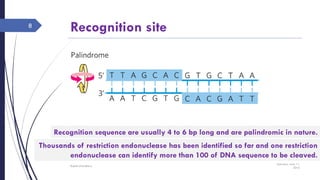
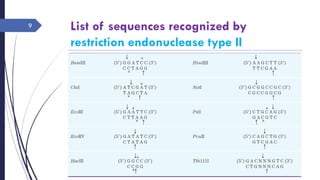
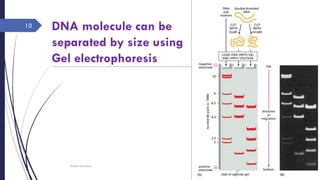
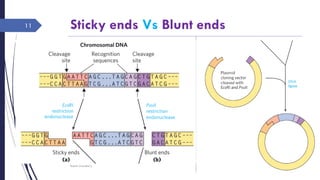
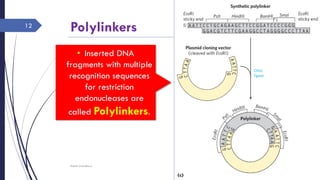
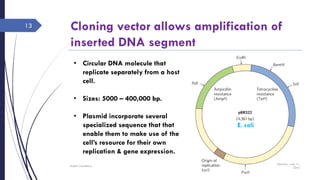
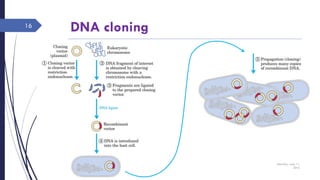
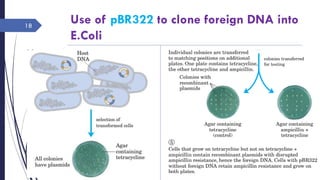
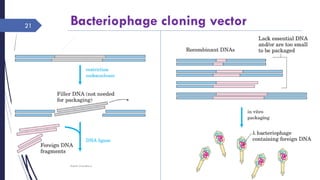
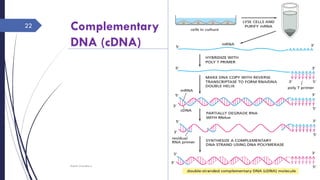
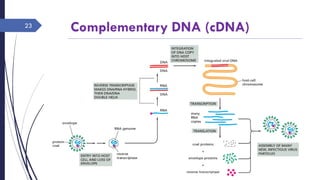
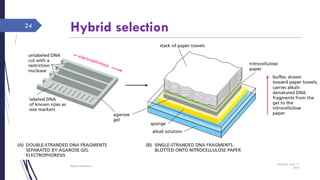
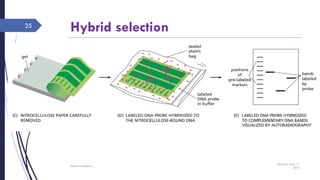
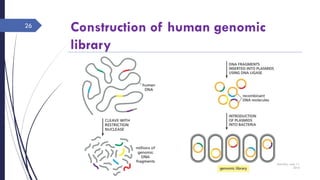
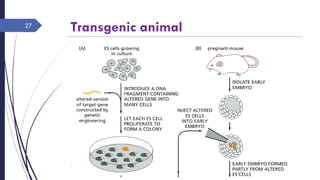
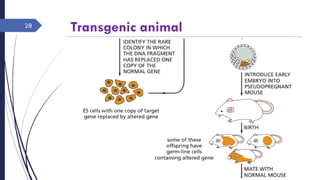
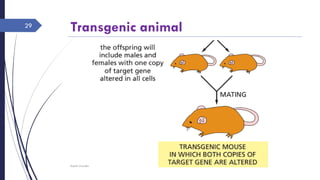
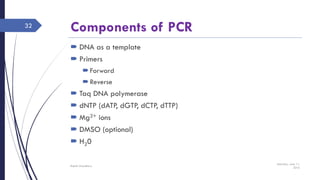
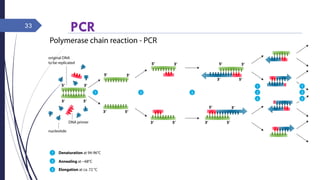
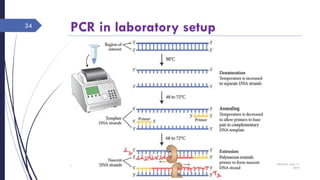
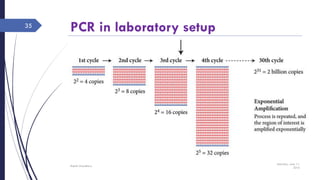
DNA cloning requires five main steps: 1) cutting DNA at specific locations, 2) selecting a replicable DNA fragment, 3) joining DNA fragments, 4) inserting recombinant DNA into host cells, and 5) identifying host cells containing the recombinant DNA. Restriction endonucleases and DNA ligases are used to cut and join DNA fragments for cloning. Plasmids and bacteriophages are common cloning vectors used to replicate and amplify recombinant DNA in host cells such as E. coli.