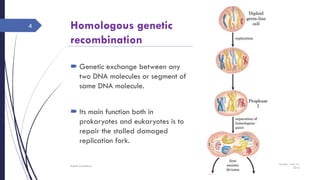
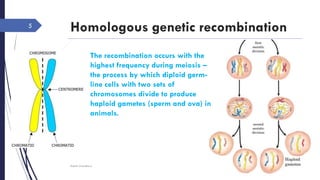
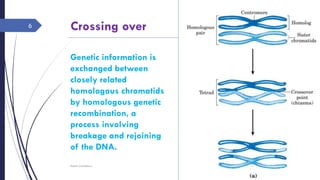
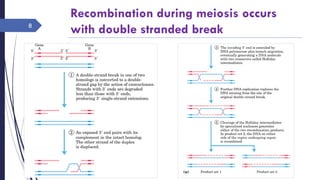
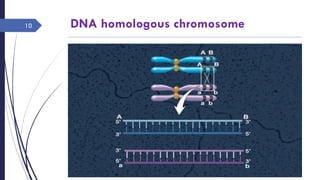
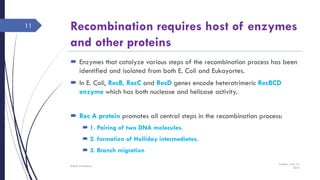
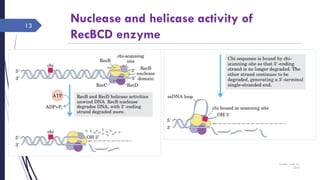
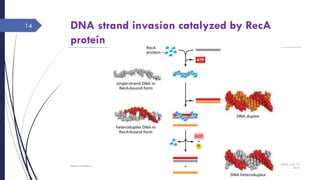
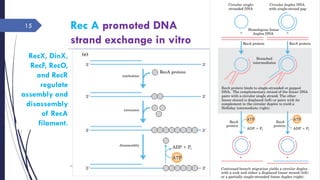
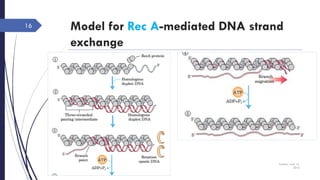
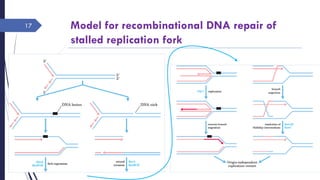
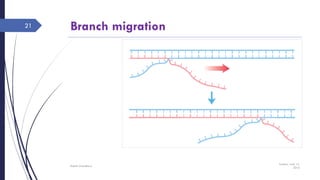
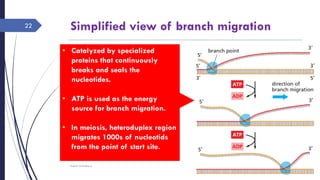
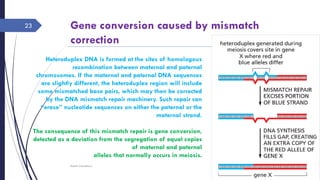
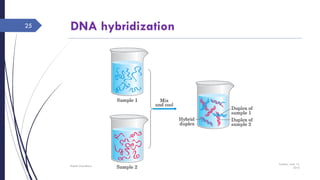
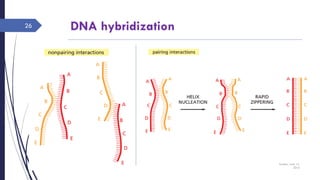
The document discusses genetic recombination, detailing its necessity for altering genomes to understand diseases. It categorizes recombination into three classes: homologous, site-specific, and DNA transposition, with a focus on the mechanisms and enzymes involved in homologous recombination during meiosis. The document also explains processes like gene conversion caused by mismatch repair and the significance of mobile genetic elements.