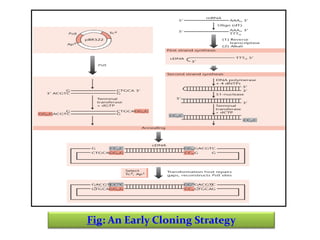
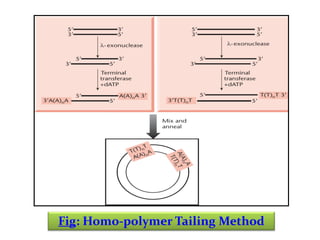
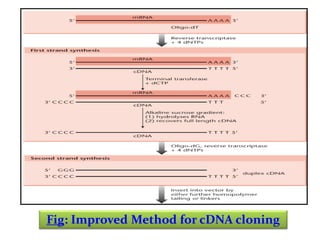
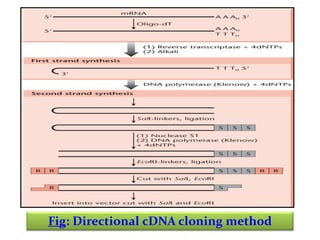
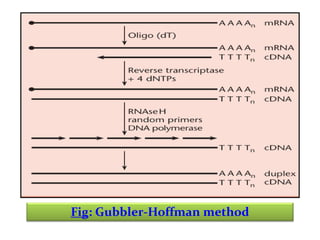
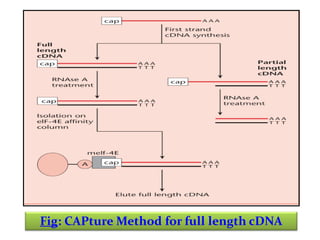
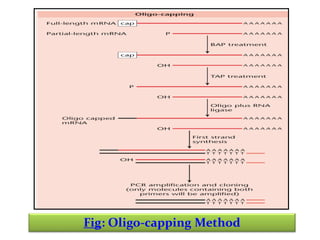
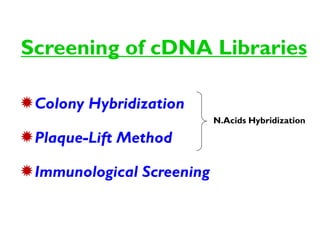
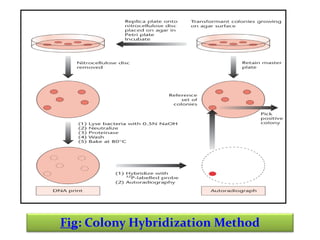
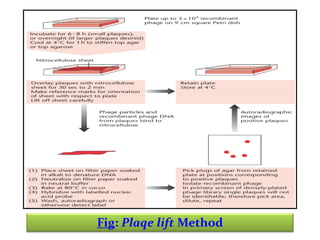
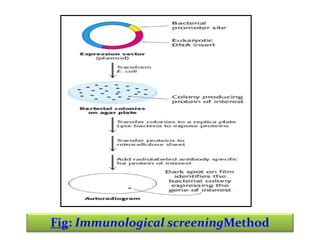
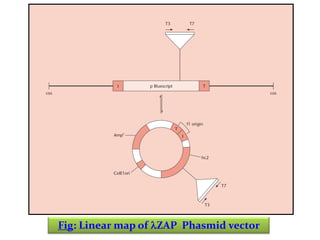
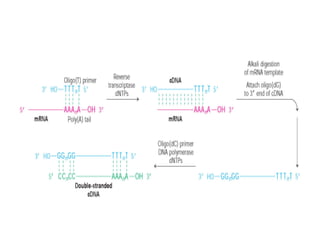
This document discusses different strategies for cloning DNA fragments from complex sources like genomic DNA or cDNA. There are two major approaches - cell-based cloning, which divides the DNA into fragments that are cloned to create a library, and directly amplifying target sequences using PCR. The document focuses on cDNA library construction, explaining that cDNA libraries reveal gene expression profiles. It describes early cDNA cloning methods and their limitations, as well as improved directional and non-directional cloning techniques. Finally, it discusses various screening methods for identifying clones of interest from cDNA libraries, including colony hybridization, plaque lifts and immunological screening.