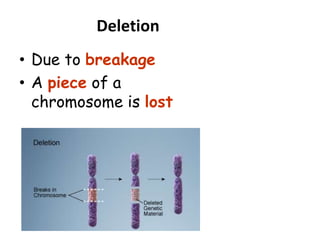
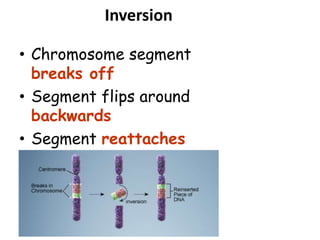
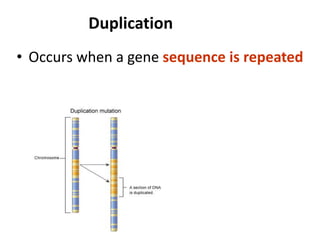
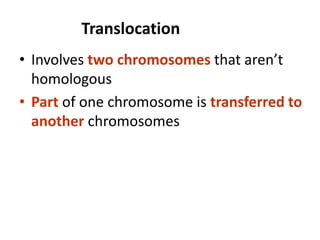
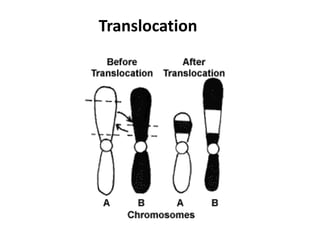
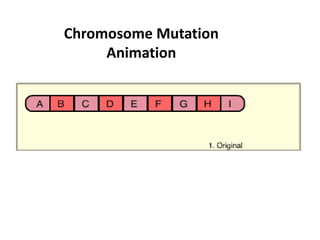
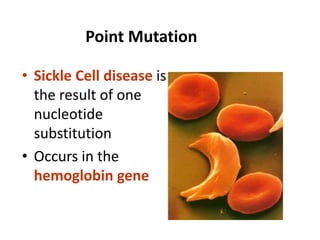
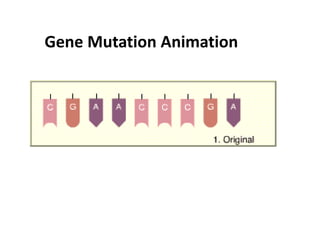
This document discusses mutation, which is a heritable change in genetic material or character of an organism. Mutations can be caused spontaneously or induced by mutagens like radiation. There are different types of mutations including point mutations, which change a single nucleotide, and chromosomal mutations, which involve changes in chromosome structure like deletions, inversions, duplications, and translocations. Mutations can occur in somatic cells or germ cells and be transmitted to offspring. Common gene mutations include point mutations, insertions, deletions, and frameshift mutations, which alter protein production. Mutation is an important source of genetic variation and has applications in crop improvement.