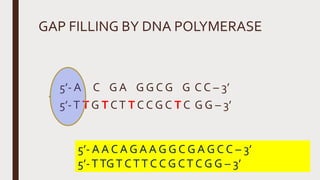
Reverse transcription of RNA into complementary DNA (cDNA) is crucial for gene transcript analysis, allowing sequencing, cloning, and gene expression validation. The process involves reverse transcriptases, which convert RNA templates into DNA, and requires steps such as template linearization and primer annealing. Downstream applications include quantitative PCR for copy number determination and gene amplification.