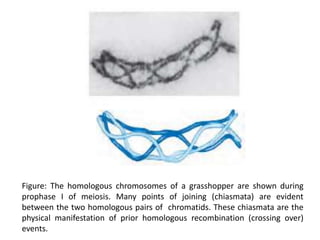
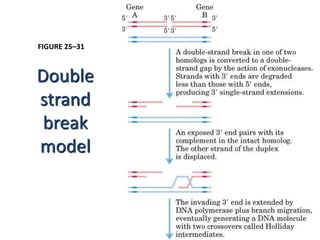
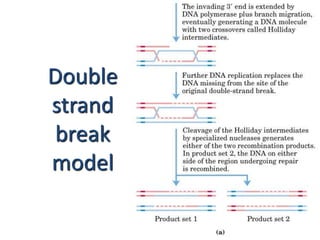
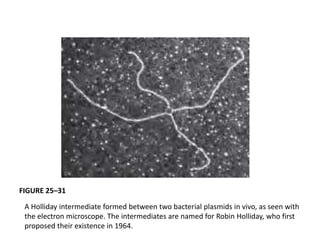
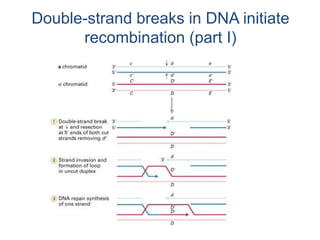
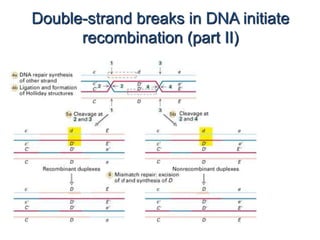
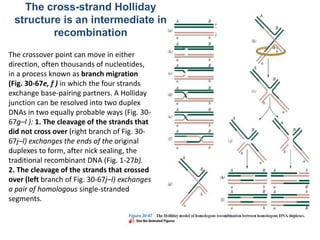
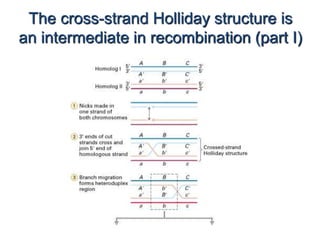
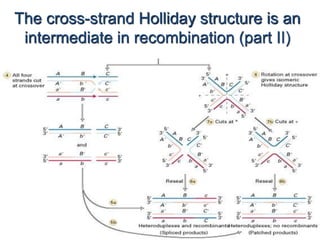
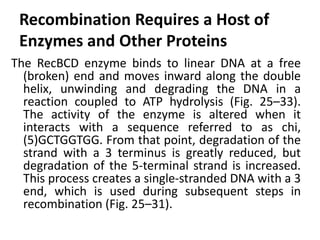
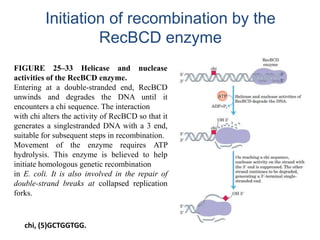
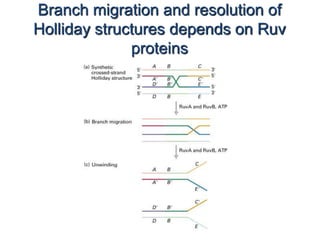
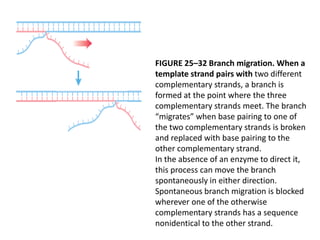
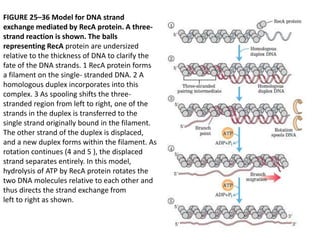
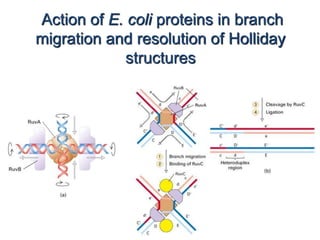
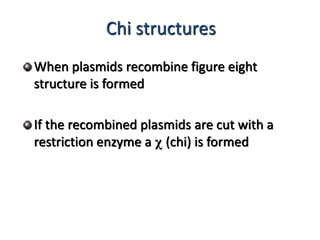
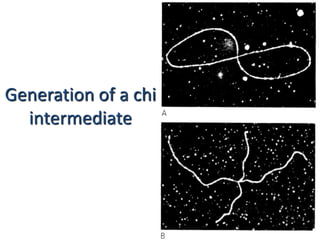
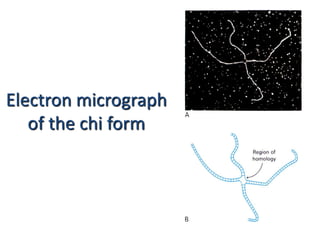
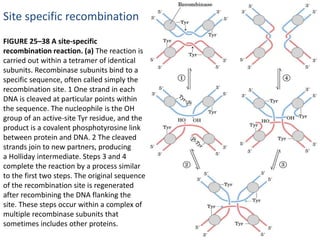
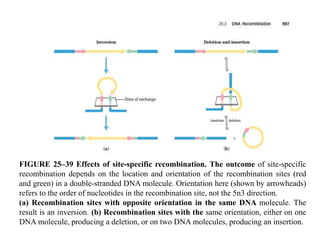
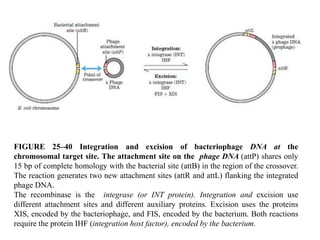
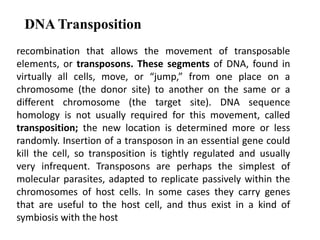
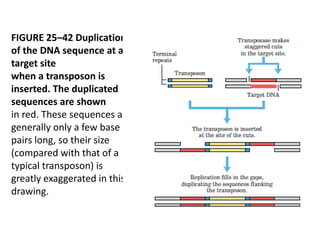
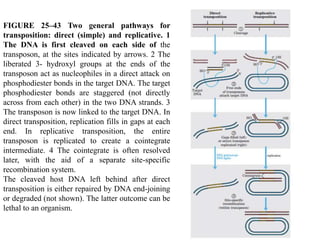
DNA recombination mechanisms are involved in DNA repair, replication, gene expression and chromosome segregation. Recombination involves the breakage and joining of DNA strands. There are three main classes of recombination: homologous recombination between similar DNA sequences, site-specific recombination occurring at particular DNA sequences, and DNA transposition where segments of DNA move to new locations. Recombination is mediated by enzymes and involves steps like strand exchange, branch migration and resolution of Holliday junction structures to produce recombinant DNA products.