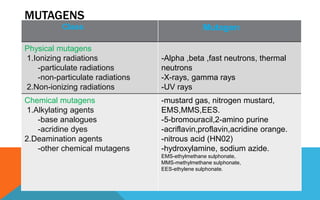
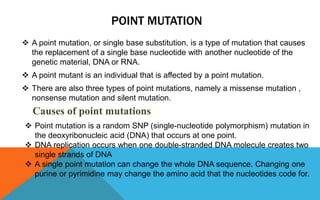
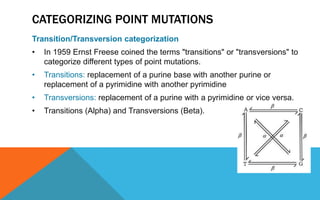
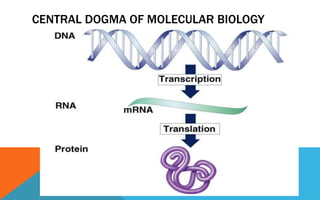
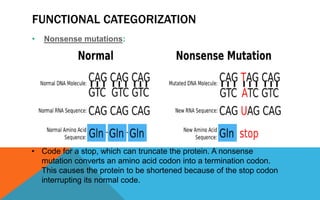
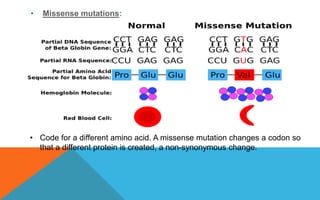
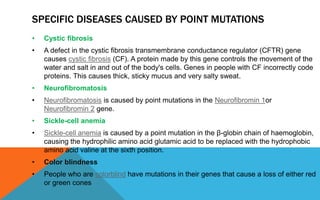
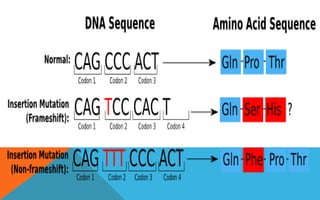
Mutations are heritable changes in an organism's genetic material. They arise from errors in DNA replication or distribution and can cause sudden changes in characteristics. There are two main types of mutations - gene mutations, which alter the sequence of a single gene, and chromosomal mutations, which involve changes in chromosome number or structure. Point mutations specifically change a single DNA nucleotide, and can be further classified as transitions, transversions, nonsense, missense, or silent mutations depending on their effects. Frameshift mutations insert or delete DNA nucleotides, altering the reading frame and resulting in abnormal proteins. Many diseases like cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and cancer are caused by specific point or frameshift mutations.