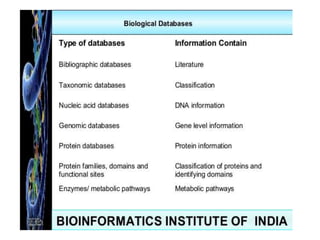
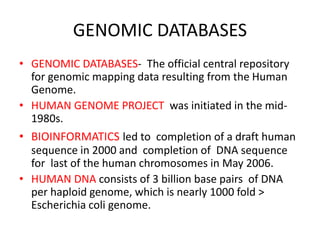
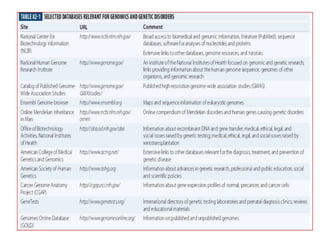
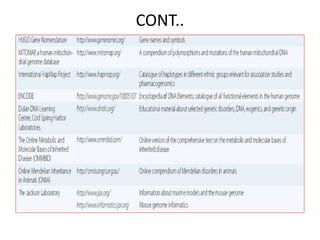
This document discusses genomic databases. It begins by defining key terms like genes, genomes, and genomics. It then describes categories of biological databases including those for nucleic acid sequences, proteins, structures, and genomes. It provides many examples of genomic databases for both non-vertebrate and vertebrate species, including databases for bacteria, fungi, plants, invertebrates, and humans. The final sections note that genomic databases collect genome-wide data from various sources and that databases can be specific to a single organism or category of organisms.