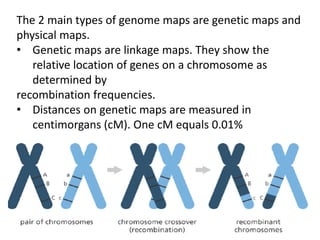
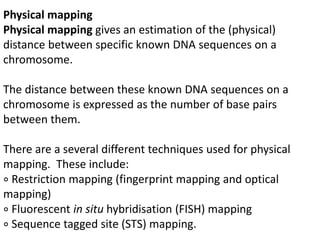
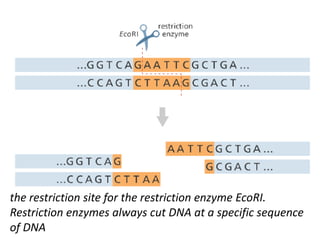
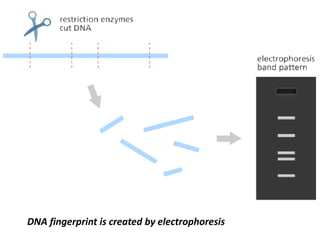
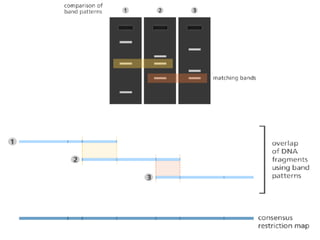
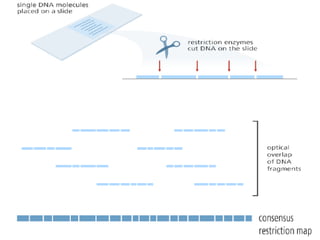
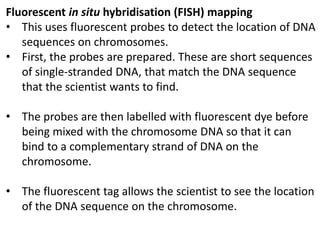
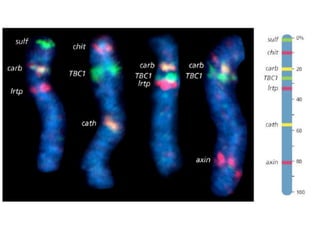
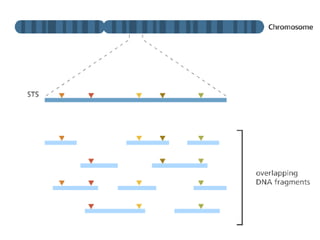
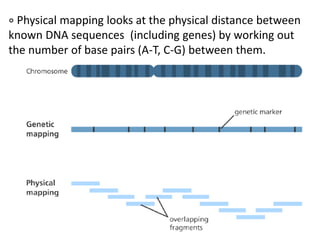
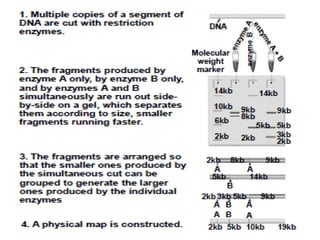
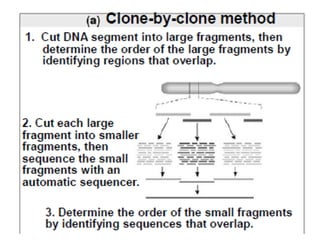
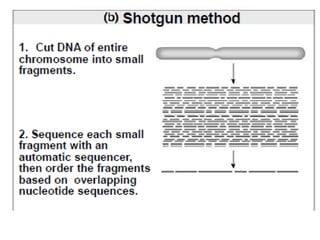
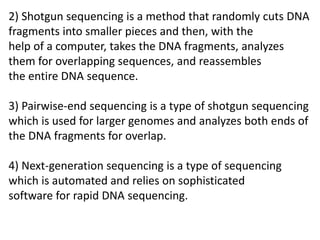
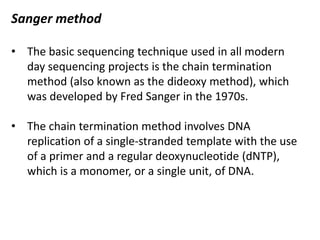
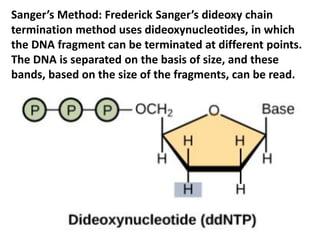
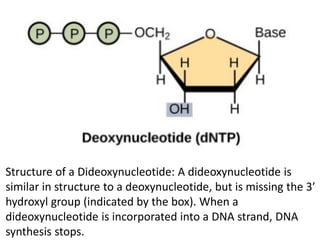
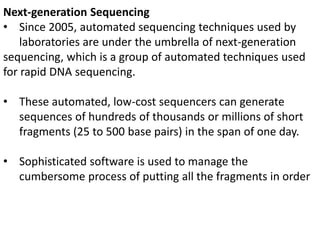
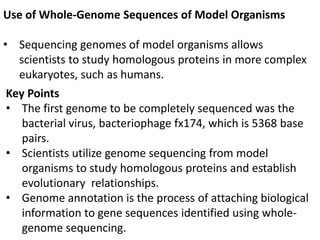
A genome is the complete DNA content within an organism's nucleated cells, with humans having 46 chromosomes. The Human Genome Project aimed to sequence the human genome and identify genes, while various mapping techniques, such as genetic and physical mapping, provide information on gene locations. Modern sequencing methods, including Sanger and next-generation sequencing, have advanced the understanding of genomes and facilitated research across various biological fields.