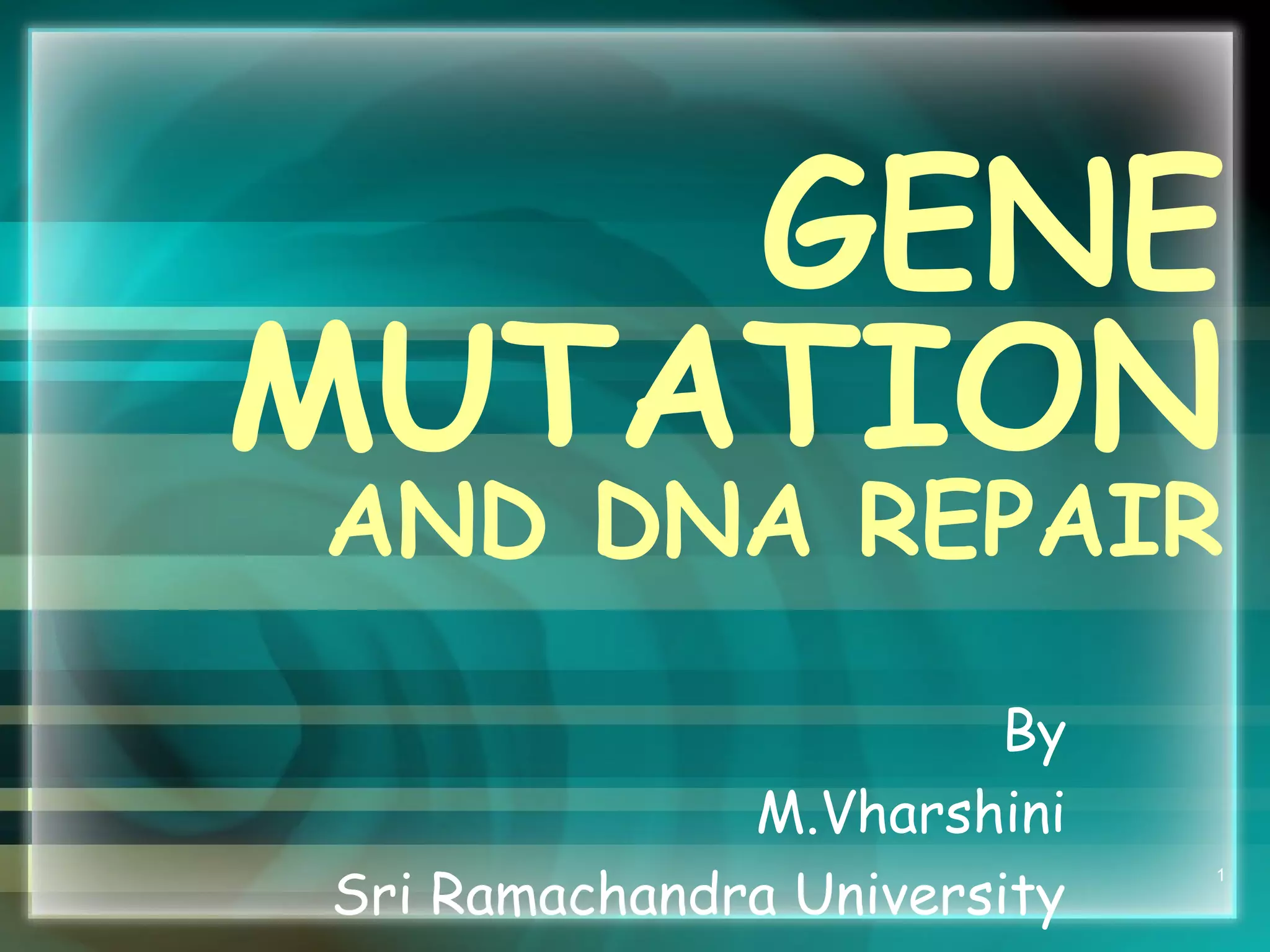
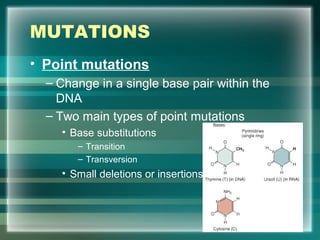
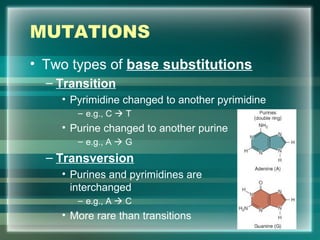
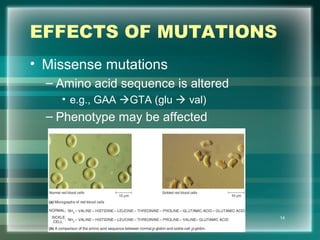
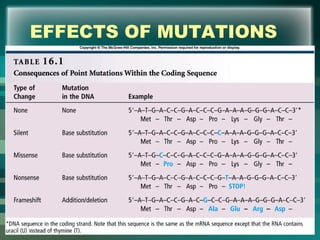
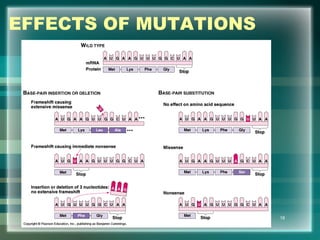
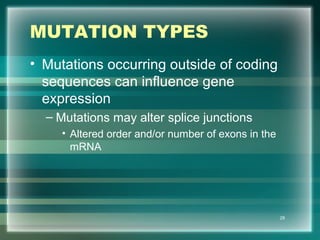
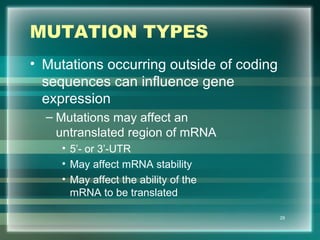
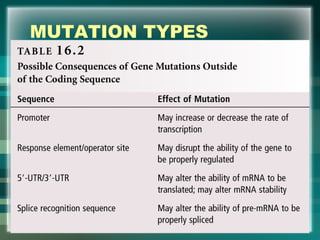
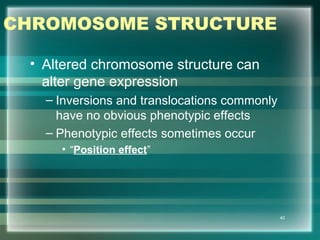
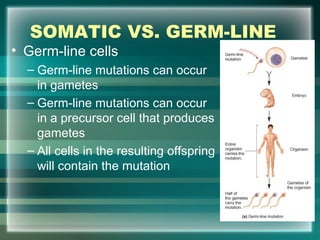
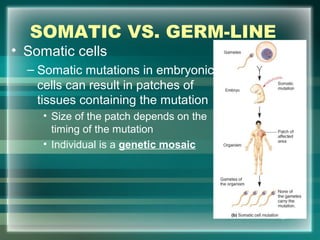
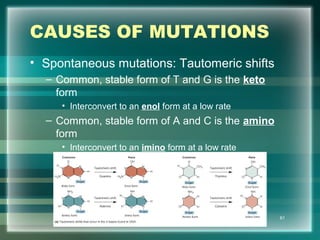
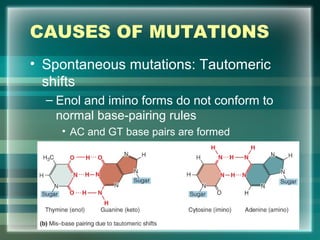
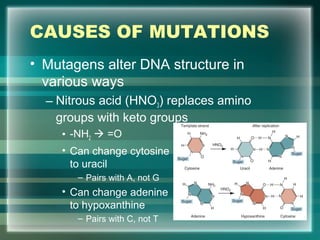
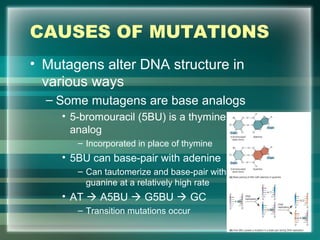
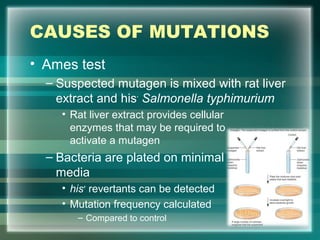
This document discusses genetic mutations and DNA repair. It defines mutations as heritable changes in genetic material that can provide genetic variation and be the basis for evolution. Mutations can be caused spontaneously during DNA replication or cell division, or can be induced by environmental mutagens. The majority of mutations are neutral or harmful, with a small percentage being beneficial. Different types of mutations are described, including point mutations, insertions, deletions, and trinucleotide repeats. The effects of mutations on genes and proteins are explained. The timing of mutations as either germline or somatic is an important factor. Causes of spontaneous mutations like depurination and deamination are outlined.