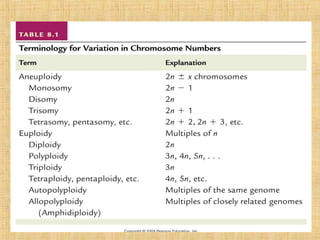
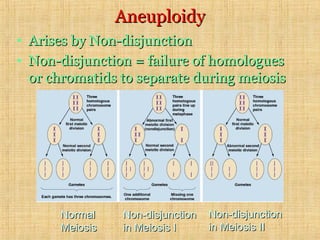
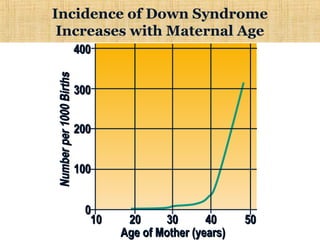
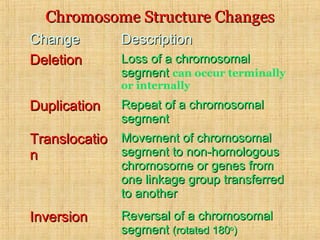
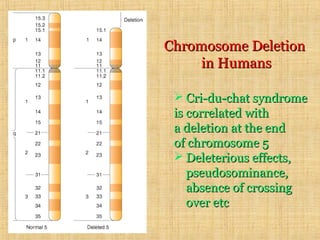
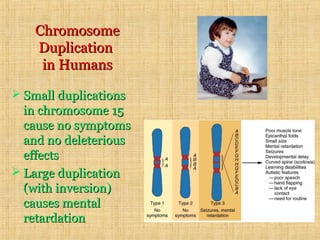
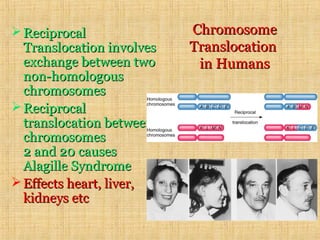
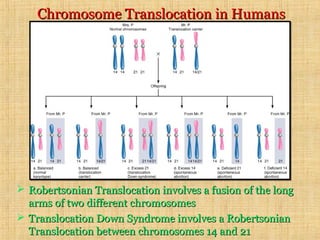
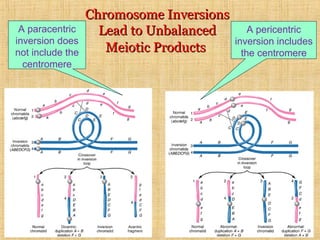
Chromosomal mutations are changes in chromosome structure or number that can be caused by physical or chemical agents. There are two main types of chromosomal mutations: structural changes including deletions, duplications, translocations, and inversions, and numerical changes such as aneuploidy where there is an excess or deficiency of a single chromosome. Examples of aneuploidies in humans are Down syndrome, Edward syndrome, and Patau syndrome. Chromosomal mutations can have varying effects depending on the genes involved, from no symptoms to developmental delays or medical conditions.