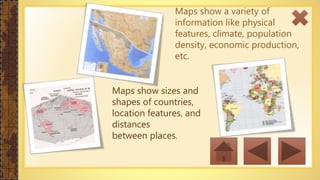
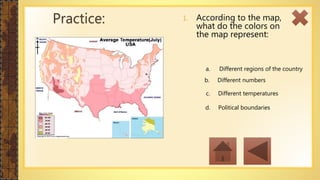
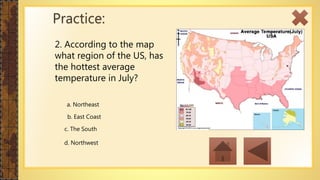
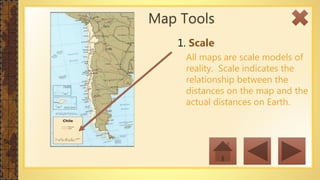
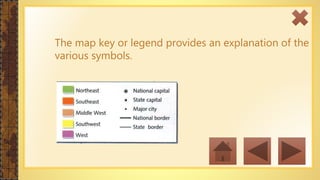
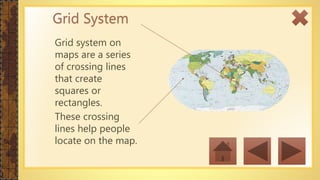
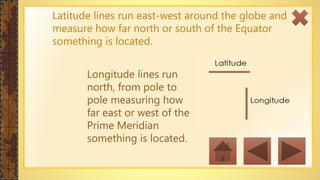
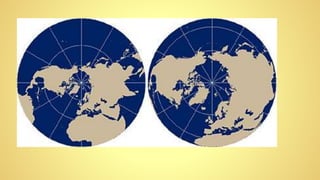
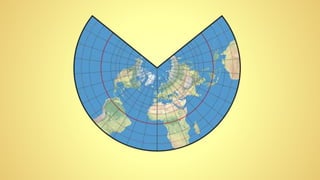
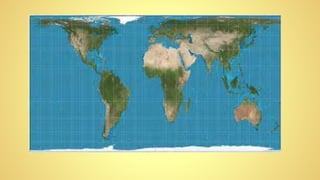
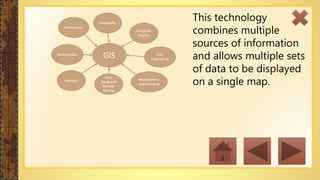
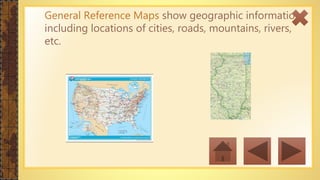
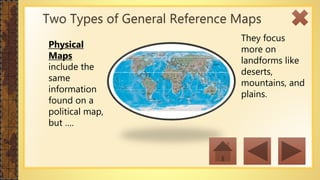
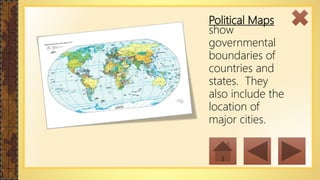
This instructional module aims to refresh first-year high school students' map reading skills by teaching them to identify map types, use mapping tools like latitude and longitude, and understand map projections and GIS technology. The module includes practice exercises, objectives for each section, and a post-test upon completion. It concludes by emphasizing the importance of distinguishing between general reference maps and thematic maps.