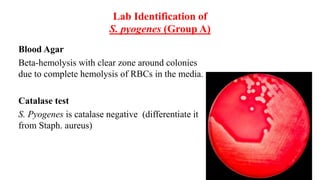
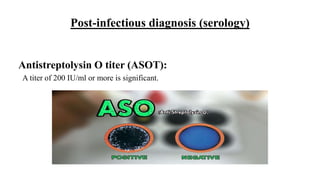
This document summarizes methods for identifying different Streptococcus bacteria from clinical specimens. It describes how S. pneumoniae appears as gram-positive diplococci and forms green colonies on blood agar due to alpha-hemolysis. Identification involves optochin susceptibility testing, where S. pneumoniae is optochin sensitive. S. pyogenes forms beta-hemolytic colonies on blood agar and is identified using catalase and bacitracin tests. Antistreptolysin O titer and API 20 Strep tests can diagnose previous streptococcal infections.