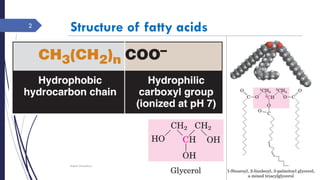
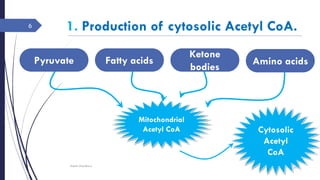
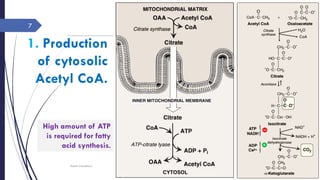
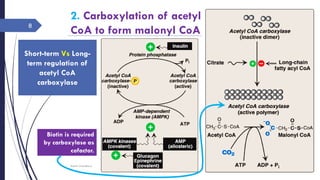
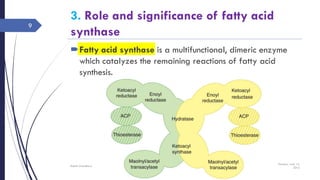
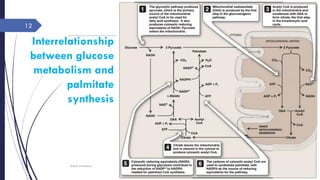
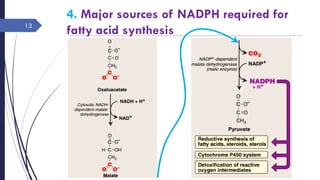
This document summarizes the de novo synthesis of fatty acids. It discusses that fatty acid synthesis primarily occurs in the liver and lactating mammary glands using acetyl CoA, ATP, NADPH, Mn2+, and biotin. The first step is the production of cytosolic acetyl CoA from mitochondrial acetyl CoA. Acetyl CoA is then carboxylated to form malonyl CoA by acetyl CoA carboxylase. Fatty acid synthase is a multifunctional enzyme that catalyzes the remaining reactions. The major sources of NADPH required are the pentose phosphate pathway and conversion of malate to pyruvate in the cytosol. Palmitate, a 16 carbon