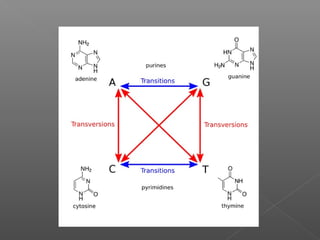
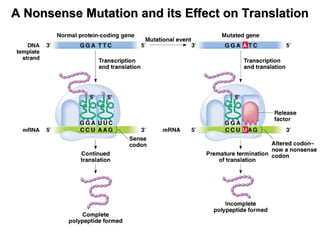
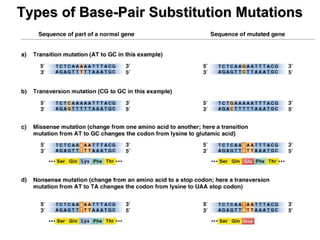
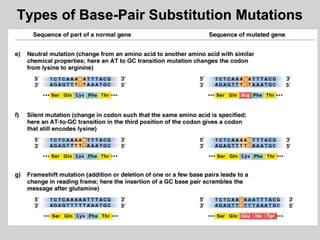
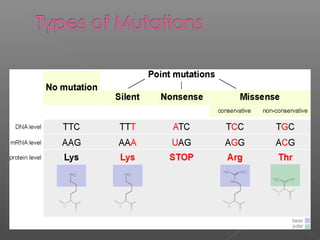
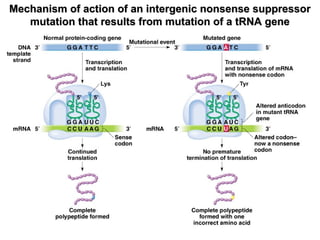
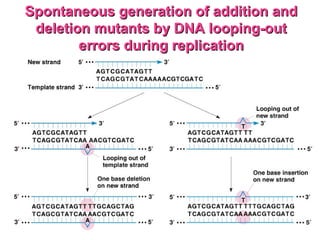
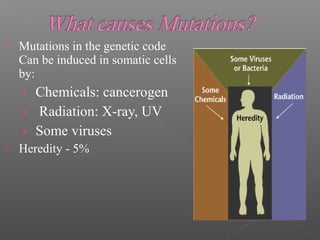
This document discusses different types of mutations, how they arise, and their effects. It distinguishes between adaptations to the environment versus heritable changes due to mutations in genetic material. Mutations can be defined by their location (e.g. gene, chromosome), type (e.g. point, frameshift), and effects (e.g. missense, nonsense). They can occur spontaneously or be induced by mutagens and may have varying consequences depending on whether they are in somatic or germ-line cells.