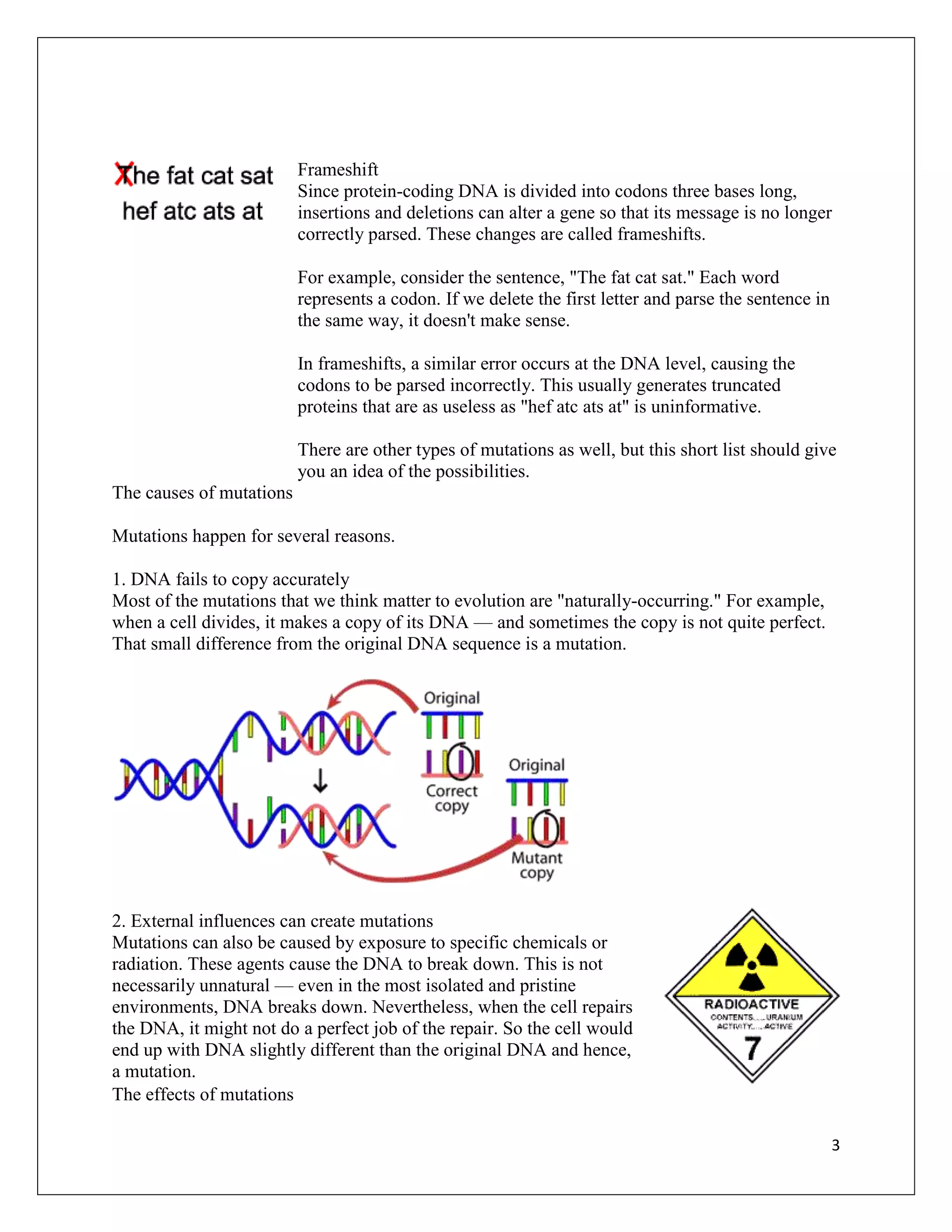
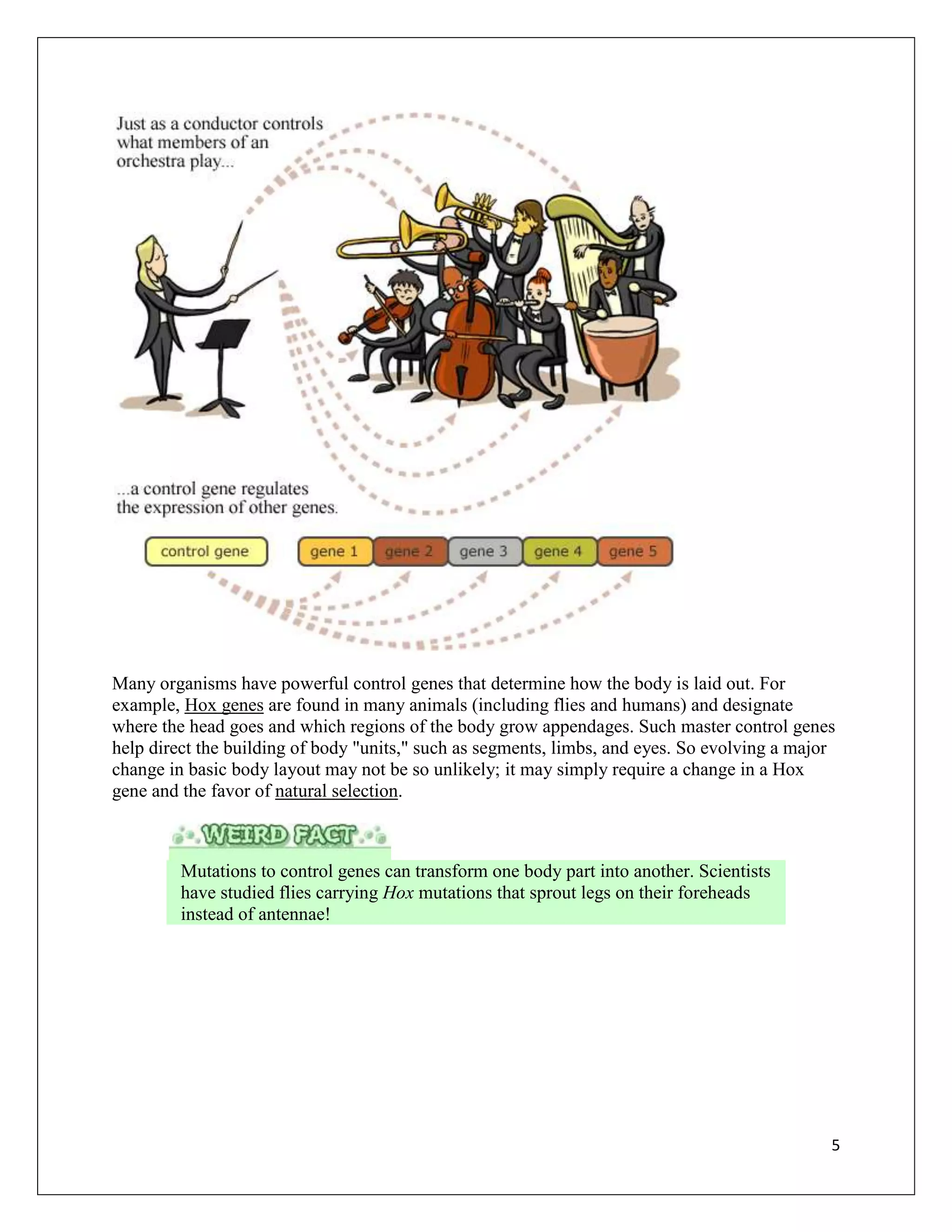
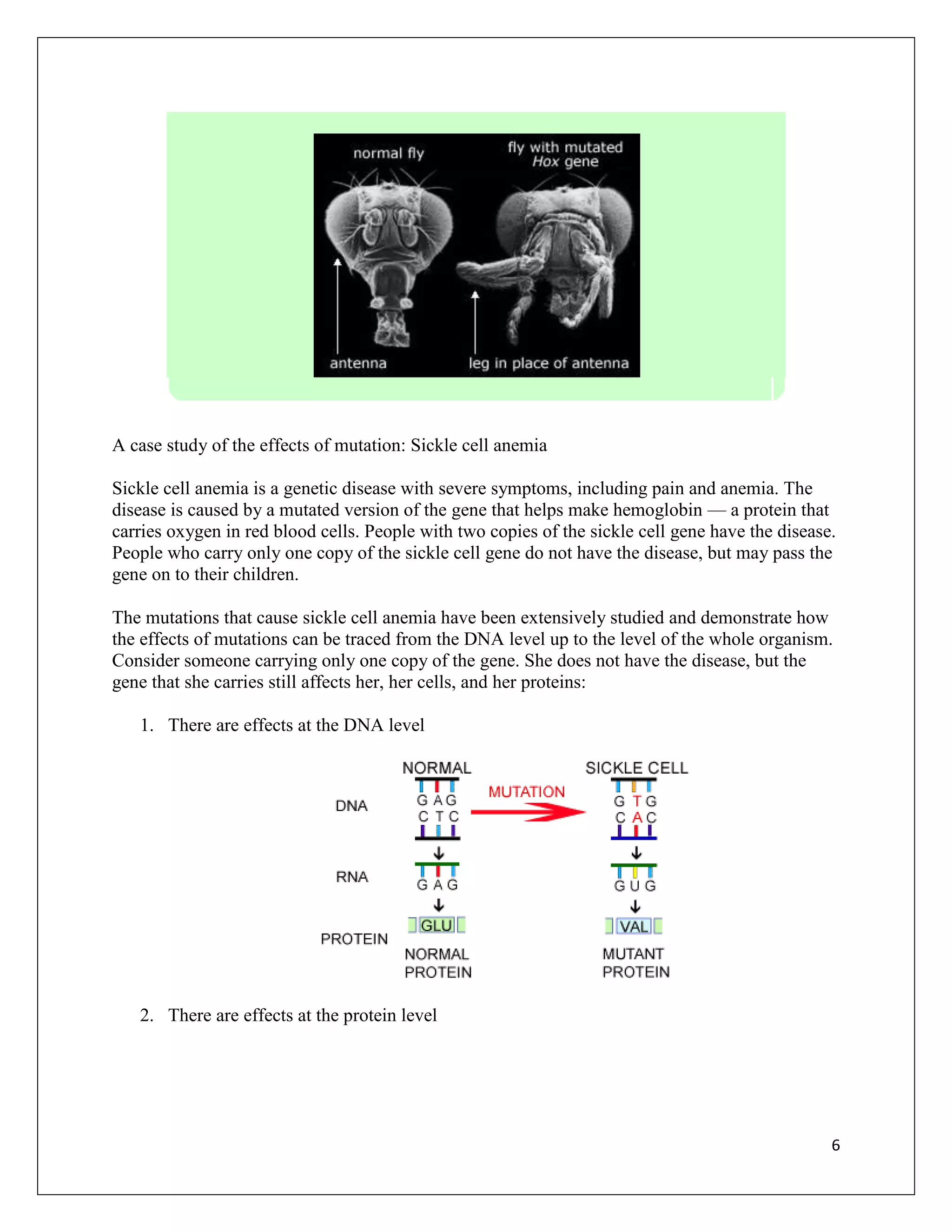
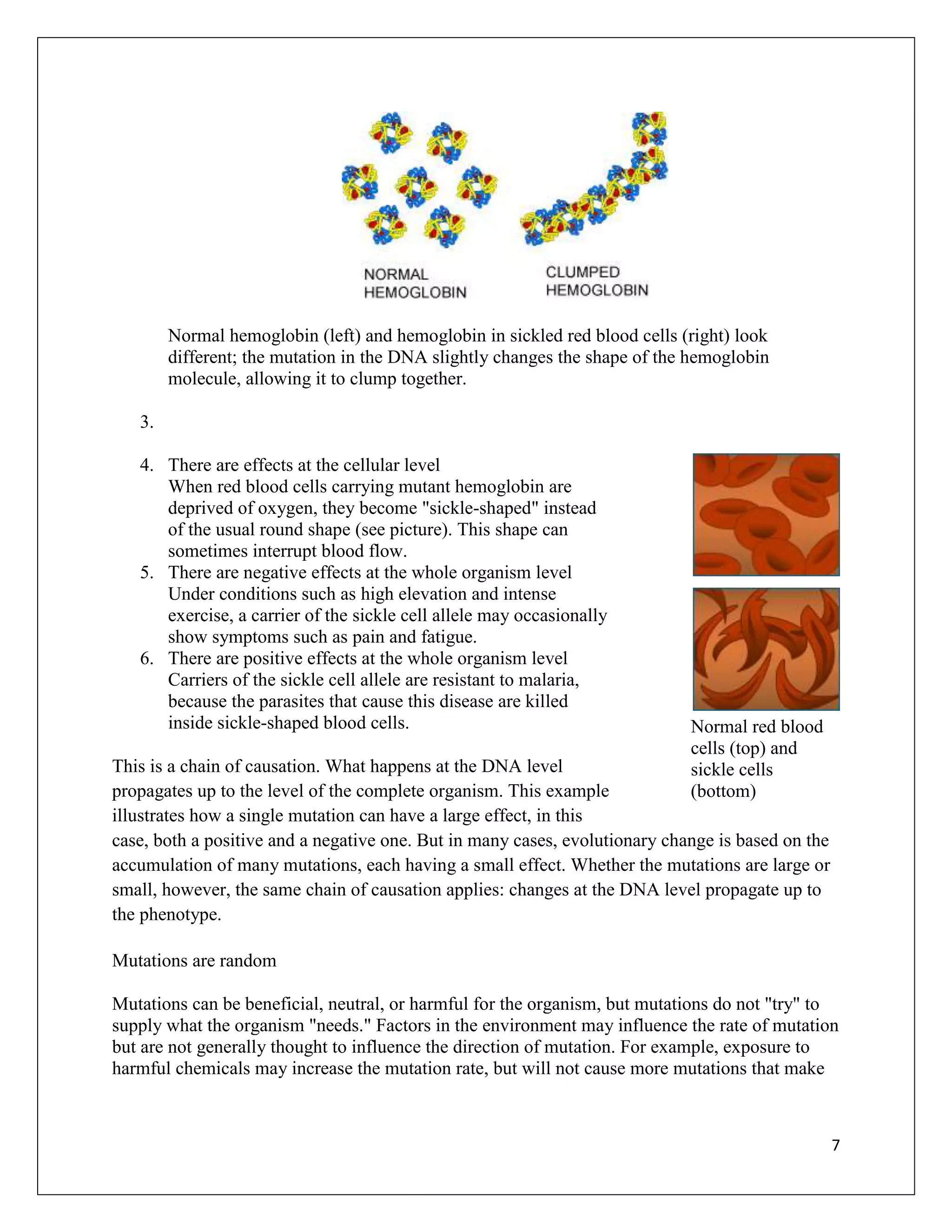
Mutations are changes in DNA that can occur for various reasons and have different effects. A single mutation can range from having no observable effect to causing serious genetic disorders. The document examines mutations at the molecular, cellular, organismal, and evolutionary levels through examples like sickle cell anemia. It describes the random nature of mutations and how an experiment by Esther and Joshua Lederberg provided evidence that antibiotic resistance arises from pre-existing mutations rather than being induced by antibiotic exposure.