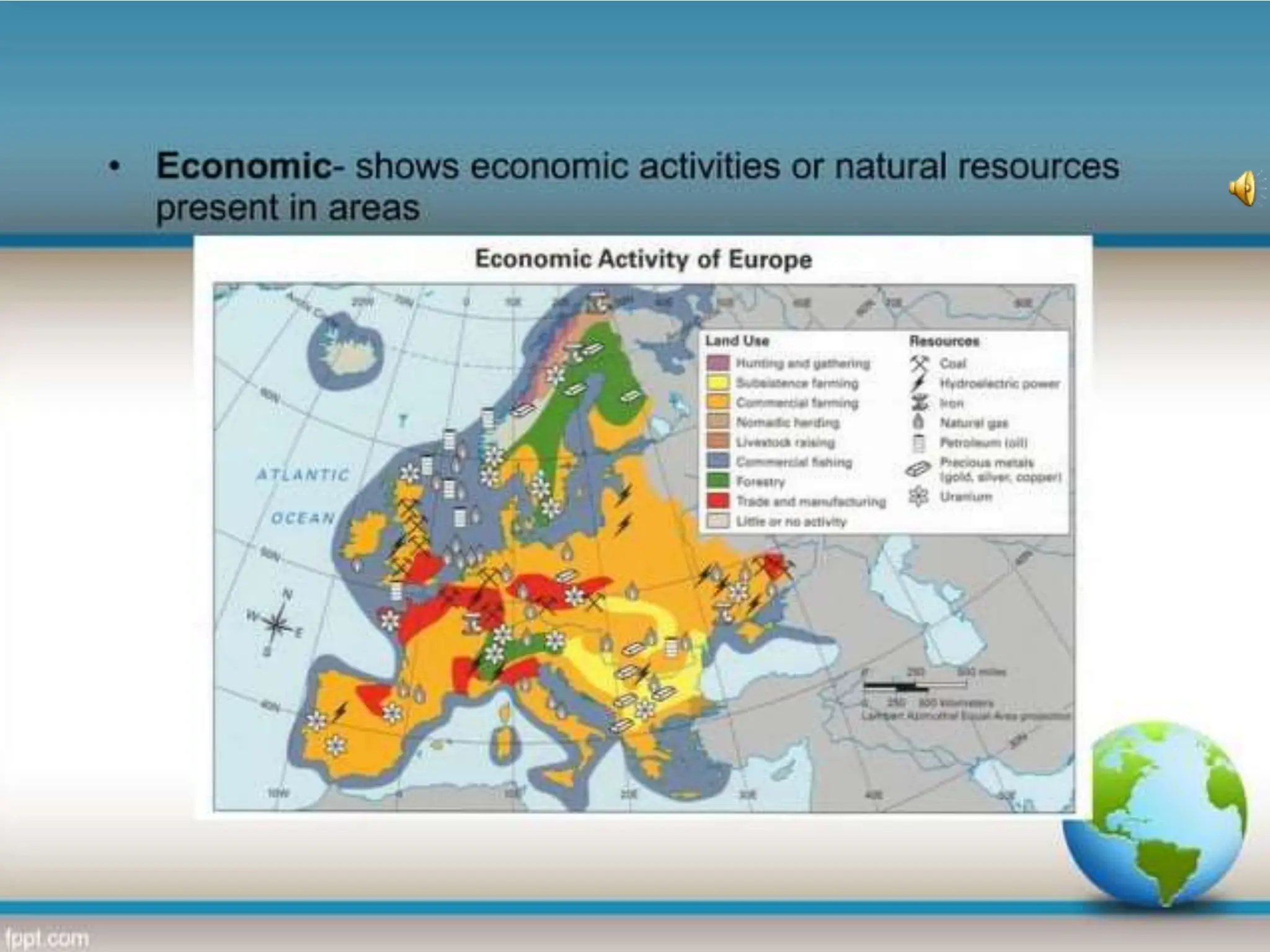
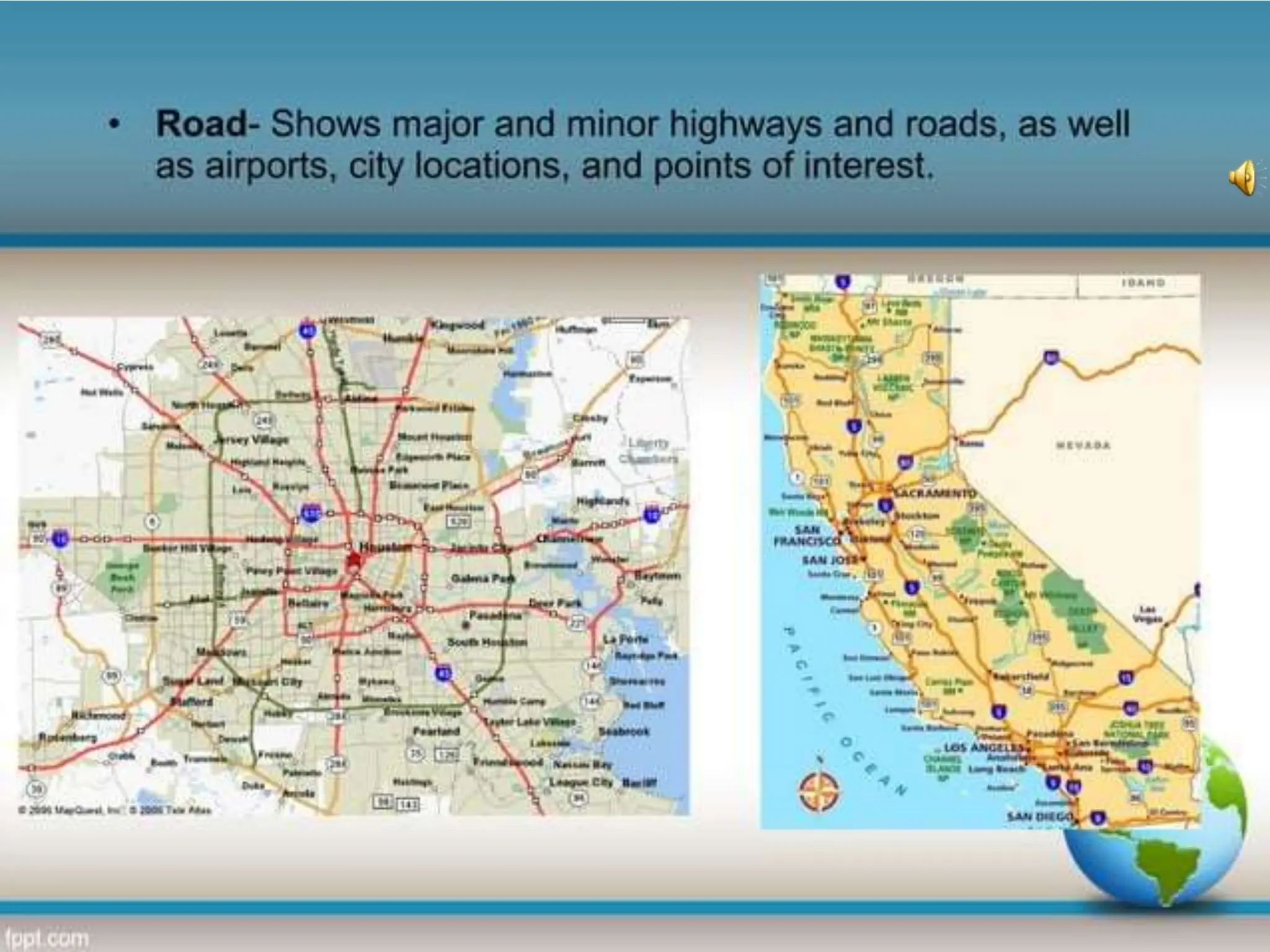
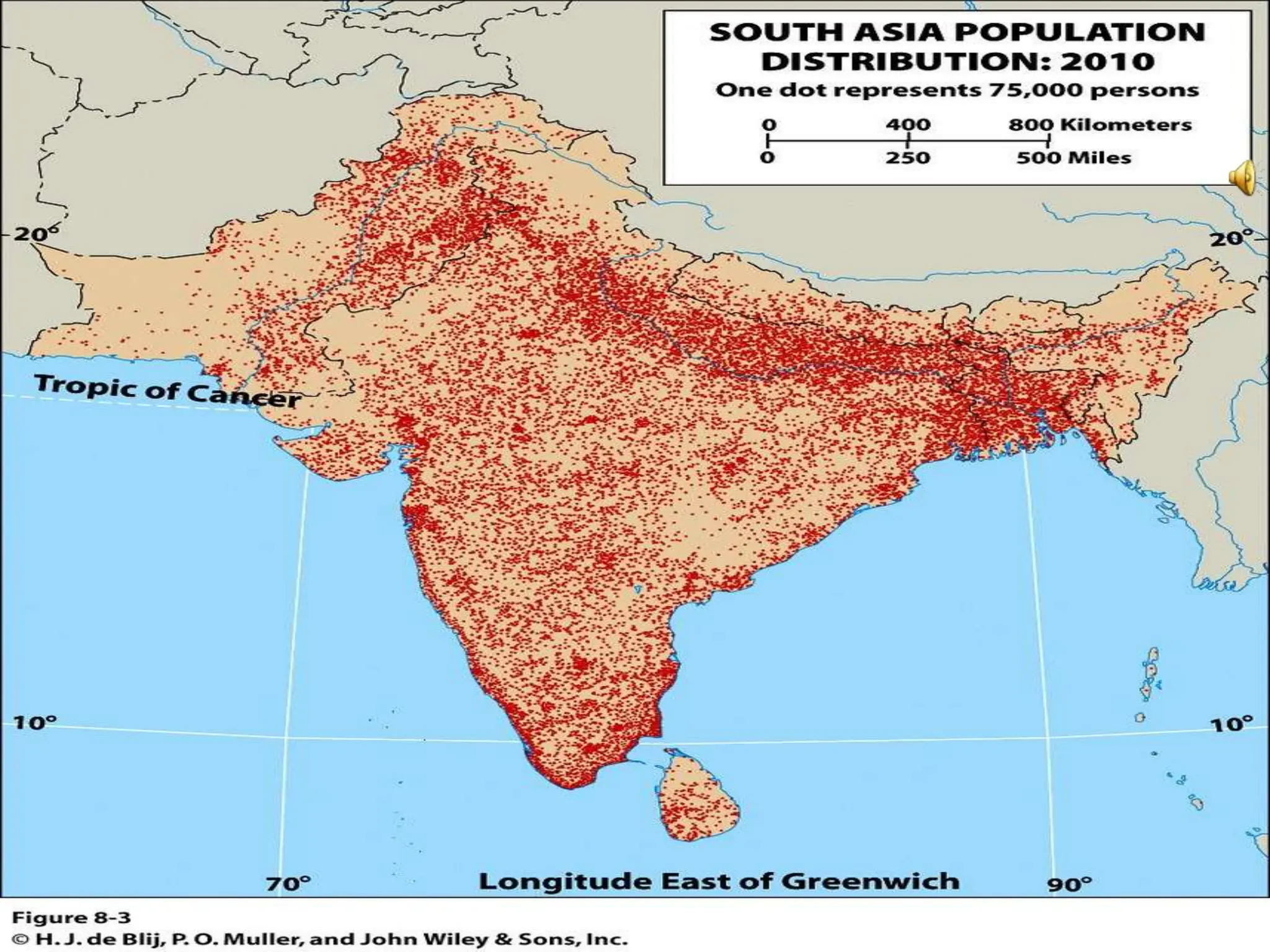
This document provides an overview of important concepts for map reading skills. It discusses key components of maps, including the title, scale, direction, grid system, projection, and legend. It also covers cardinal directions, latitude and longitude lines, and how to locate places using their coordinates. The purpose is to teach life skills for interpreting and navigating using maps.