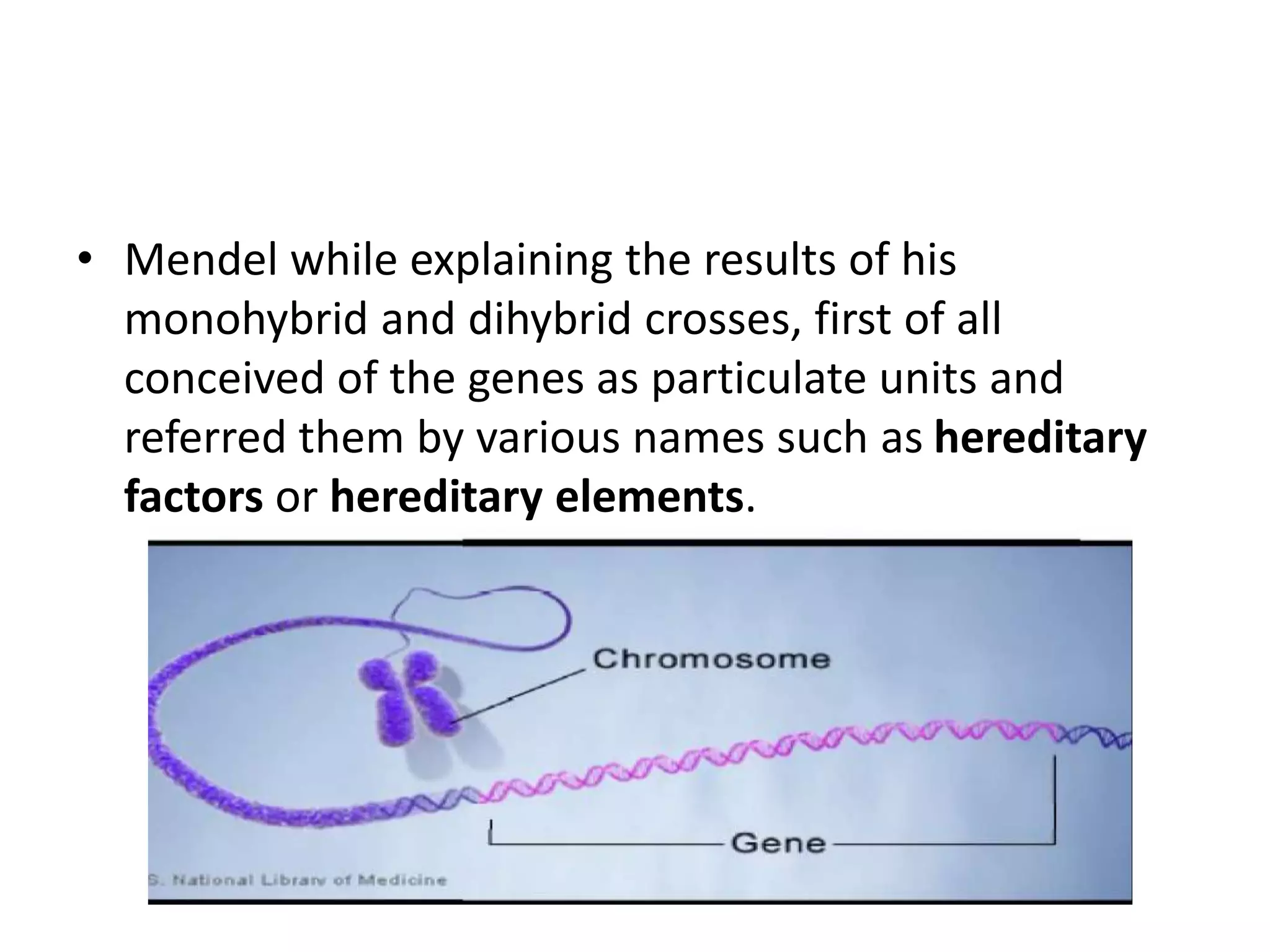
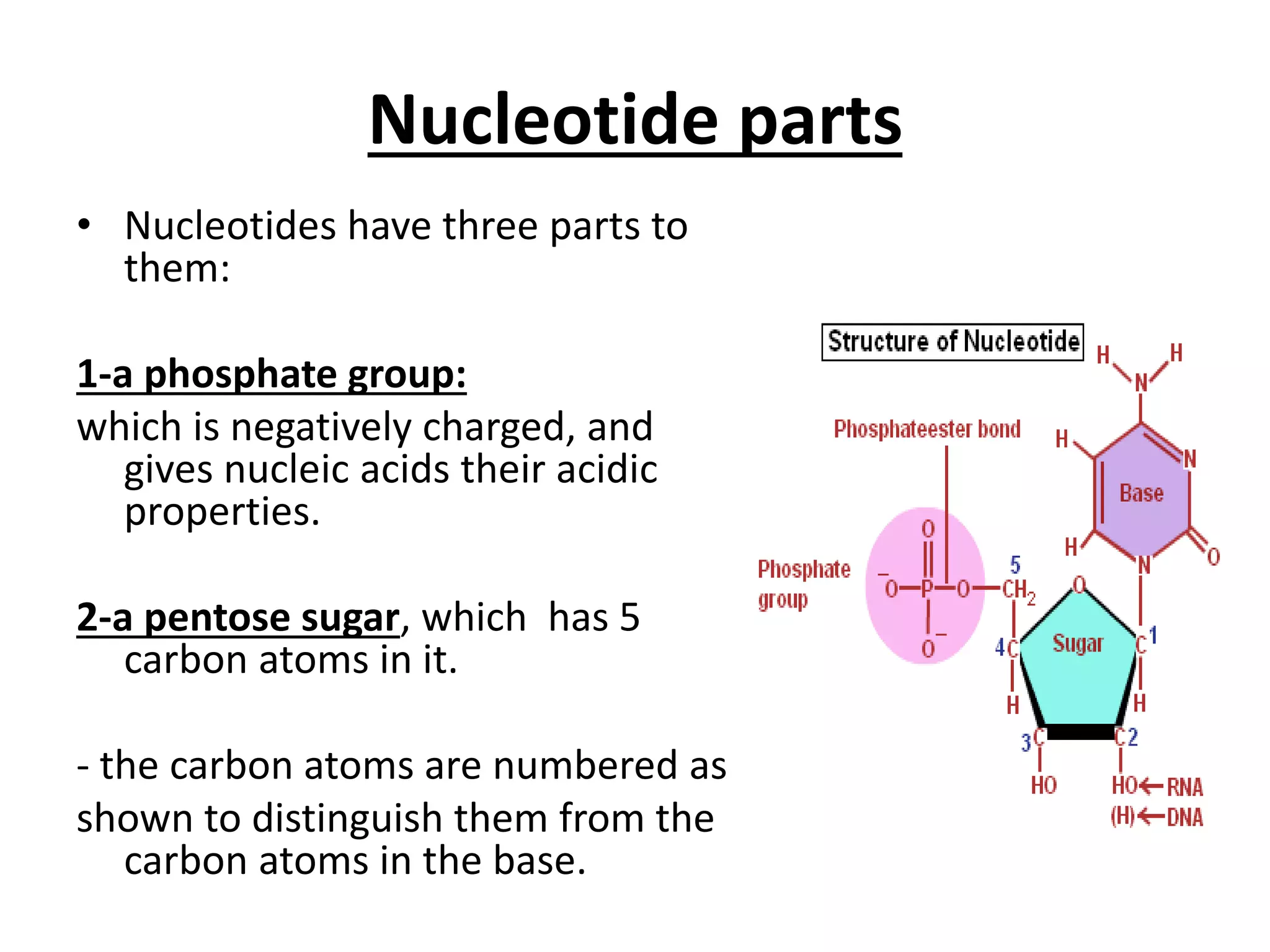
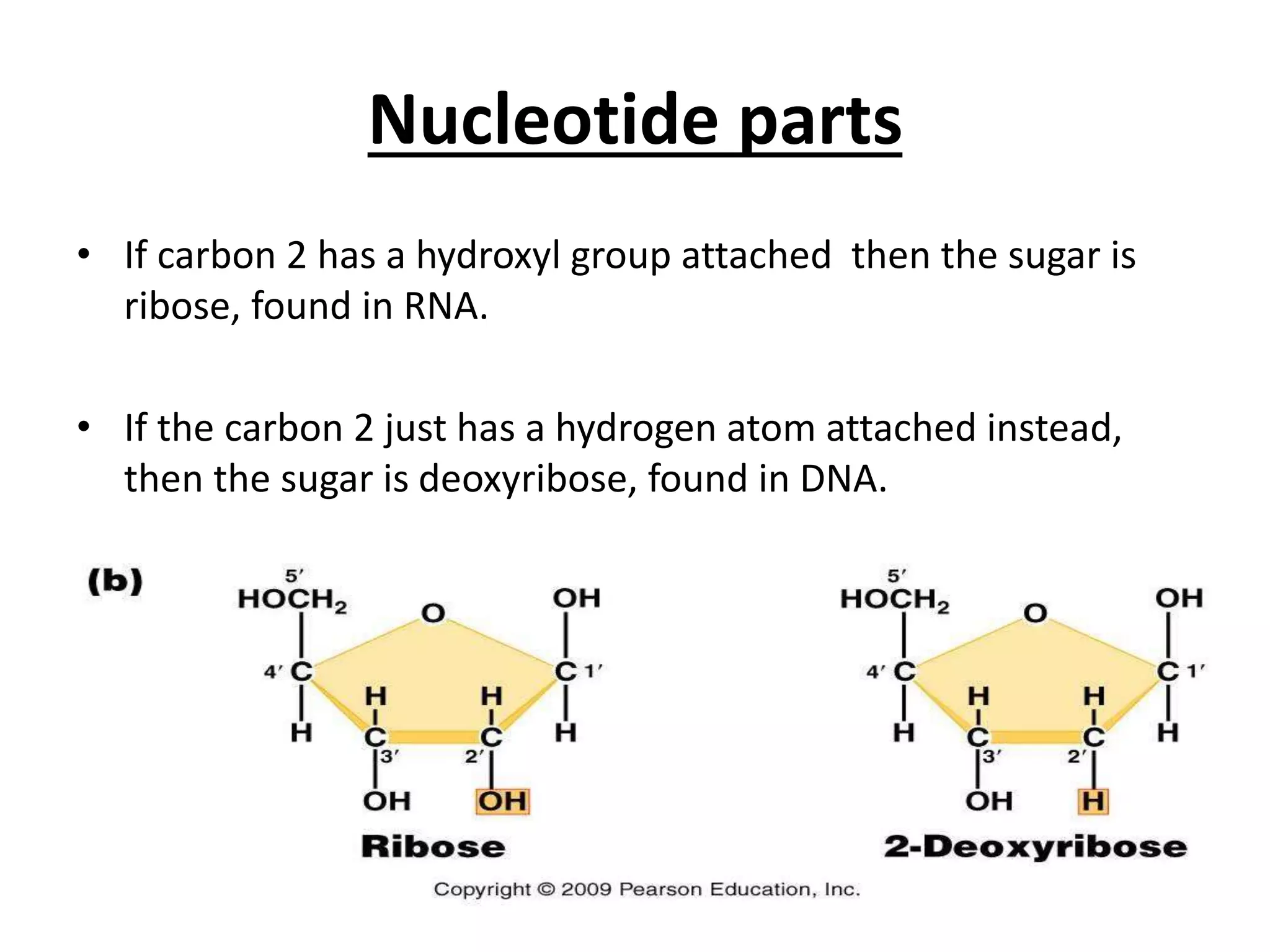
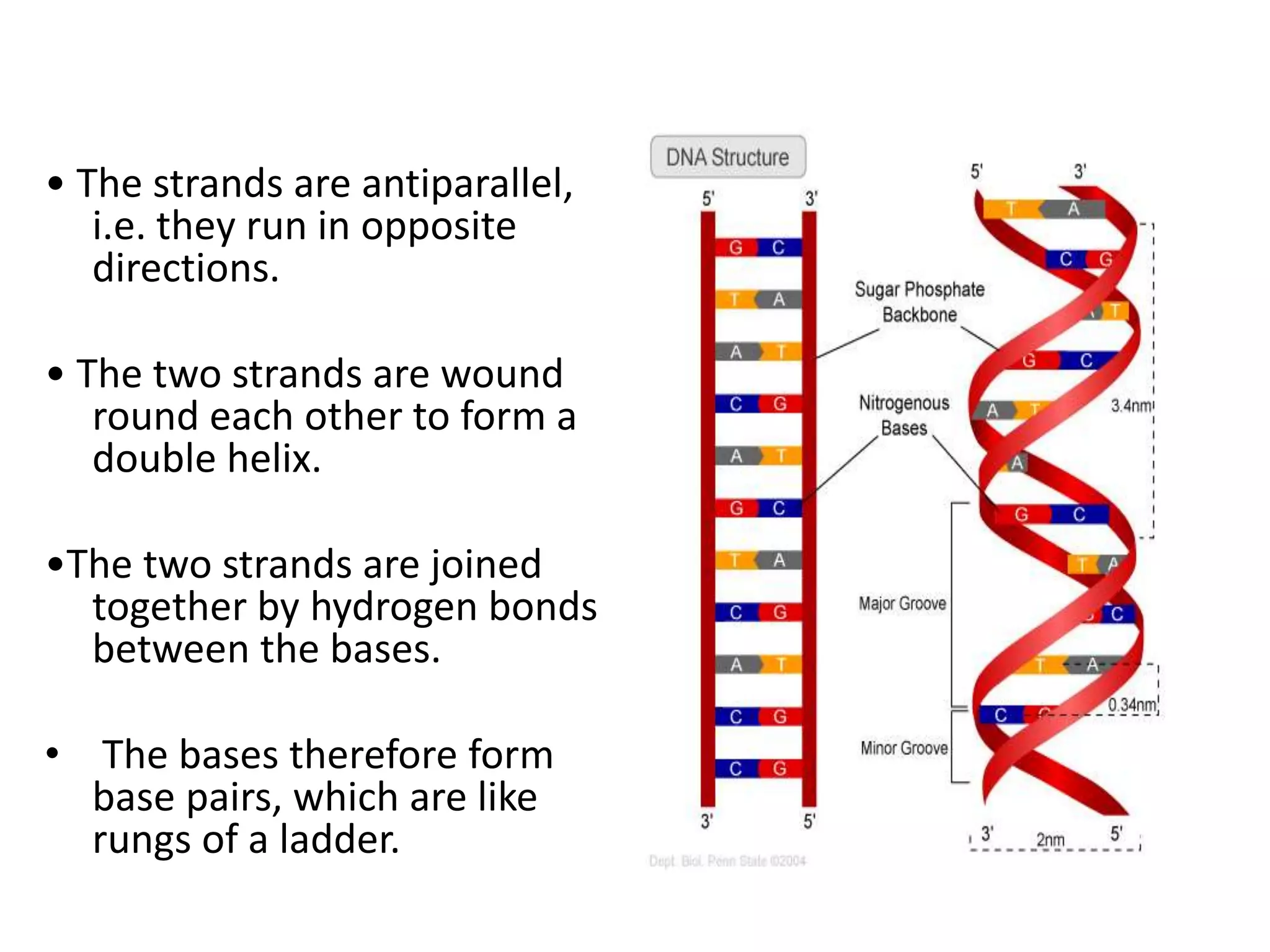
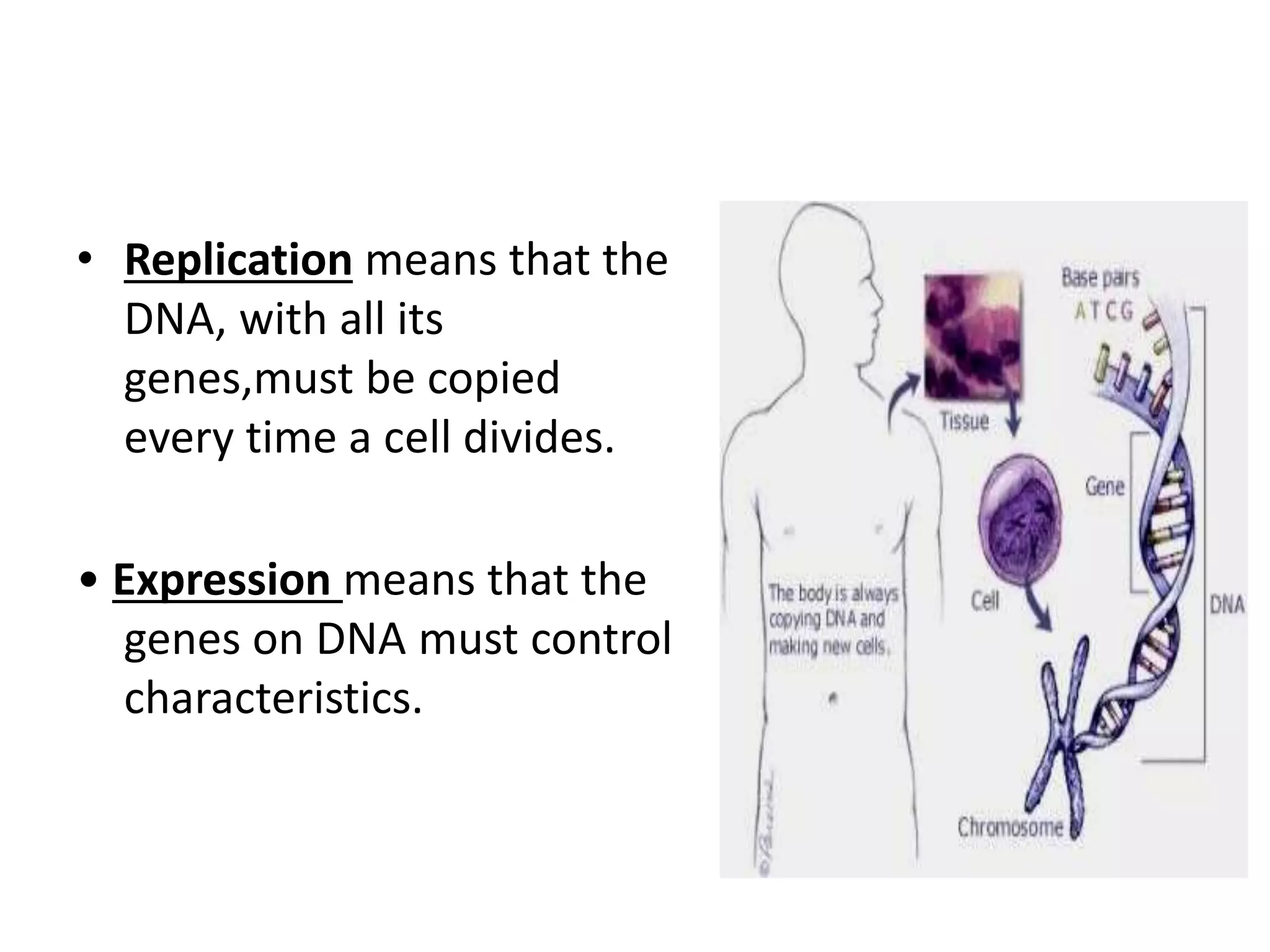
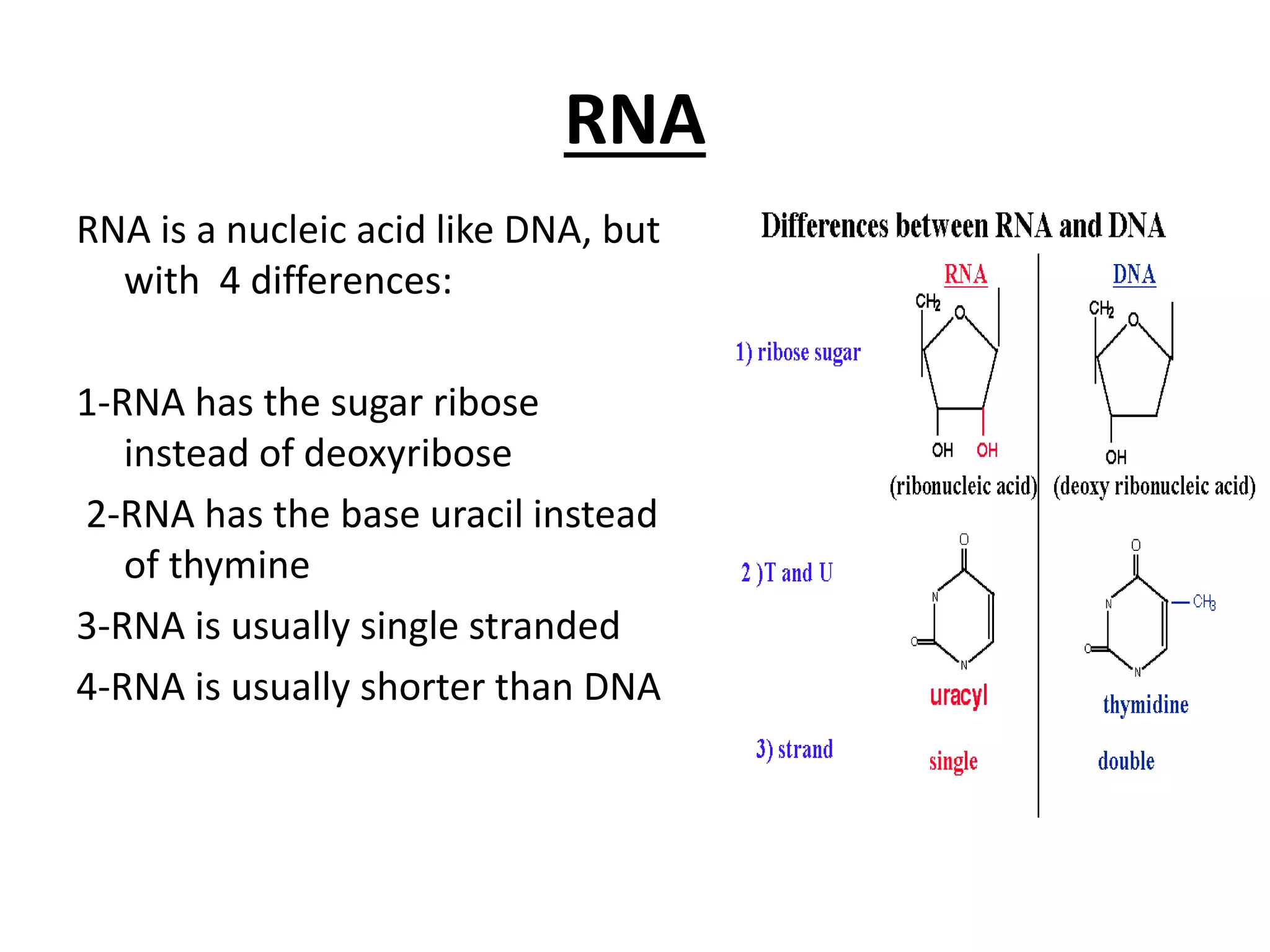
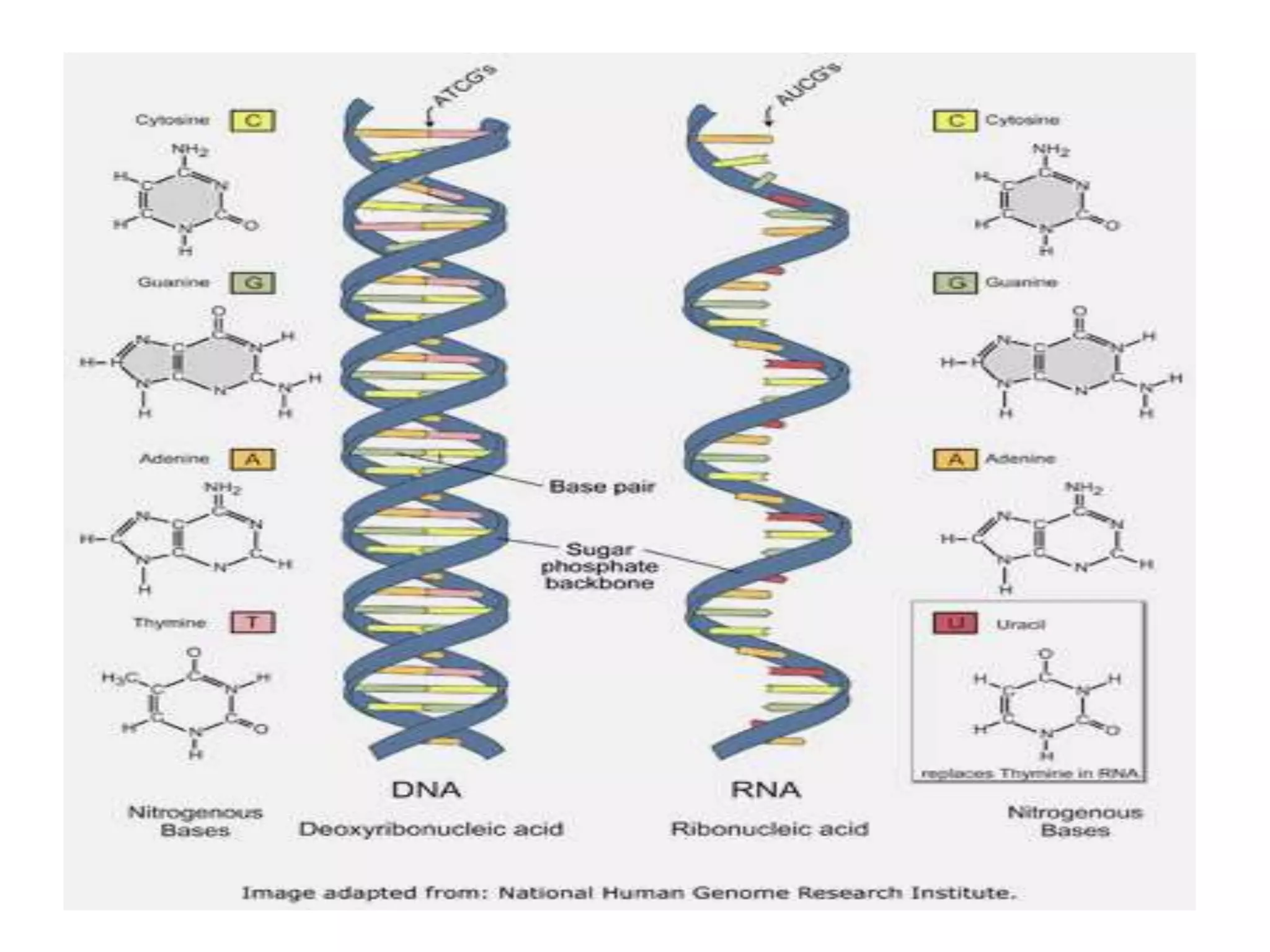
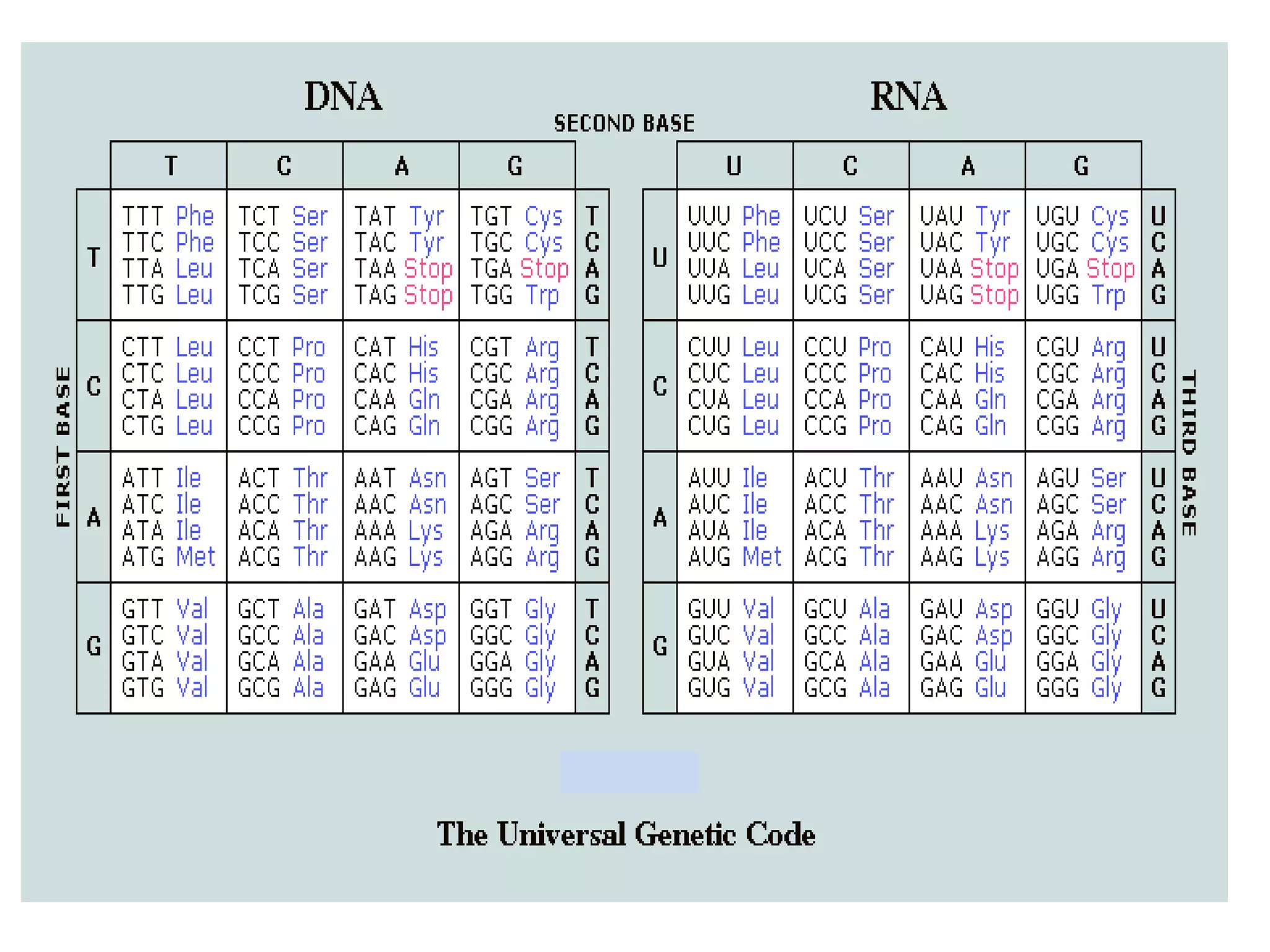
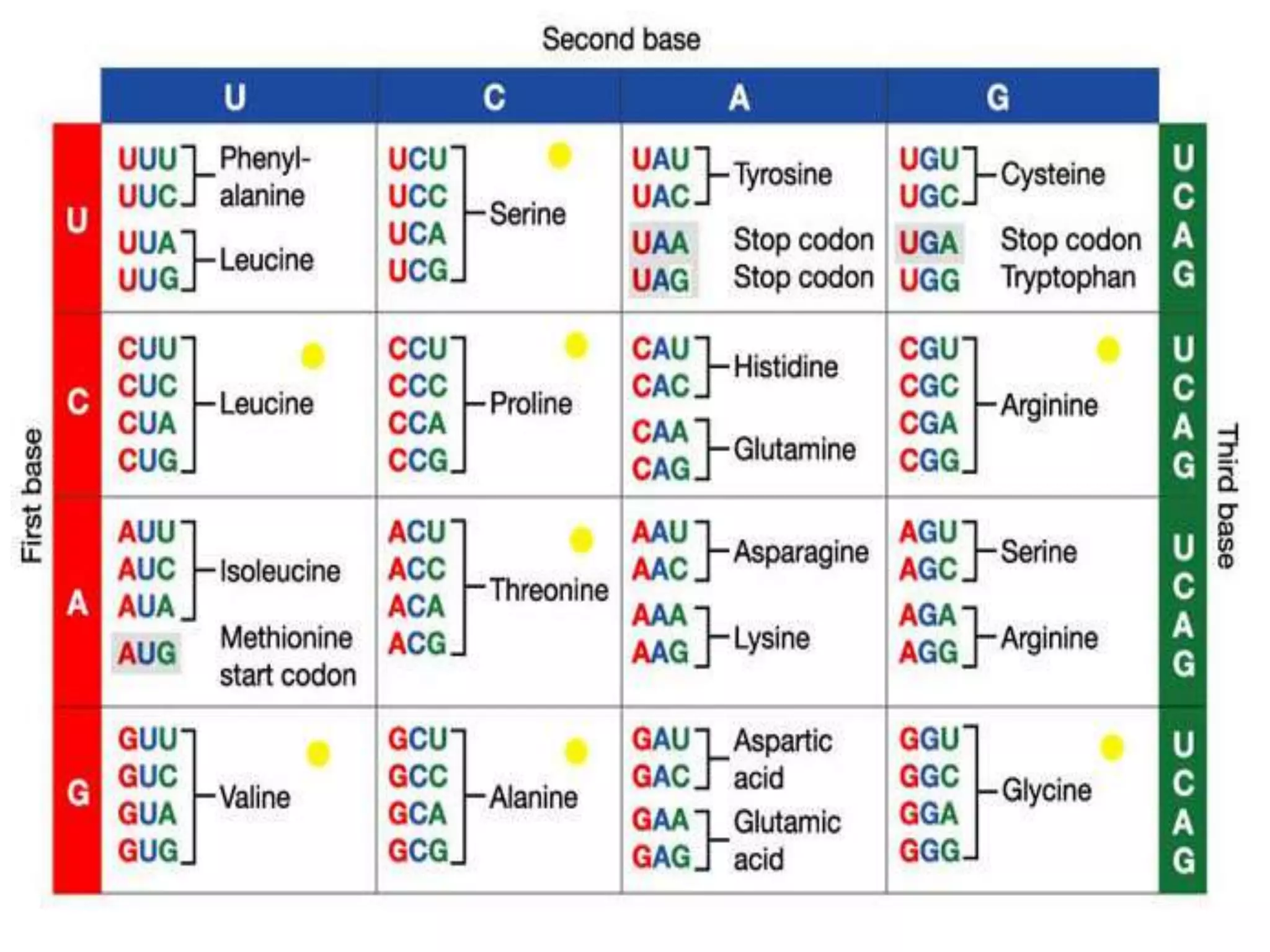
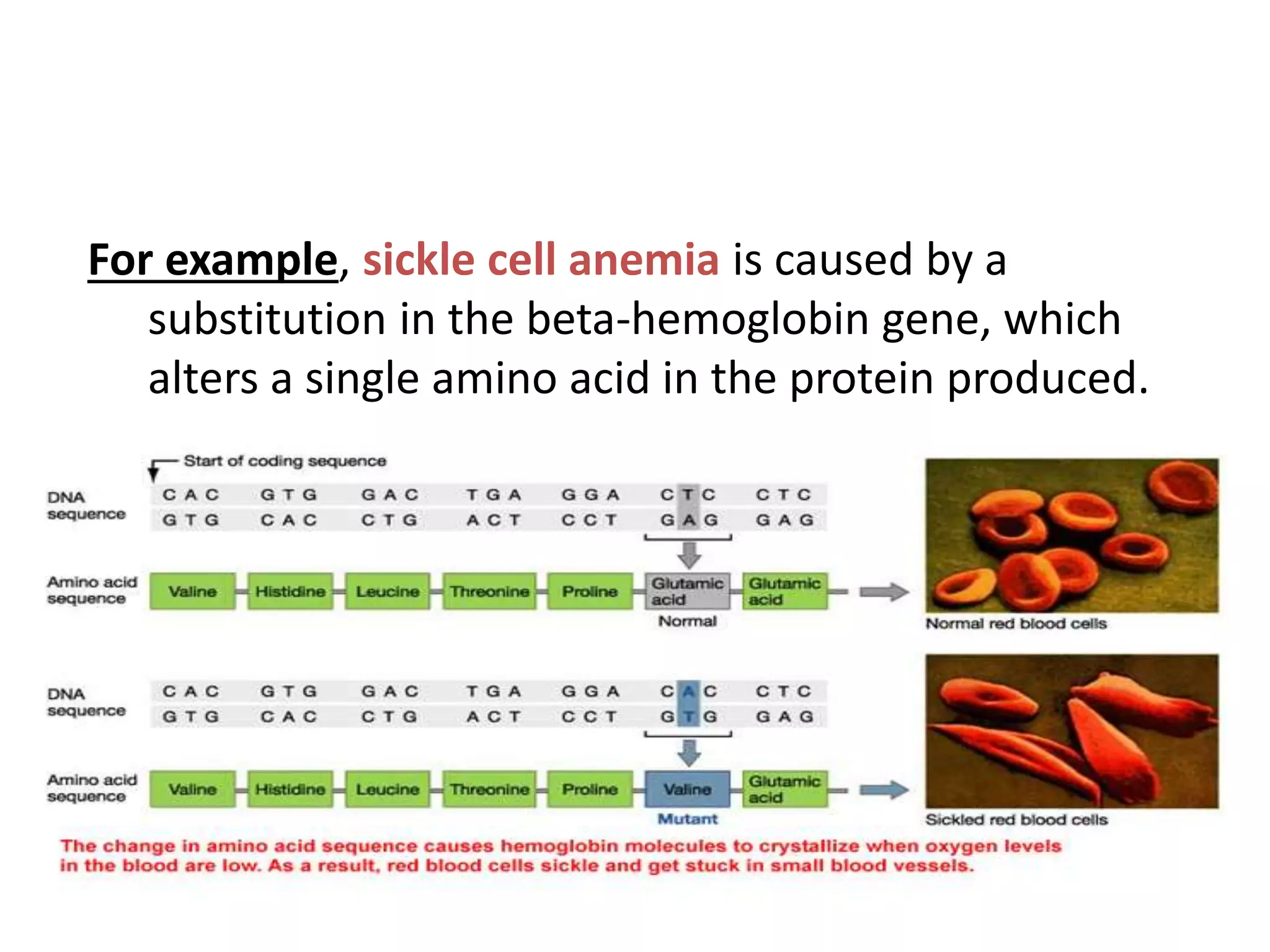
Gene mutations can occur in several ways:
1) Substitutions exchange one DNA base for another and may alter the resulting protein. Sickle cell anemia is caused by a substitution.
2) Insertions add extra DNA bases. Huntington's disease results from repetitive CAG insertions.
3) Deletions remove sections of DNA. Cystic fibrosis stems from a deletion in the CFTR gene.
4) Frameshifts alter gene parsing and produce truncated proteins. Tay-Sachs disease arises from a frameshift mutation in the HEXA gene.