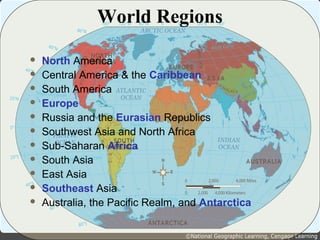
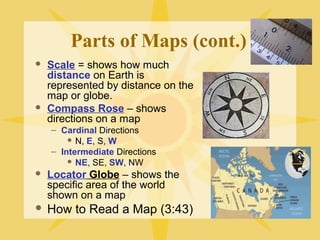
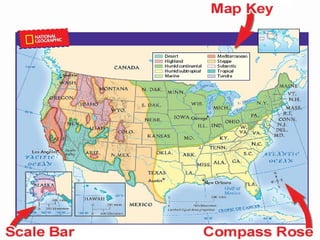
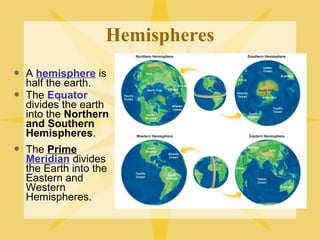
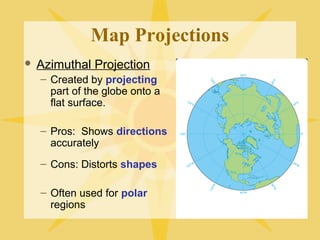
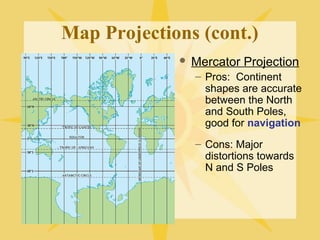
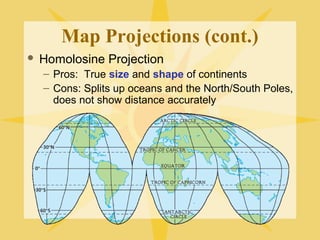
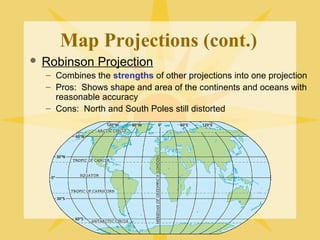
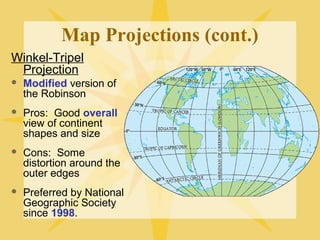
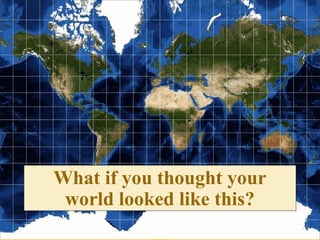
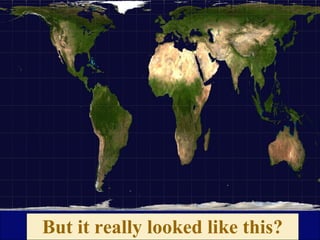
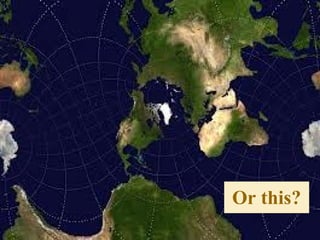
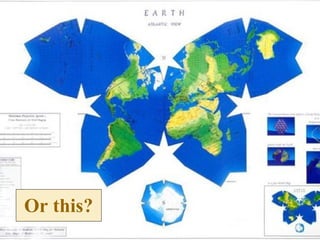
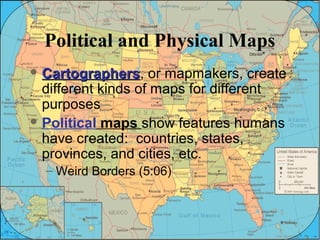
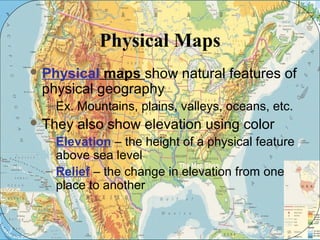
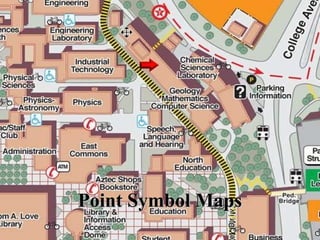
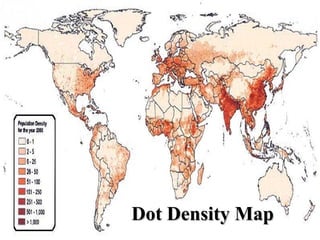
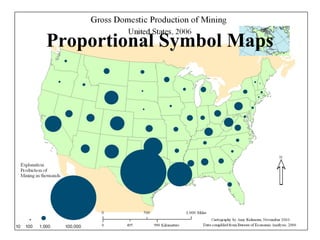
The document provides an overview of geography, exploring its importance, five themes, and essential concepts such as spatial thinking, location, and the use of maps. It outlines various map types, including political, physical, and thematic maps, as well as discusses map projections and their distortions. The content emphasizes the significance of geography in understanding human and environmental interactions across different regions of the world.