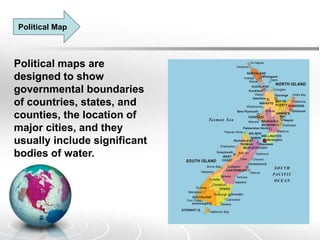
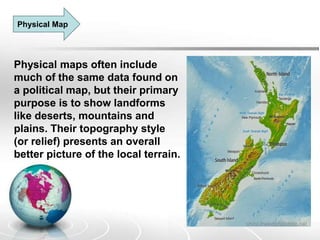
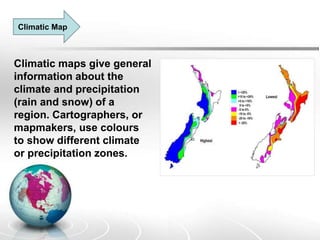
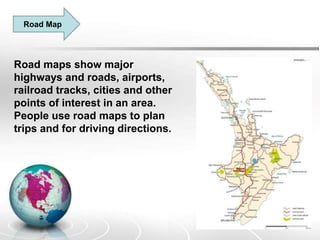
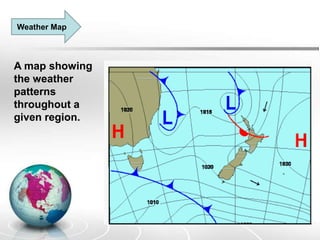
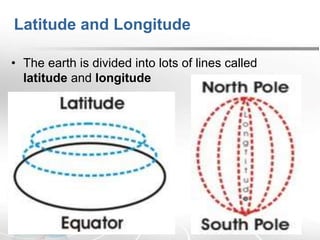
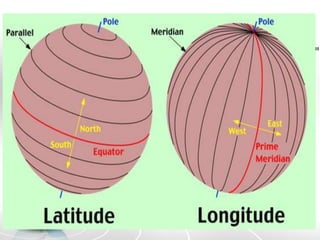
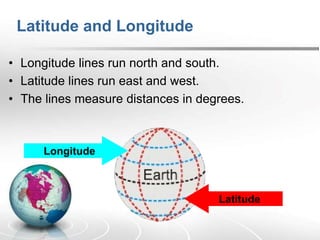
The document provides an overview of maps, detailing their definitions, types, features, and the systems of latitude and longitude used for navigation. It outlines various types of maps, such as political, physical, climatic, road, weather, resources, and topographic maps, each serving distinct purposes. Additionally, it explains latitude and longitude lines that help in geographic orientation, including the significance of the equator and the prime meridian.