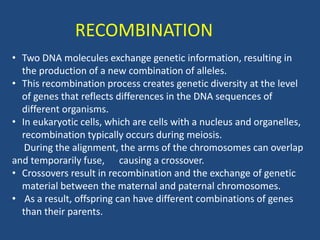
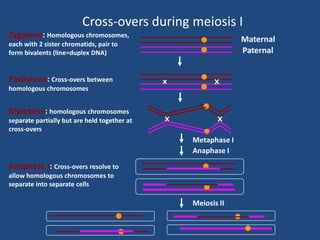
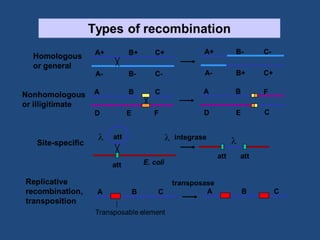
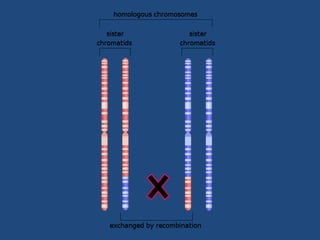
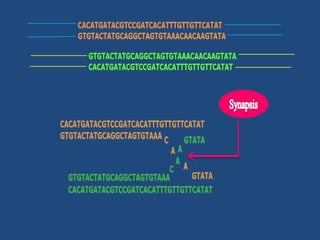
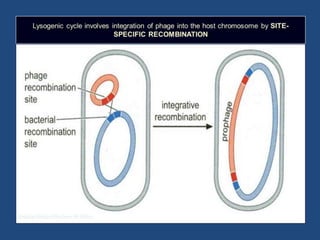
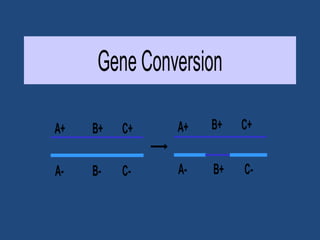
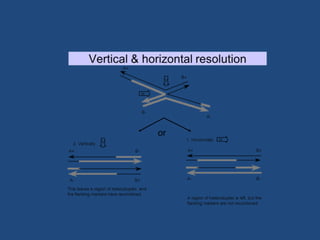
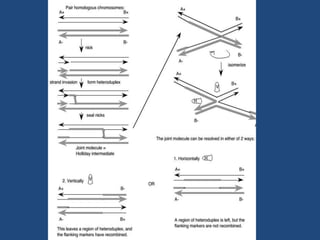
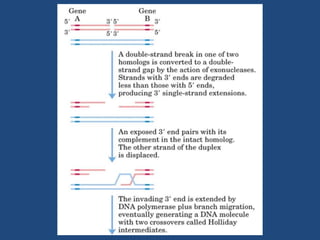
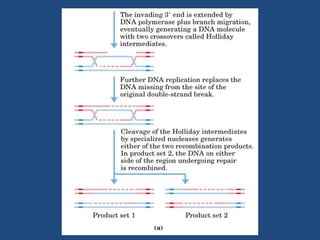
Recombination is the process where two DNA molecules exchange genetic information, creating genetic diversity, primarily occurring during meiosis in eukaryotic cells. Key models of recombination include the Holliday model and the Meselson-Radding model, which explain mechanisms like strand invasion and double-strand break repair. Various forms of recombination, including homologous and nonhomologous types, contribute to genetic variations and are essential for mapping genes on chromosomes.