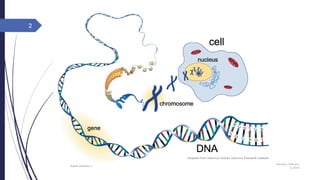
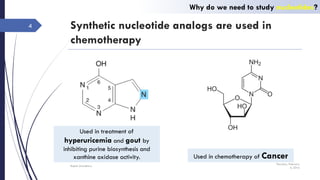
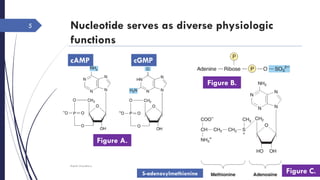
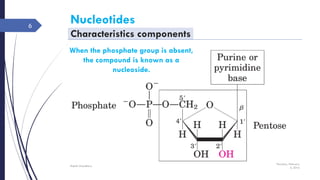
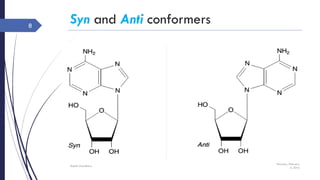
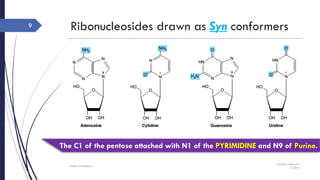
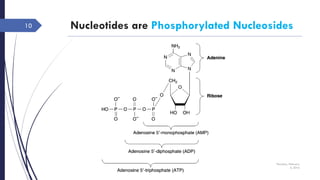
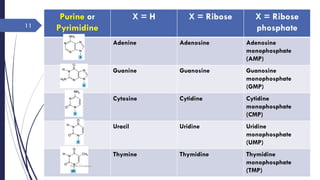
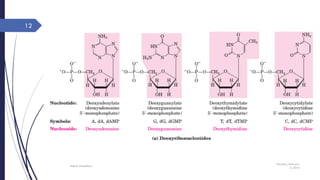
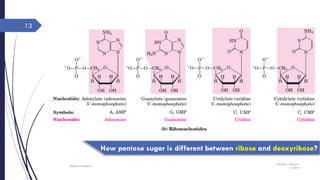
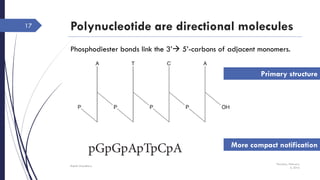
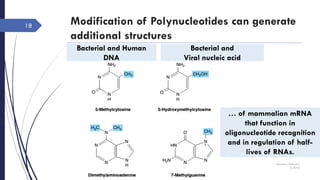
This document discusses nucleotides and their importance. Nucleotides serve as the principal donors and acceptors of phosphoryl groups in cellular metabolism and are the energy currency. They are also structural components of cofactors like vitamins. Nucleotides constitute nucleic acids DNA and RNA. Synthetic nucleotide analogs are used in chemotherapy to treat cancer and hyperuricemia. Nucleotides have diverse physiological functions and absorb ultraviolet light. They are polyfunctional acids and nucleoside triphosphates have high group transfer potential.