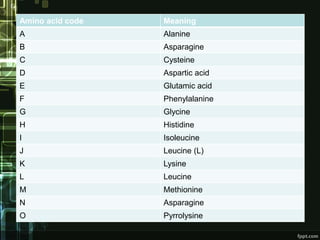
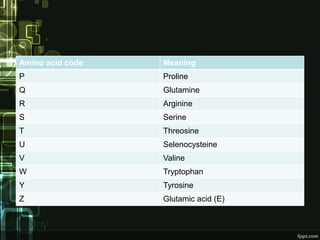
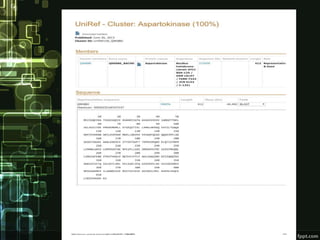
FASTA is a bioinformatics tool and biological database that is used to compare amino acid sequences of proteins or nucleotide sequences of DNA. It was first described in 1985 by Lipman and Pearson. FASTA performs fast homology searches to find similarities between a query sequence and sequences in a database. While similar to BLAST, FASTA is faster for sequence comparisons. It works by identifying patches of sequence similarity that may contain gaps. Some key FASTA programs include FASTA, TFASTA, FASTS, and FASTX/Y. FASTA is useful for applications like identification of species, establishing phylogeny, DNA mapping, and understanding protein function.