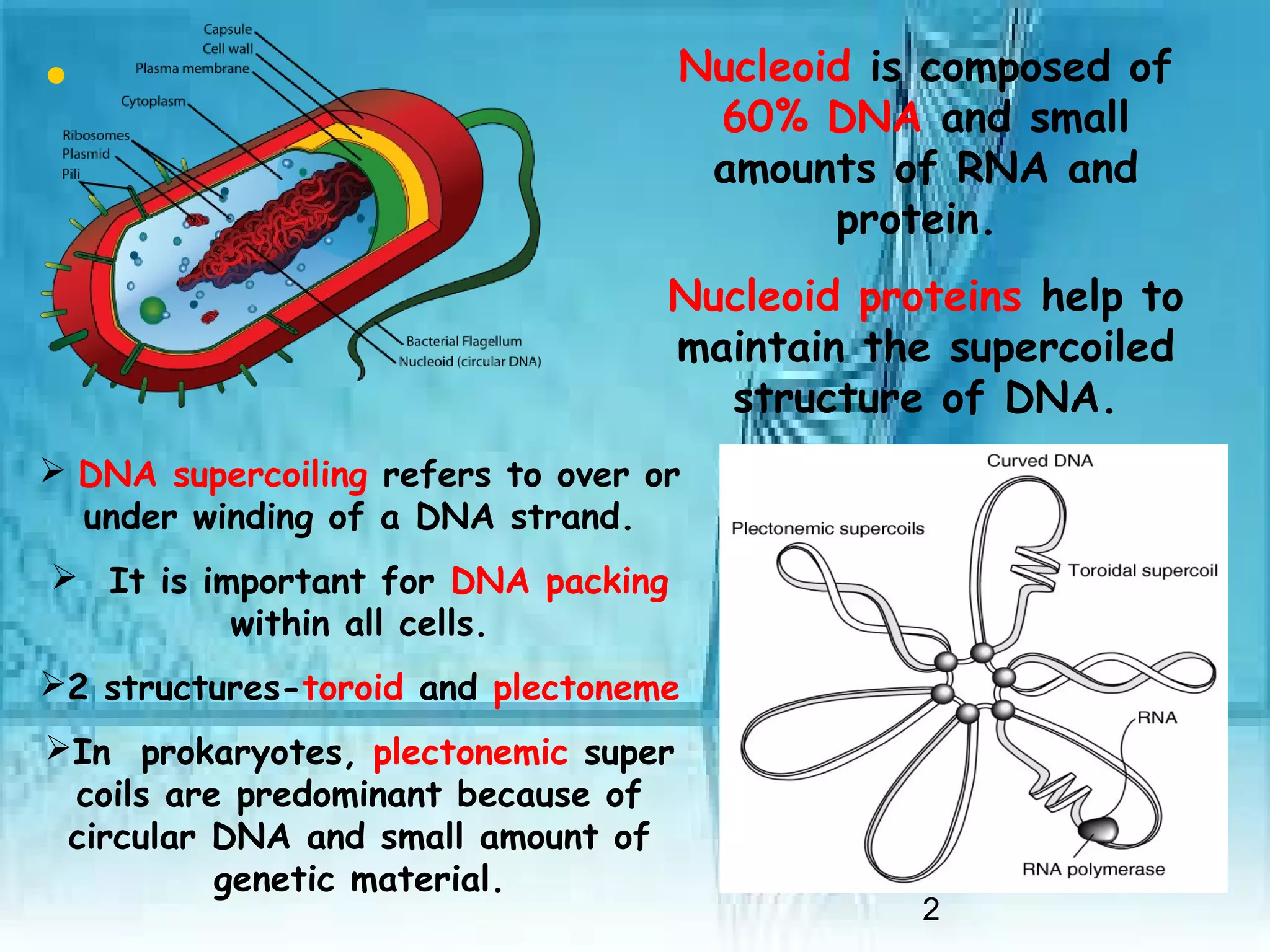
Prokaryotic genomes are circular, double-stranded DNA contained within the nucleoid. They vary in length but are generally a few million base pairs. DNA supercoiling allows for tight packing of the genome.
Eukaryotic genomes are linear chromosomes associated with histone proteins within the nucleus. The DNA is wrapped around histone octamers to form nucleosomes, compacting the genome. Eukaryotic genomes are generally larger and contain more DNA than prokaryotic genomes.
Key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes include genome size, number of chromosomes, ploidy level, association with histones, and method of compaction.