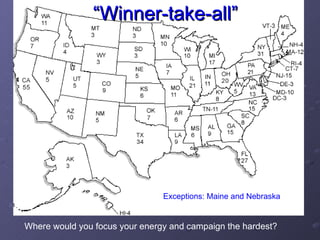
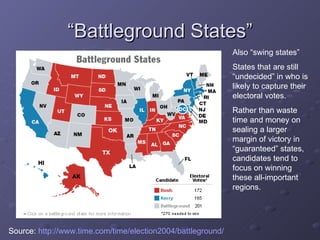
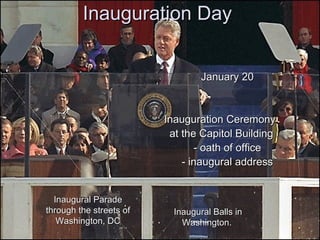
The document summarizes the process of the U.S. presidential election system from the initial testing of candidacies around 2 years out, through campaigning, primaries and caucuses, national conventions, debates, election day voting, the electoral college vote, and culminating with the inauguration of the new president on January 20th. Key aspects include fundraising requirements, primary dates and locations, the roles of the media and campaign advertising, and the focus on swing states in the final months leading up to election day.