Embed presentation
Downloaded 10 times





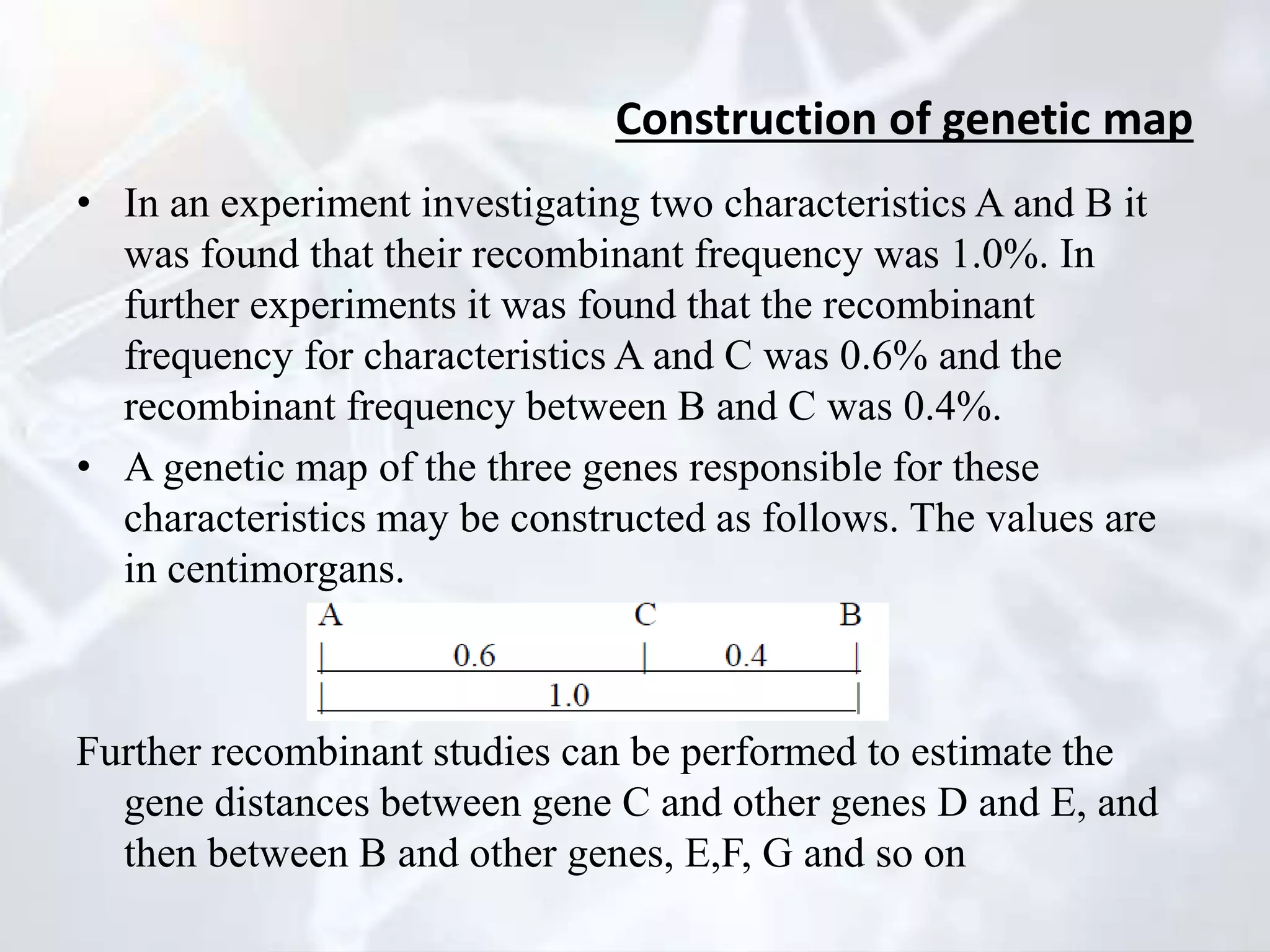







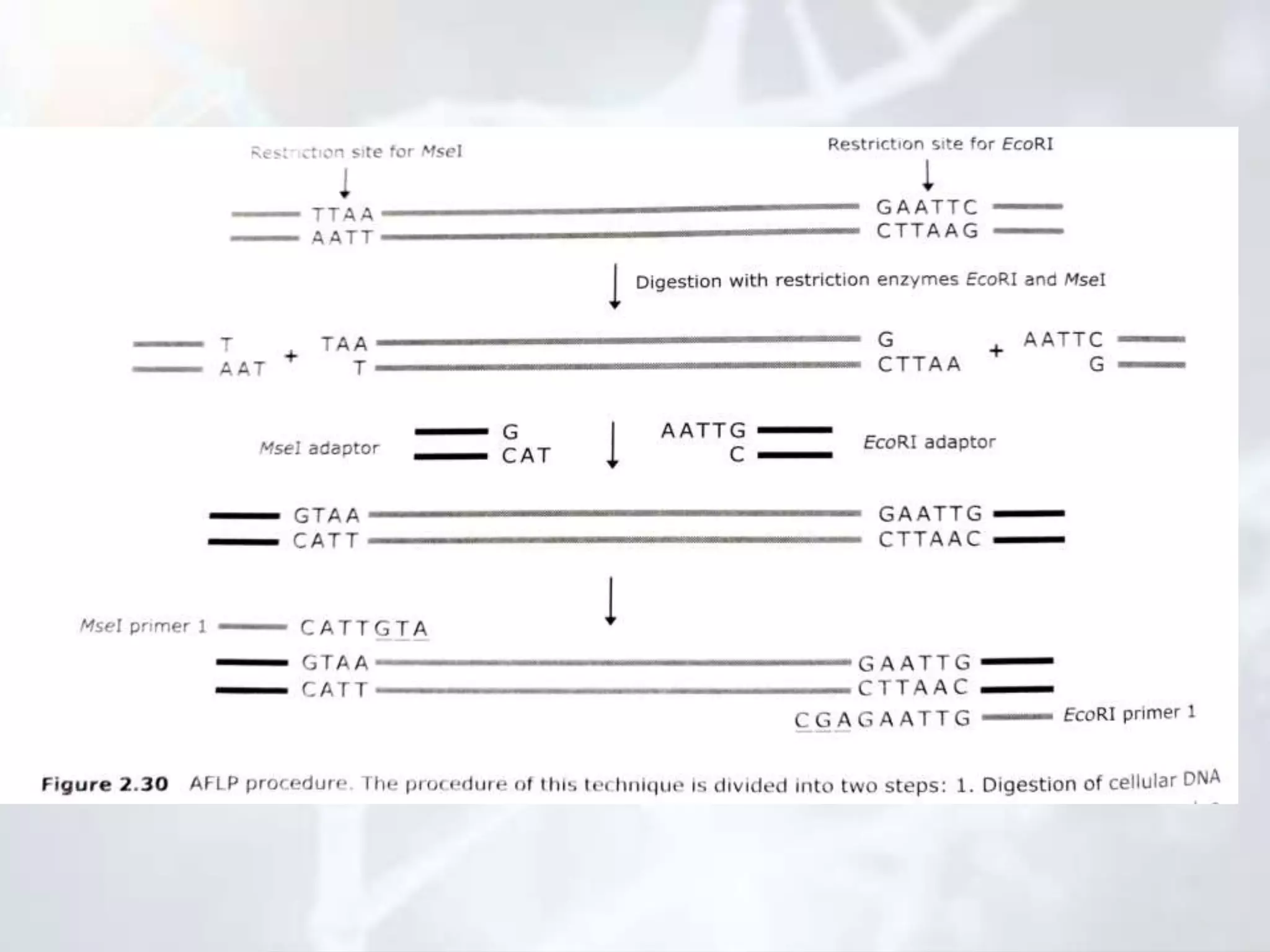

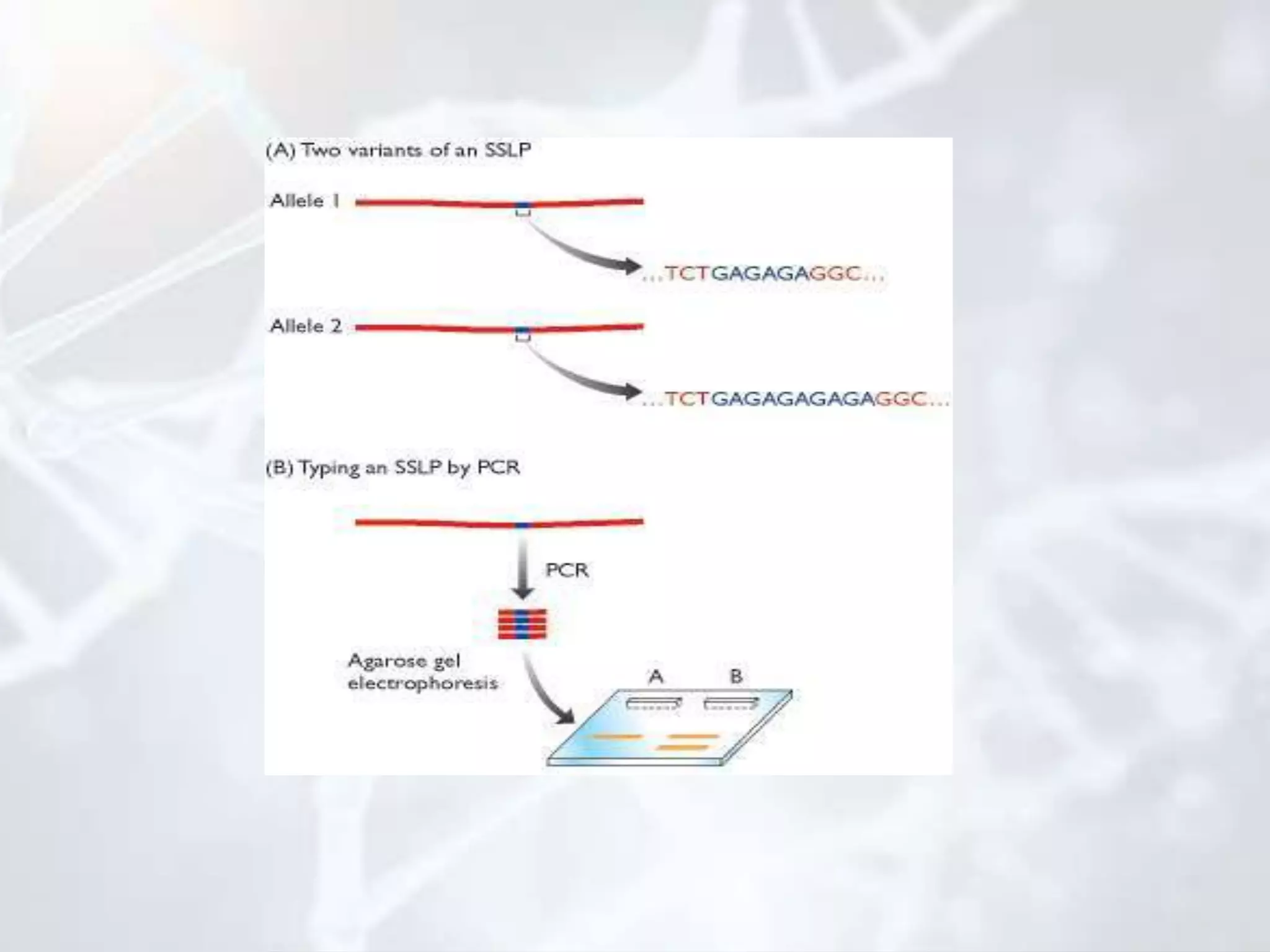



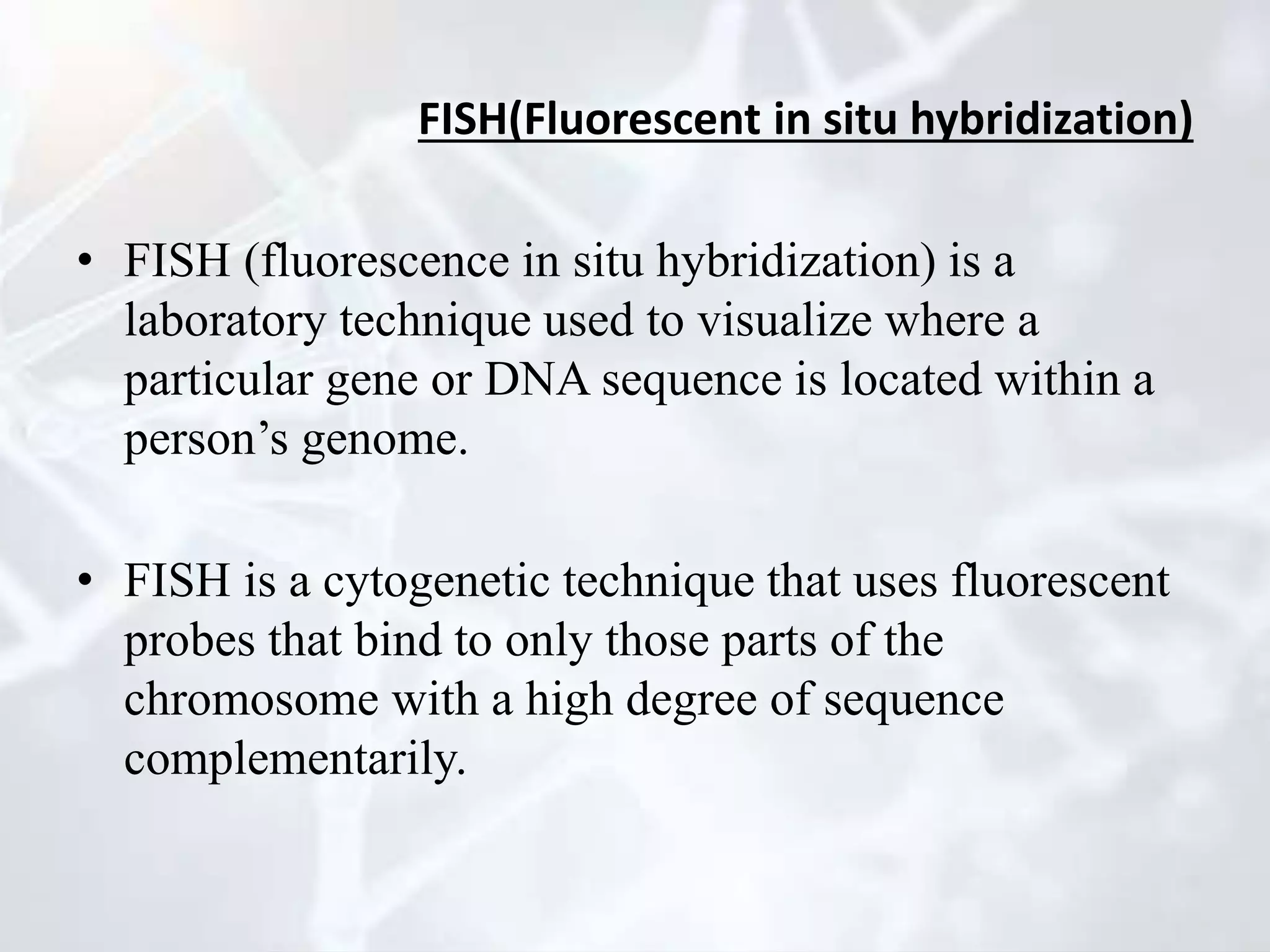
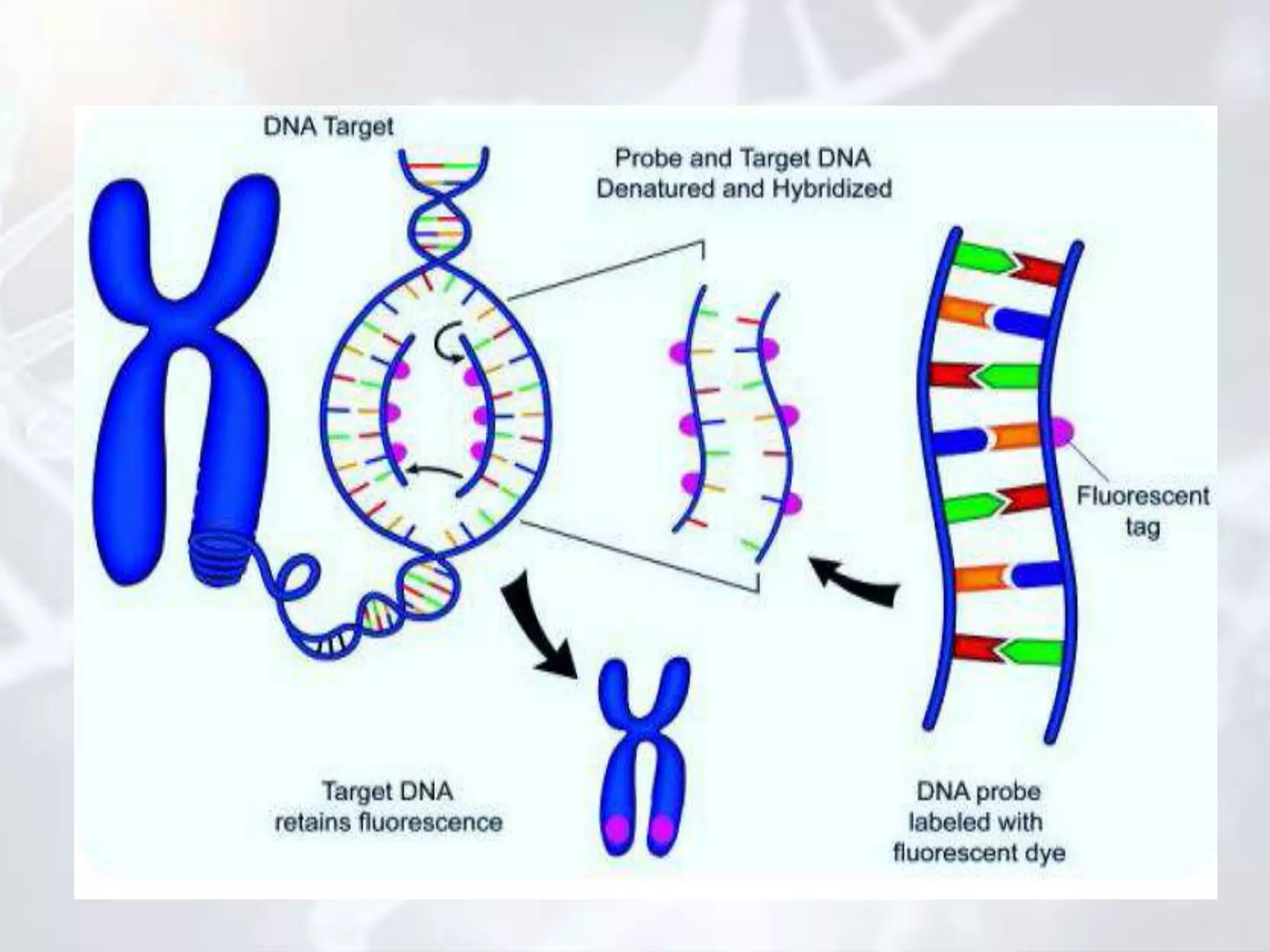





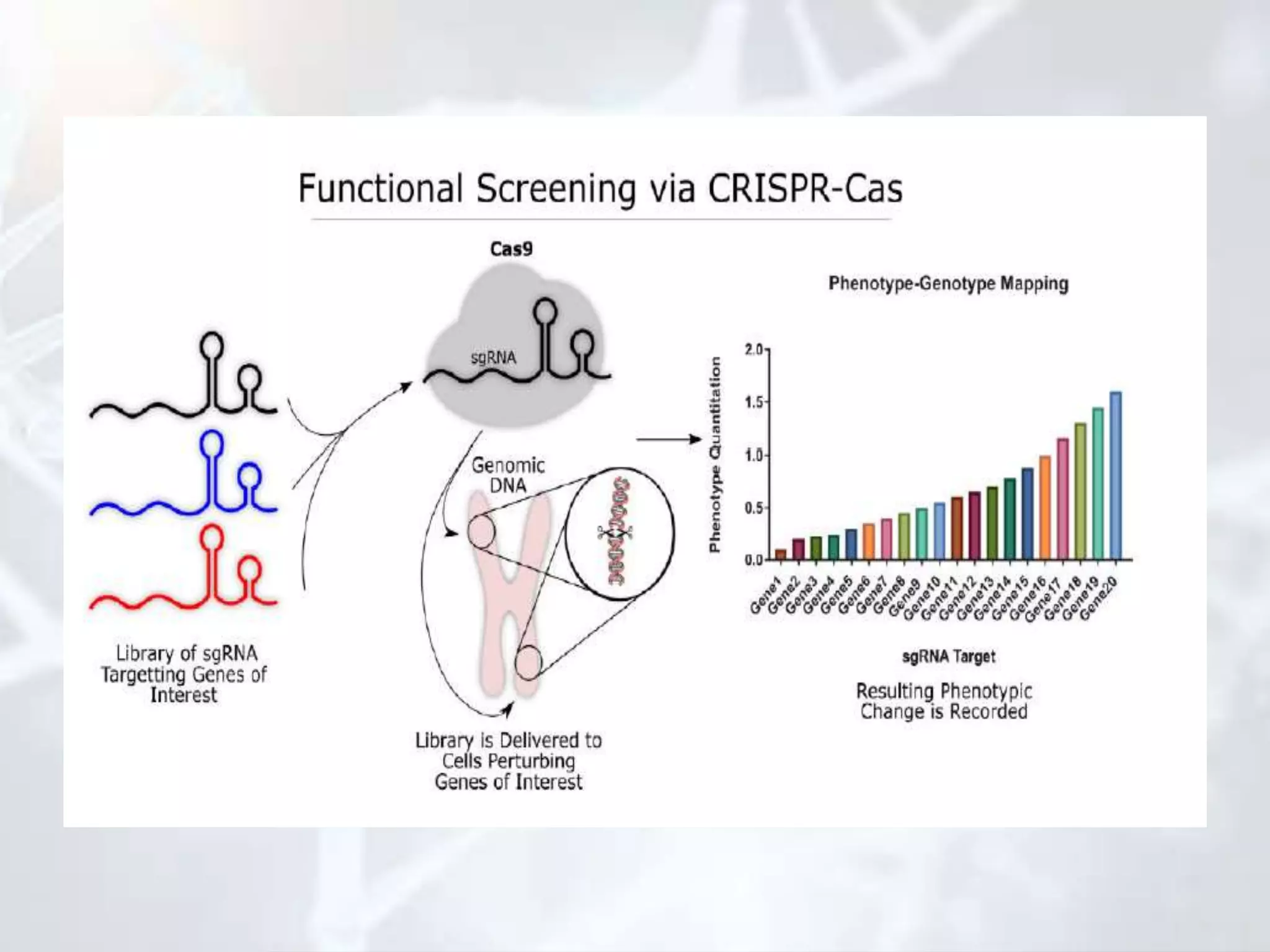
Genetic mapping involves identifying the locations and relative positions of genetic markers, such as genes, on a genome. There are two main types: genome sequencing, which determines every nucleotide, and genome mapping, which identifies landmark positions. The first genetic maps were constructed in fruit flies and allowed genes determining visible traits like eye color to be studied. Genetic mapping determines the linear order and distance between linked genes and has practical applications like diagnosing inherited human diseases. Two main types of mapping are genetic mapping using linkage analysis and physical mapping using techniques to determine absolute positions of genes. DNA markers like RFLPs, RAPDs, AFLPs, SSLPs, and SNPs are used in mapping. Physical mapping techniques include restriction mapping and fluorescent in





























